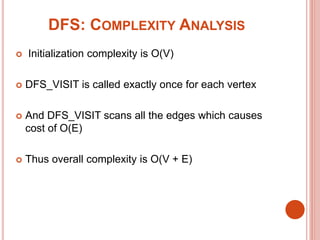
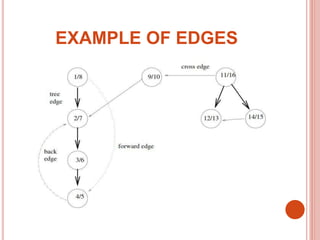
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm that explores all the vertices reachable from a starting vertex by traversing edges in a depth-first manner. DFS uses a stack data structure to keep track of vertices to visit. It colors vertices white, gray, and black to indicate their status. DFS runs in O(V+E) time and can be used for applications like topological sorting and finding strongly connected components. The edges discovered during DFS can be classified as tree, back, forward, or cross edges based on the order in which vertices are discovered.
![DEPTH FIRST
SEARCH [DFS]
By,
K.B.Snega,M.sc(cs).,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/depthfirstsearchdfs-190926145304/85/Depth-first-search-dfs-1-320.jpg)

![INTRO….
To keep track of progress DFS colors each vertex
white, gray or black. Initially all the vertices are
colored white. Then they are colored gray when
discovered. Finally colored black when finished.
Besides creating depth first forest DFS also
timestamps each vertex. Each vertex goes through
two time stamps:
Discover time d[u]: when u is first discovered
Finish time f[u]: when backtrack from u or finished
u
f[u] > d[u]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/depthfirstsearchdfs-190926145304/85/Depth-first-search-dfs-3-320.jpg)
![DFS: ALGORITHM
DFS: Algorithm
DFS(G)
1. for each vertex u in G
2. color[u]=white
3. ᴨ[u]=NIL
4. time=0
5. for each vertex u in G
6. if (color[u]==white)
7. DFS-VISIT(G,u)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/depthfirstsearchdfs-190926145304/85/Depth-first-search-dfs-4-320.jpg)
![ALGO(CONT…)
DFS-VISIT(u)
1. time = time + 1
2. d[u] = time
3. color[u]=gray
4. for each v € Adj(u) in G do
5. if (color[v] = =white)
6. ᴨ [v] = u;
7. DFS-VISIT(G,v);
8. color[u] = black
9. time = time + 1;
10. f[u]= time;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/depthfirstsearchdfs-190926145304/85/Depth-first-search-dfs-5-320.jpg)



![Depth first search [dfs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/depthfirstsearchdfs-190926145304/85/Depth-first-search-dfs-11-320.jpg)