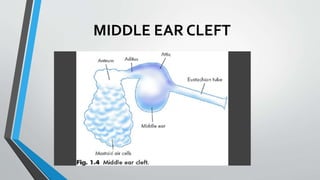
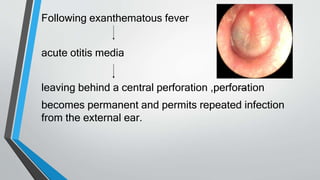
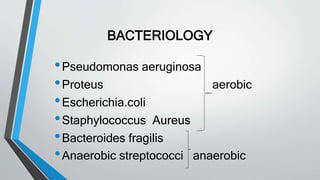
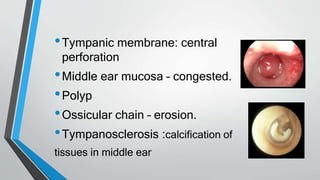
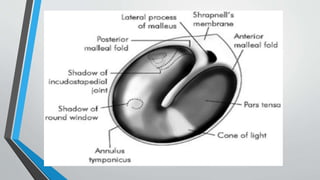
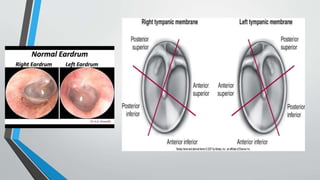
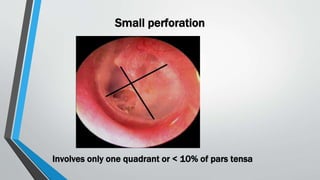
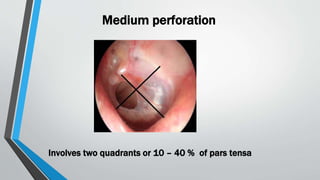
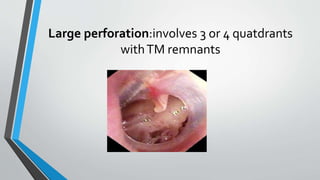
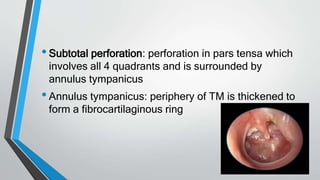
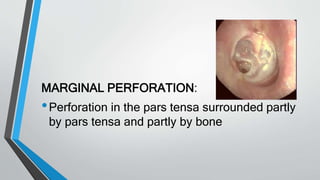
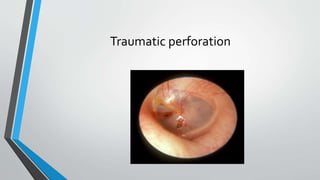
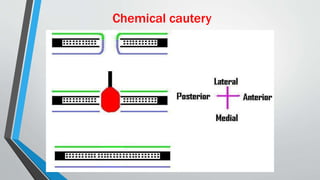
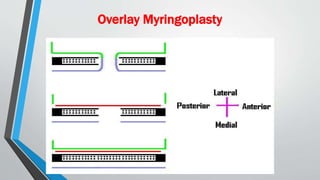
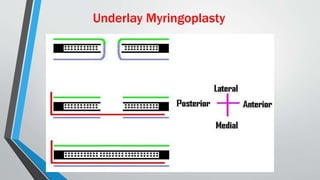
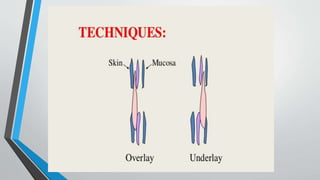
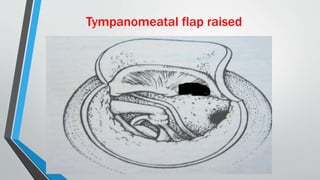
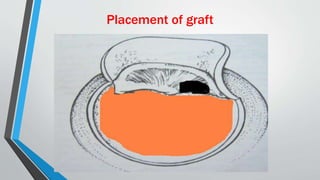
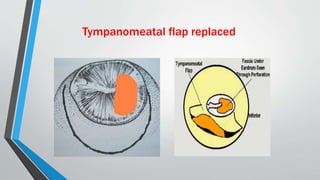
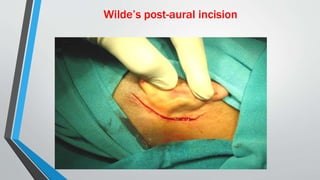
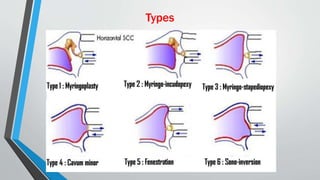
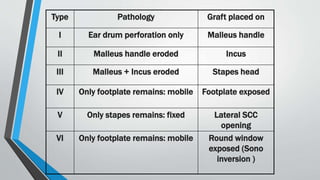
This document discusses chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM), specifically the tubotympanic type. It defines CSOM and describes the anatomy of the middle ear cleft. It discusses the epidemiology, types, etiology, clinical features, investigations and treatment of tubotympanic CSOM. Non-surgical treatment includes aural toilet, antibiotics, and antihistamines. Surgical treatments covered are myringoplasty to repair perforations, and tympanoplasty for more extensive middle ear reconstruction.