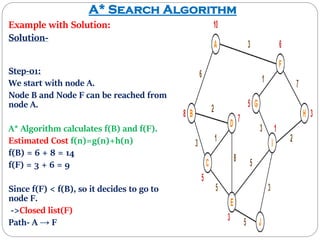
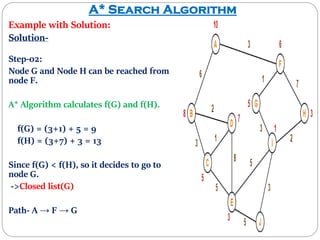
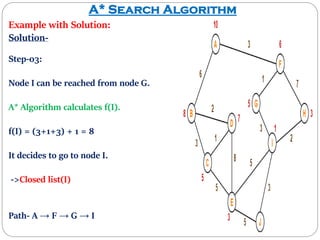
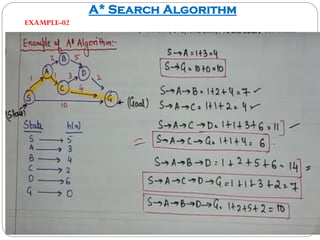
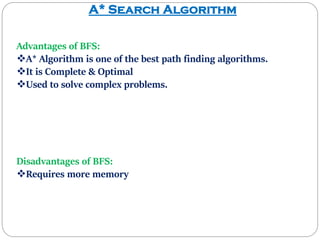
The document discusses the A* search algorithm, a heuristic search technique for finding the shortest path using estimated costs. It details the algorithm's function, implementation steps, and comparisons with other methods like breadth-first search. Advantages of A* include its completeness and optimality, while its main disadvantage is higher memory usage.