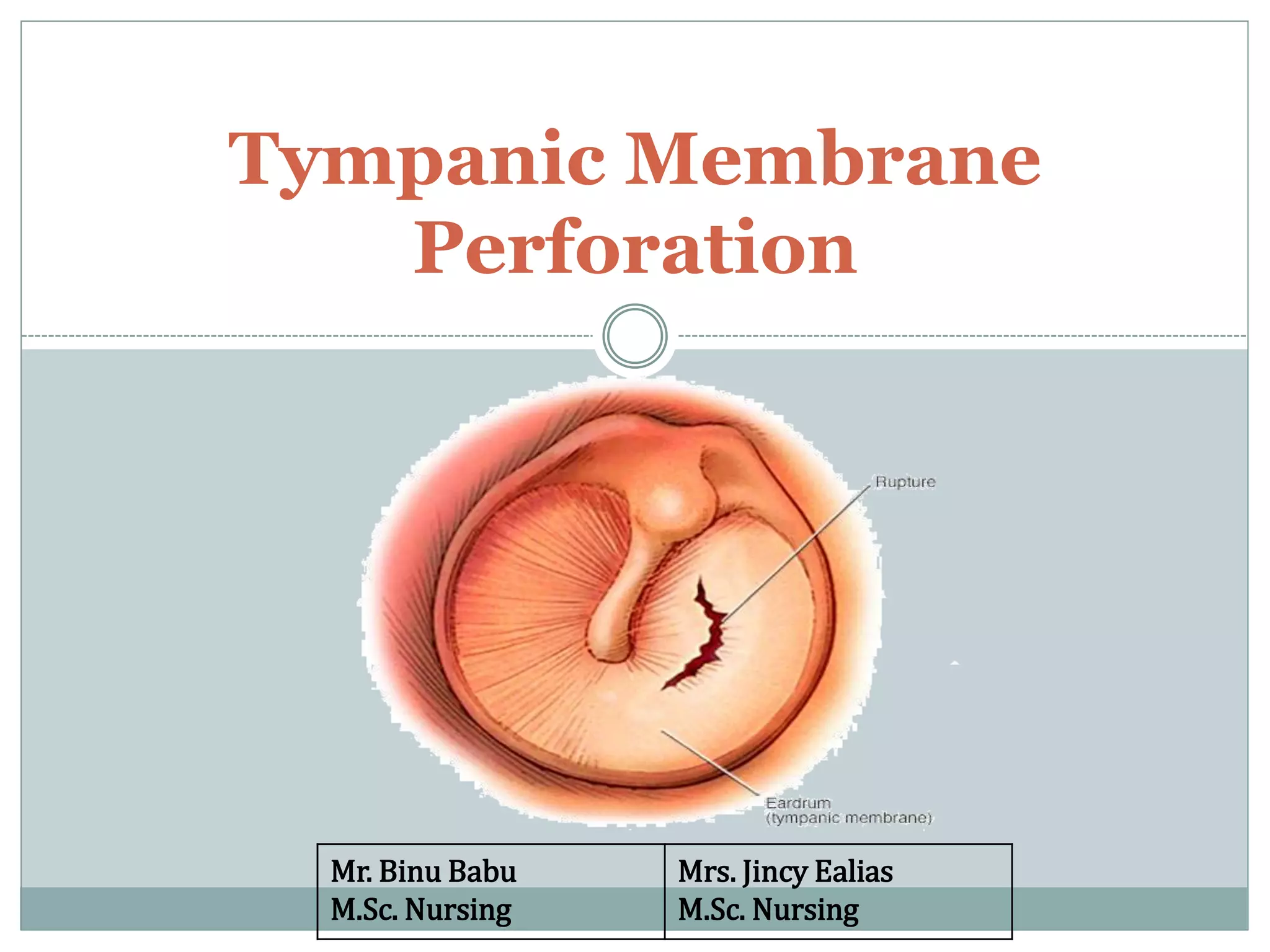
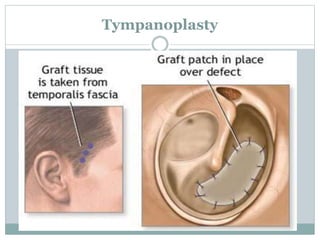
This document discusses tympanic membrane perforation, which is a rupture of the eardrum. It can be caused by ear infections, trauma, or foreign objects in the ear canal. Symptoms include ear pain, bleeding, hearing loss, and drainage from the ear. Diagnosis involves examination of the ear. Small perforations may heal on their own with antibiotics and pain medication, while larger perforations require surgery like myringoplasty or tympanoplasty to repair the eardrum. Post-operative care involves keeping the ear dry and avoiding heavy lifting or air pressure changes for a few weeks.