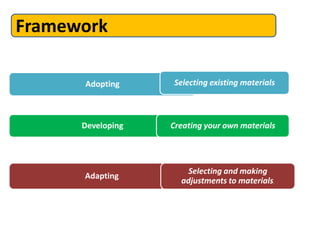
The document outlines principles and frameworks for designing language teaching materials, emphasizing the importance of aligning materials with educational objectives and learner needs. It categorizes materials by purpose, format, and creator, and discusses the processes of adopting, developing, and adapting materials for effective language teaching. Key principles include ensuring materials are engaging, relevant, and promote authentic language use while catering to individual learner differences.