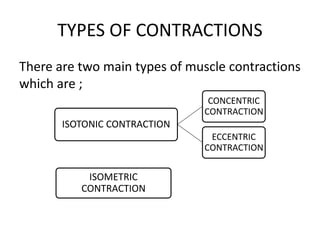
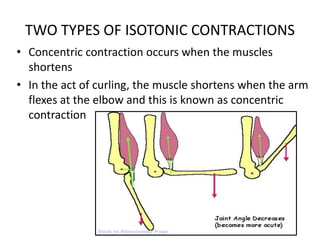
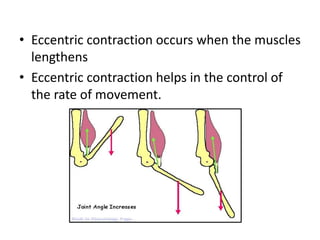
There are three main types of muscle contractions: isotonic, isometric, and eccentric/concentric contractions. Isotonic contractions involve constant tension as the muscle length changes, and can be concentric (shortening) or eccentric (lengthening). Isometric contractions do not involve a change in muscle length, as tension is generated without movement. Proper understanding of contraction types is important for exercise and injury prevention.