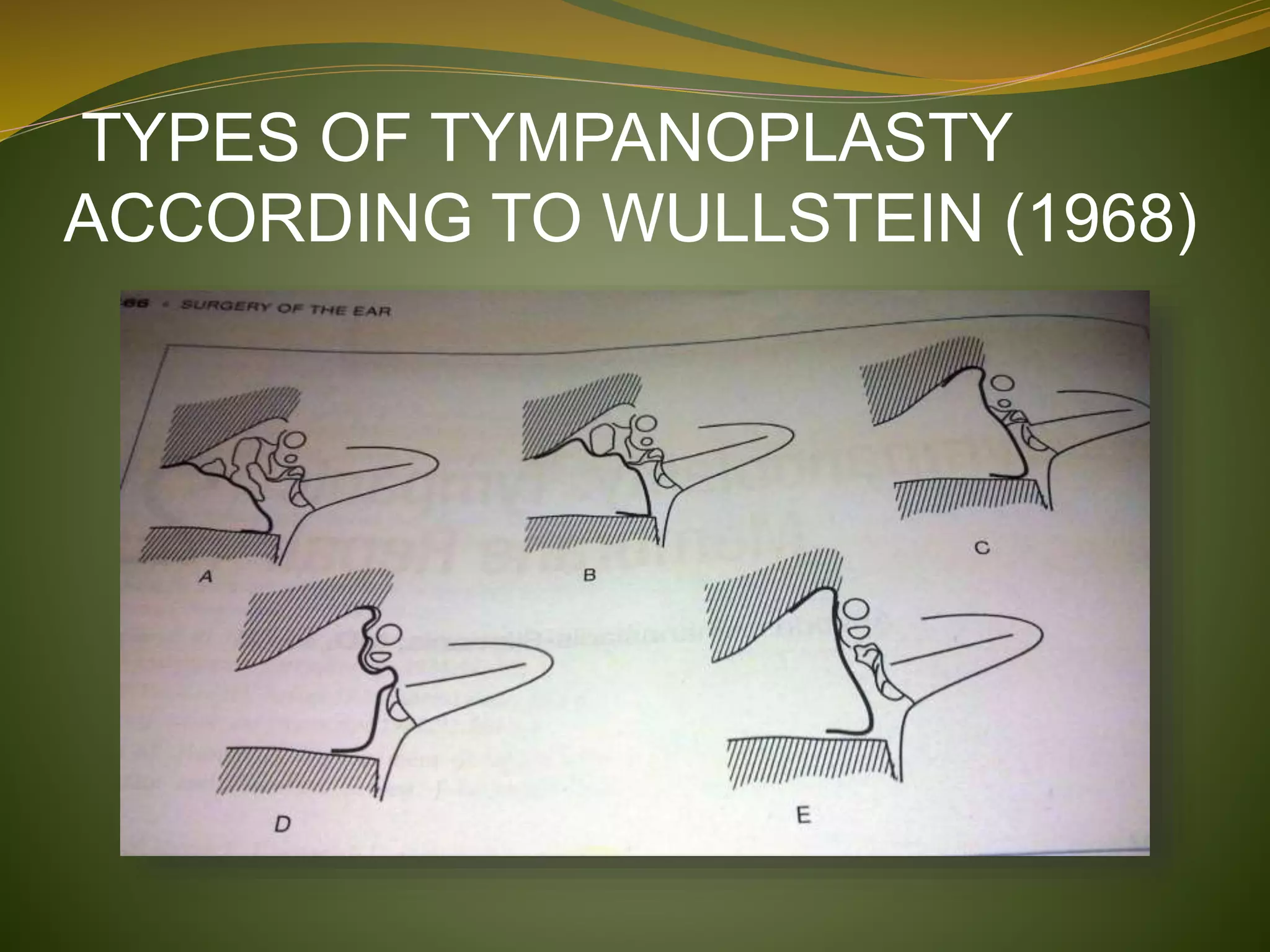
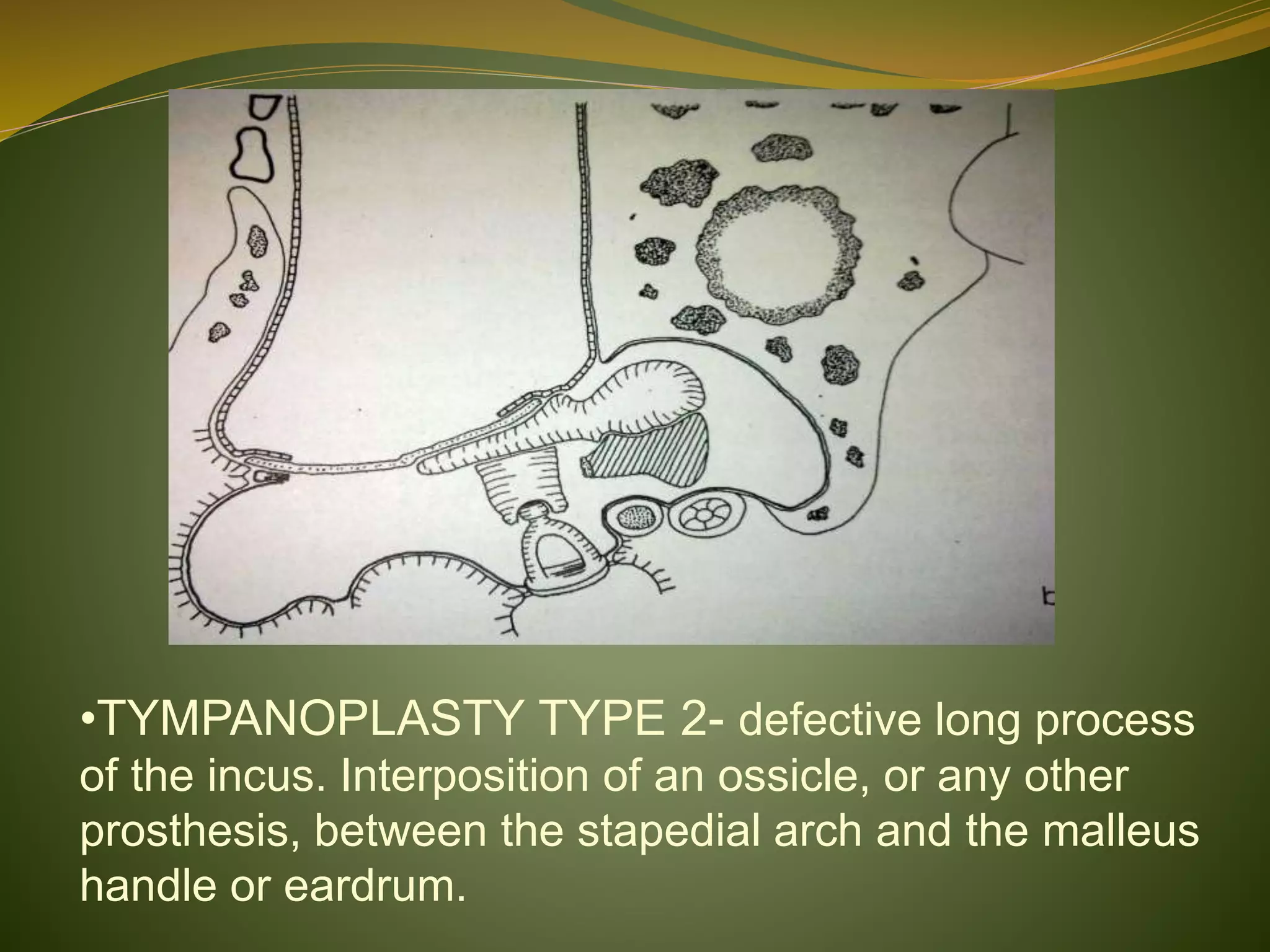
This document defines tympanoplasty and provides a history and overview of the procedure. It begins by defining tympanoplasty as a procedure to eradicate disease in the middle ear and reconstruct the hearing mechanism, with or without grafting of the tympanic membrane. It then discusses the history of developments in tympanoplasty techniques from the 1950s onward. The document outlines the aims, objectives, types based on various classification systems, indications, contraindications and steps of performing tympanoplasty.