Embed presentation
Downloaded 48 times


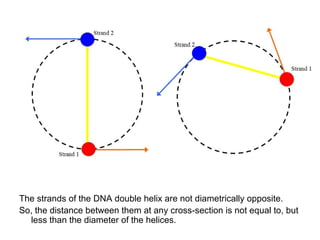
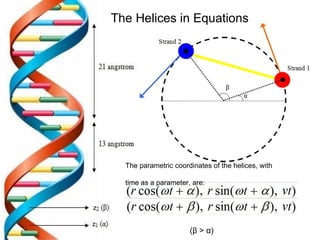




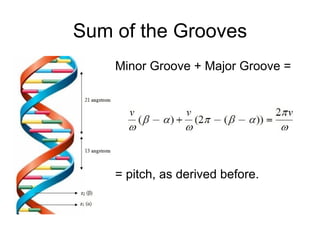

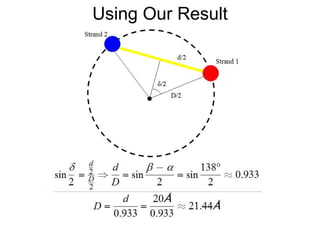


1) The DNA double helix structure has two helical strands that are skewed and not directly opposite each other, resulting in a distance between the strands at any cross-section that is less than the diameter of the helices. 2) The structure of the two helical strands can be defined mathematically using parametric coordinates, where the angle θ increases by 2π with each turn of the helix. 3) The pitch of the helix, or vertical rise of one complete turn, can be calculated using the parametric coordinates and angles of the two helical strands.











