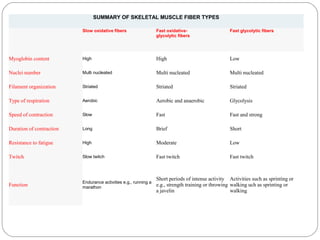
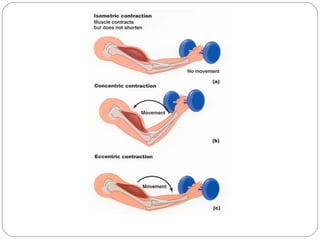
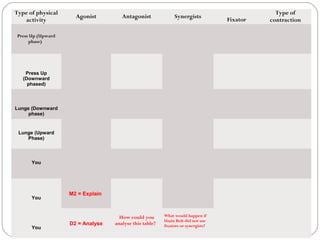
This document discusses the types of muscle fibers and their characteristics. It describes three main types of muscle fibers: slow oxidative fibers, fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers, and fast glycolytic fibers. For each fiber type, it provides information on their myoglobin content, number of nuclei, filament organization, type of respiration, speed and duration of contraction, resistance to fatigue, twitch type, and general function.