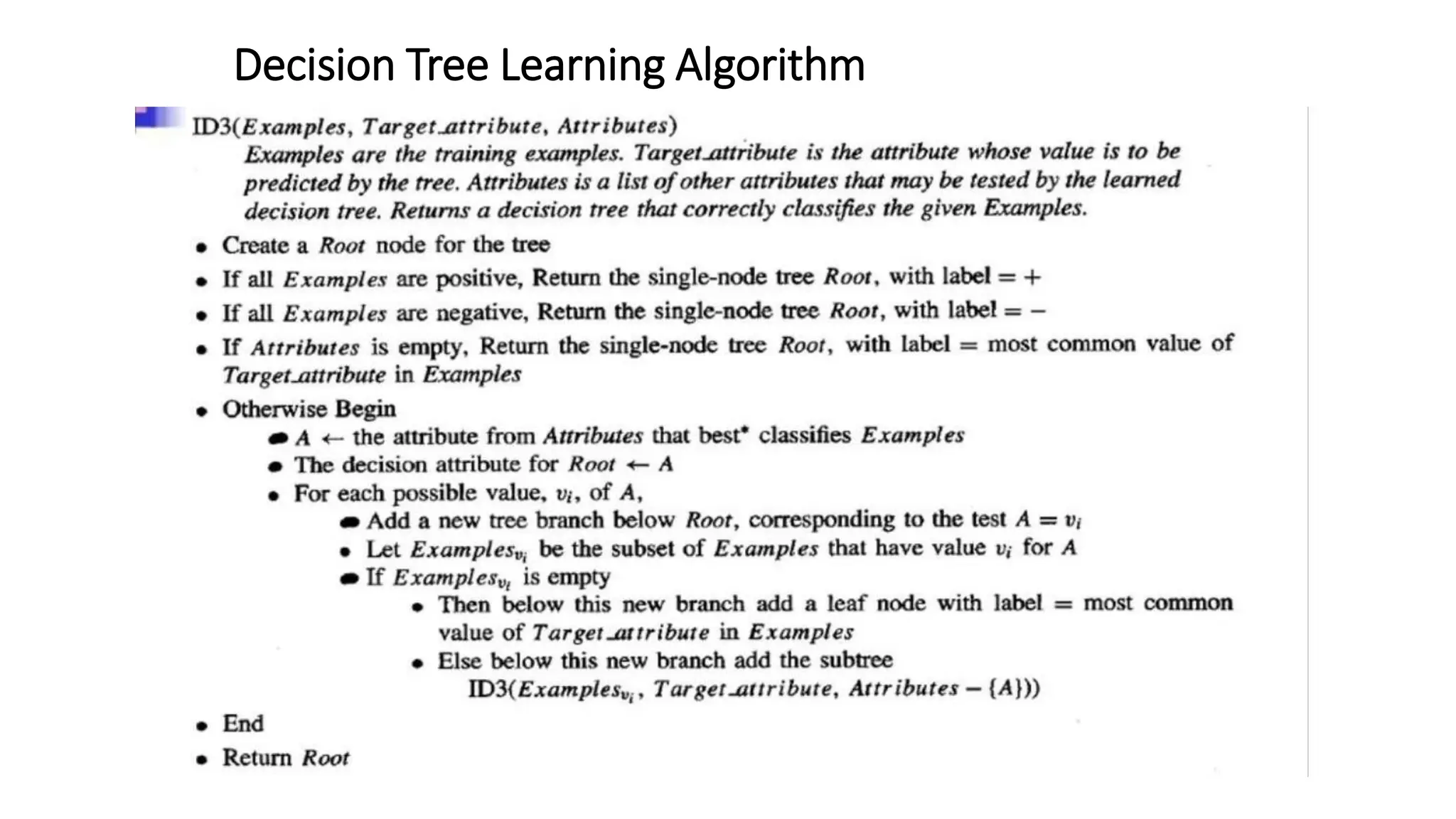
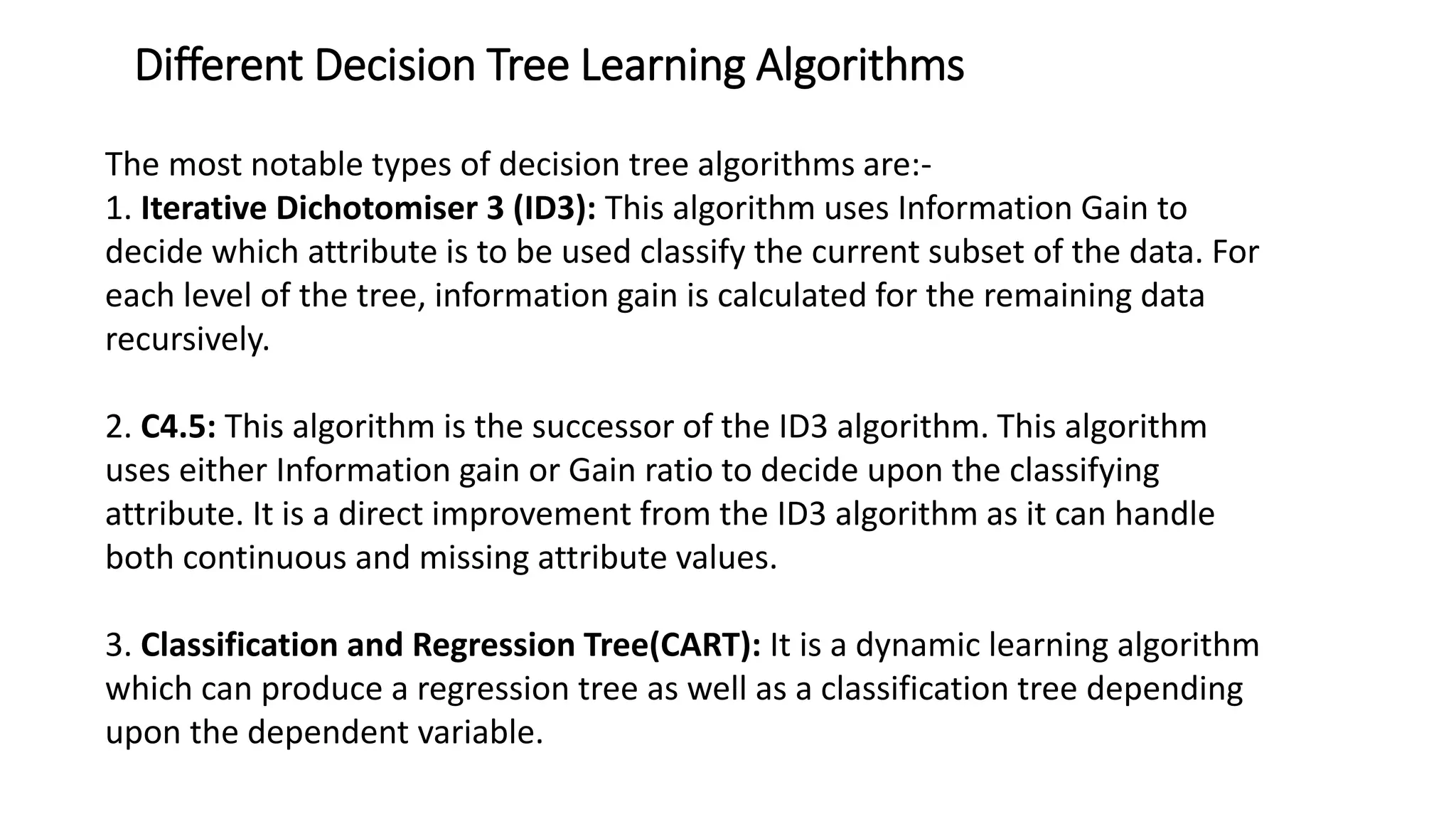
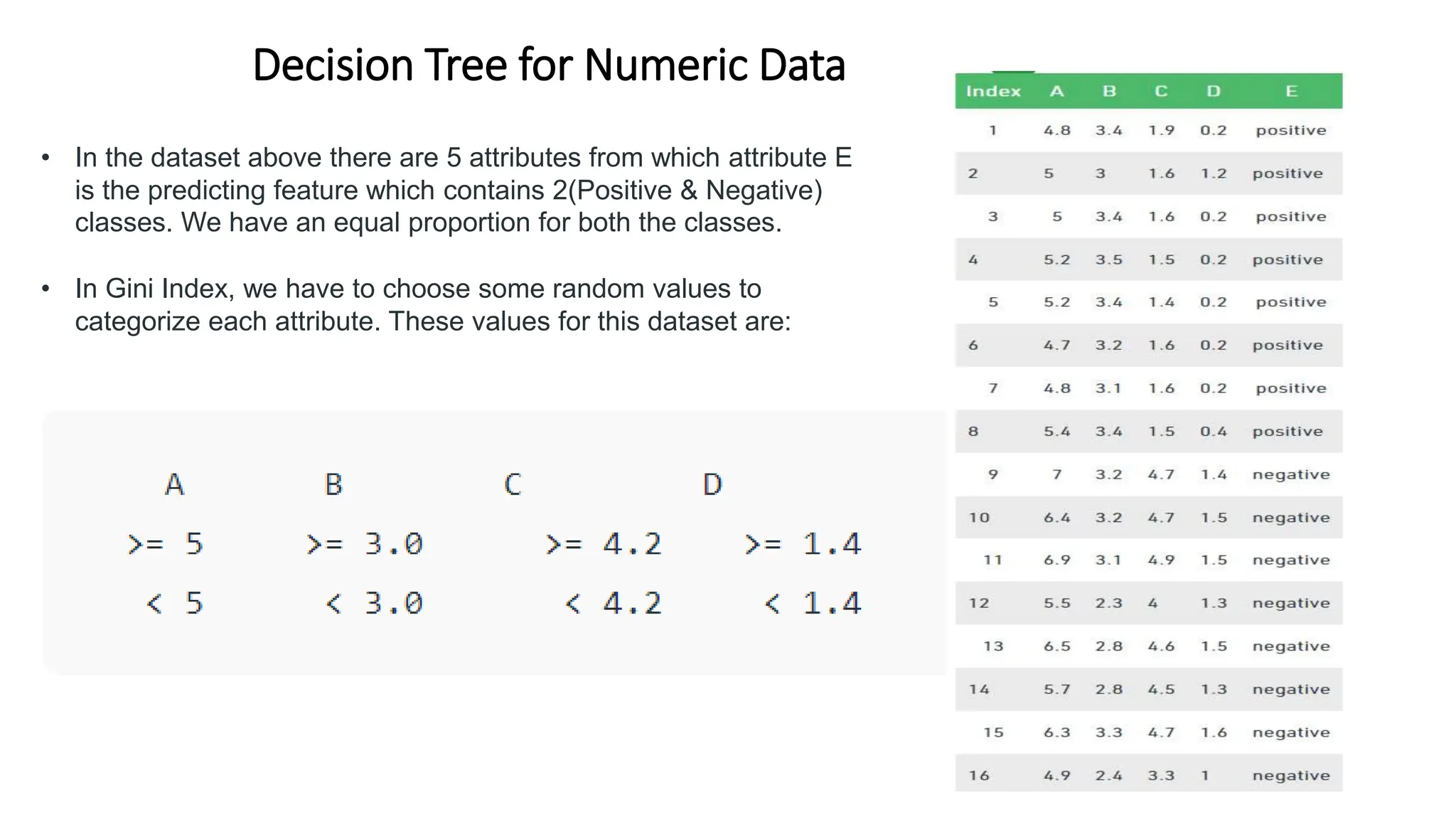
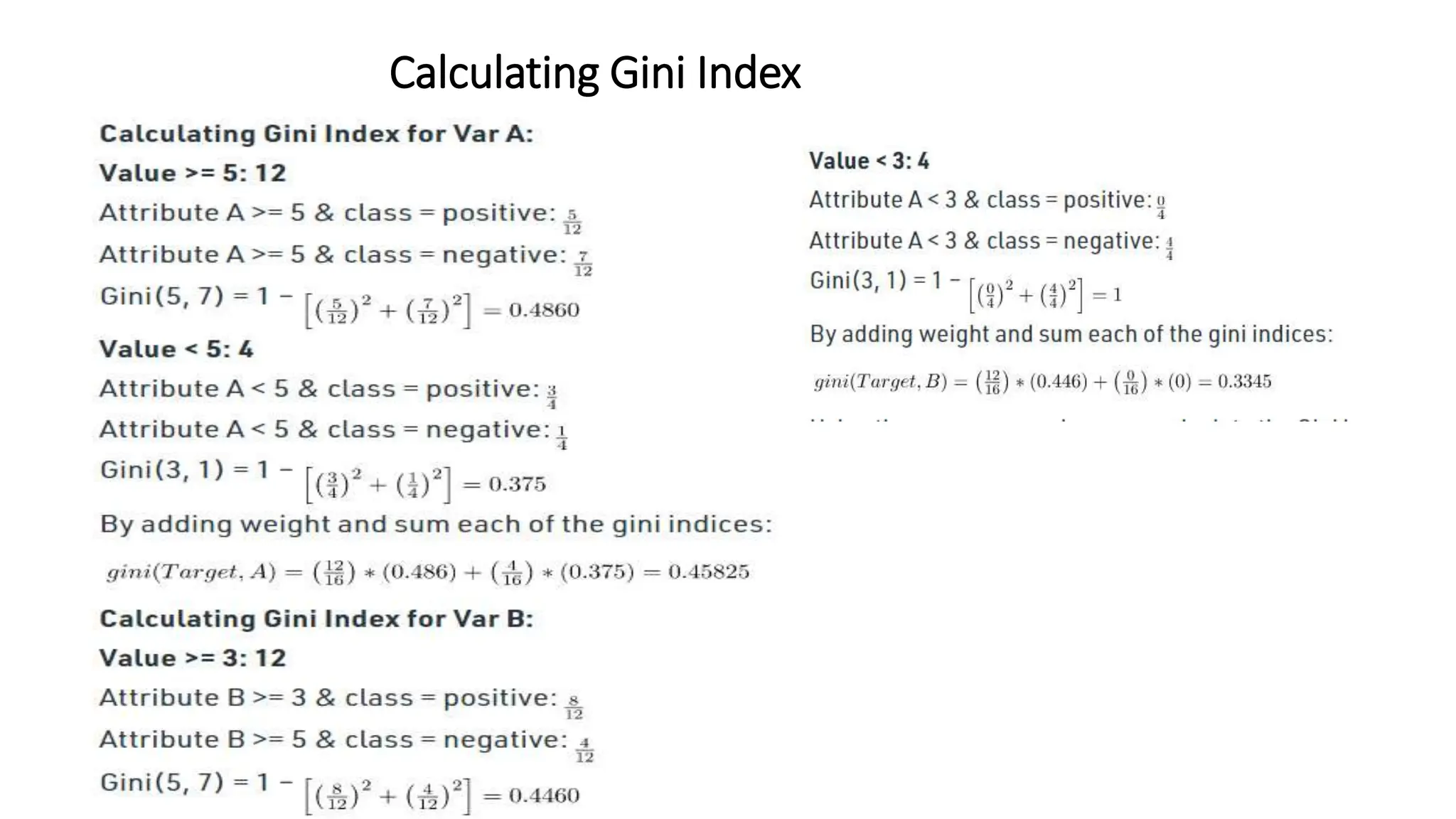
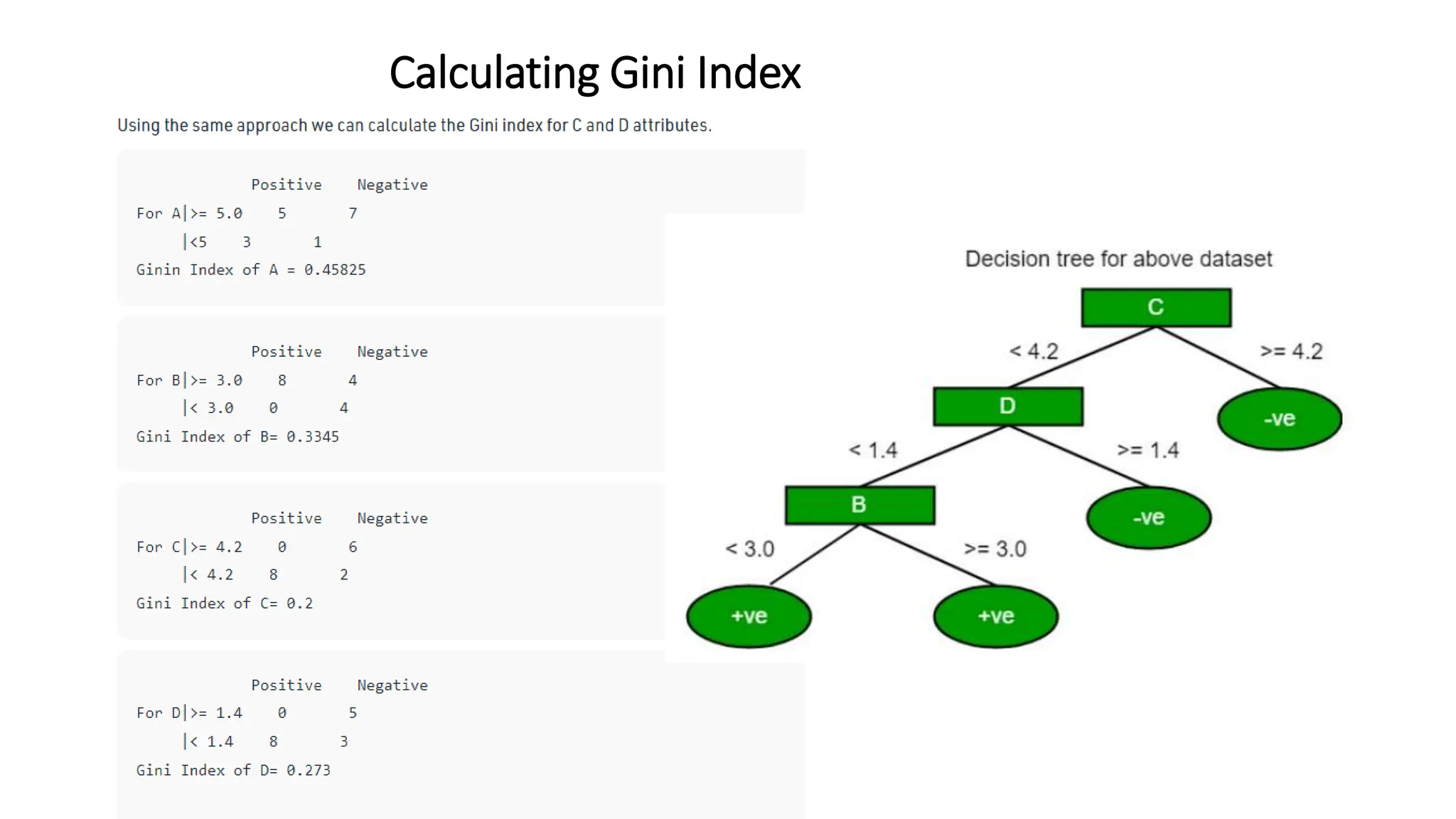
The document discusses decision tree learning algorithms. It explains that a decision tree is a tree-structured model that tests attributes to predict an output. The ID3 algorithm selects the attribute with the highest information gain at each step and recursively builds the tree. Different algorithms like ID3, C4.5 and CART are described, along with measures used to select nodes like entropy, information gain, and Gini index. It also discusses handling numeric data and provides references for further information.