Embed presentation

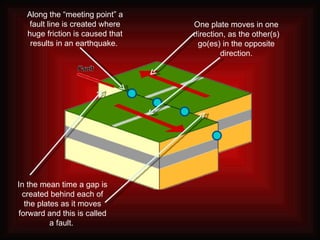





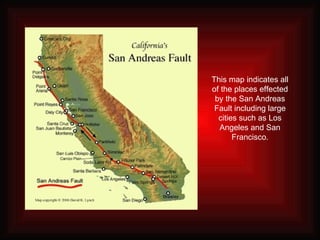









- Conservative (passive) plate boundaries occur where two tectonic plates slide horizontally past one another in opposite directions, causing friction and earthquakes along the fault line where they meet. - As the plates move, a gap is created behind each one called a fault. The best known example is the San Andreas Fault in California, where the Pacific and North American Plates slide past each other. - Major earthquakes, like the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, are caused by the built-up friction along the fault line being suddenly released as the plates shift. These earthquakes can cause widespread damage.
















