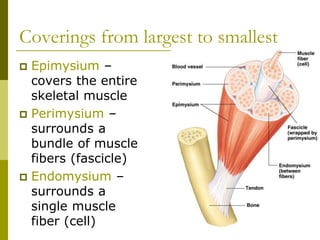
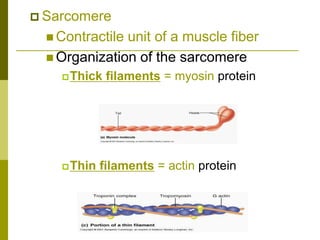
The muscular system is composed of three types of muscles - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle allows for body movement by contracting and shortening. It is organized into fascicles containing bundles of striated muscle fibers. Muscle fibers contain sarcomeres, the basic contractile units composed of overlapping actin and myosin filaments. Nerve stimulation triggers calcium release and the sliding of filaments, causing muscle contraction. Contraction relies on aerobic and anaerobic metabolism to regenerate ATP. As muscles contract and relax, they create forces to facilitate various body motions through their attachments to bones and other structures.