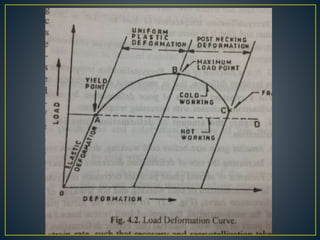
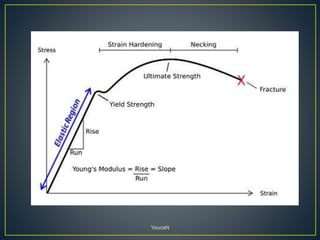
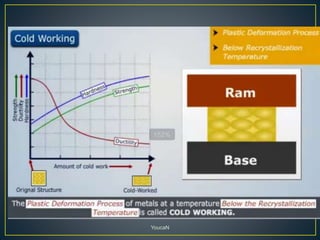
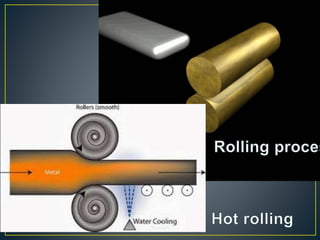
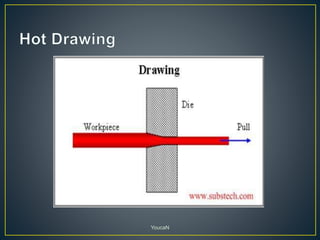
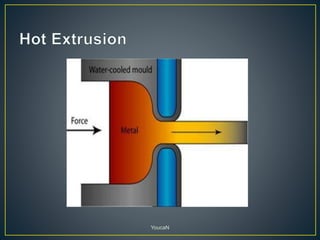
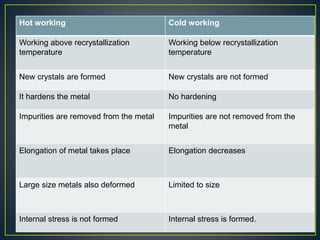
1. Cold working is the plastic deformation of metals at a temperature below the recrystallization temperature, while hot working occurs above the recrystallization temperature.
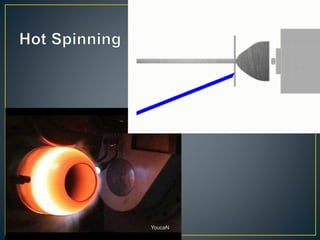
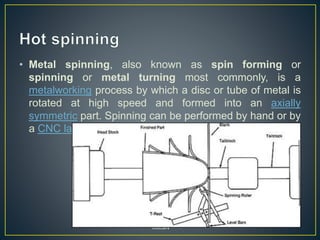
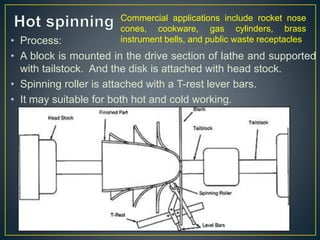
2. Metal spinning is a metalworking process that forms an axially symmetric part by rotating a disc or tube of metal at high speed against a spinning roller. It can be done by hand or CNC lathe.
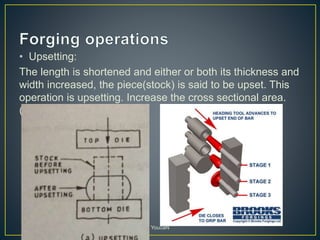
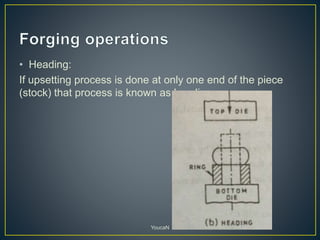
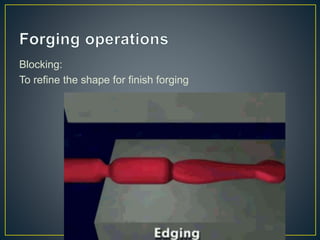
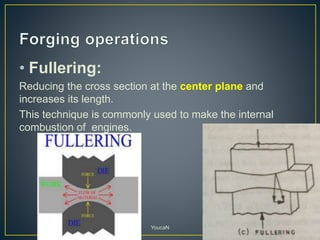
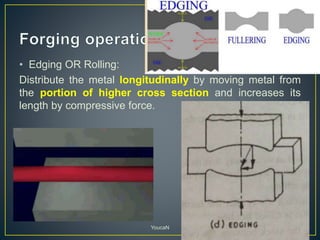
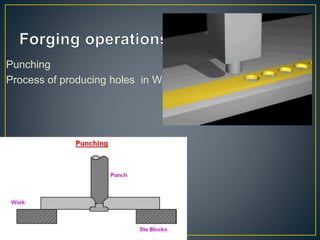
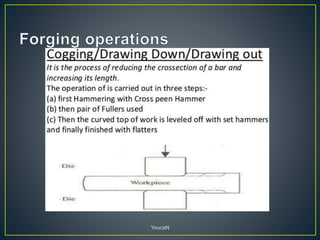
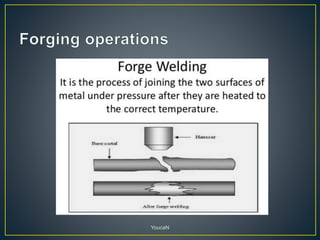
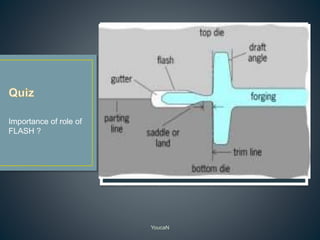
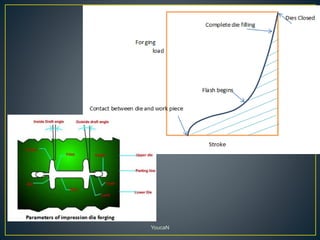
3. Forging processes like upsetting, heading, blocking, and fullering are used to refine the shape of metals for finishing. Punching and blanking are shearing processes used to produce holes.