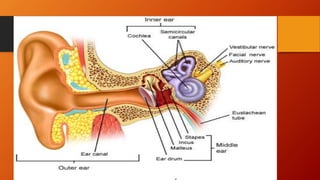
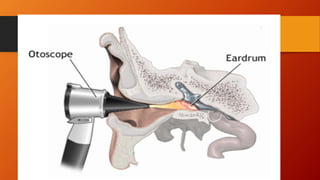
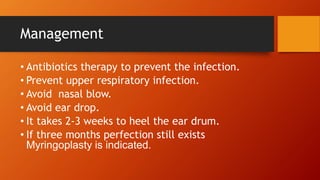
Tympanic membrane perforation is a rupture or hole in the eardrum. It can be caused by direct force like ear wax removal or an indirect force like loud noises. Symptoms include ear pain, fullness, discharge from the ear, and hearing loss. Diagnosis involves examination of the ear. Treatment involves antibiotics to prevent infection along with rest and avoiding loud noises or water in the ear. Small perforations may heal on their own but larger ones require surgery to repair the eardrum.