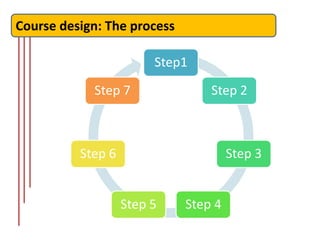
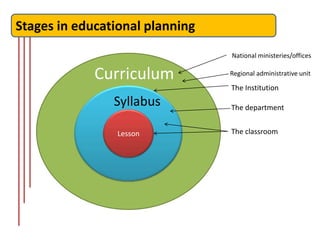
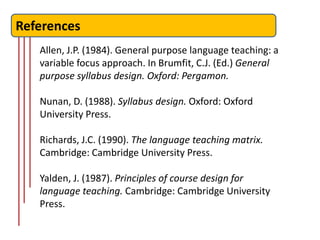
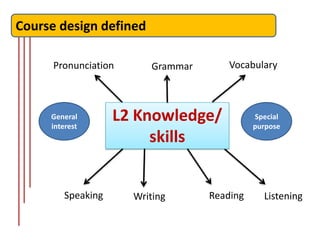
The document outlines the fundamentals of language course design, emphasizing its significance for teachers in developing language knowledge and skills. It distinguishes between syllabus and curriculum, elaborating on their definitions, roles, and the planning process involved in educational settings. Furthermore, it provides a systematic approach to course design and highlights reflection points for educators to consider in their teaching context.


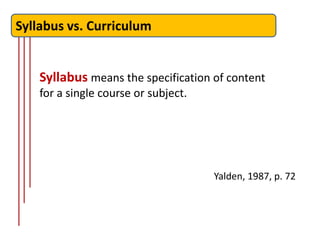
![Syllabus vs. Curriculum
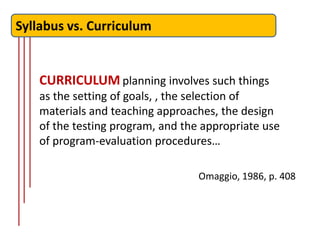
CURRICULA are concerned with making
general statements about language learning,
learning purpose and experience, evaluation
and the relationships between teachers and
learners… [ they also include] banks of learning
items and suggestions about how these might
be used in class
Nunan, 1988, p. 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/languagecoursedesign-121224080321-phpapp02/85/Language-course-design-8-320.jpg)