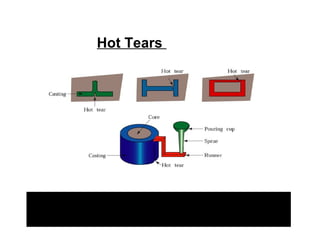
This document discusses common casting defects such as surface defects, internal defects, incorrect chemical composition, and unsatisfactory mechanical properties. It defines casting defects and explains how they reduce output and increase production costs. Specific defects covered include swell, fins, gas holes, shrinkage cavities, hot tears, and cold shuts. For each defect, the causes and remedies are described. Even in modern foundries, the rejection rate can be as high as 20% of total castings produced due to these defects.