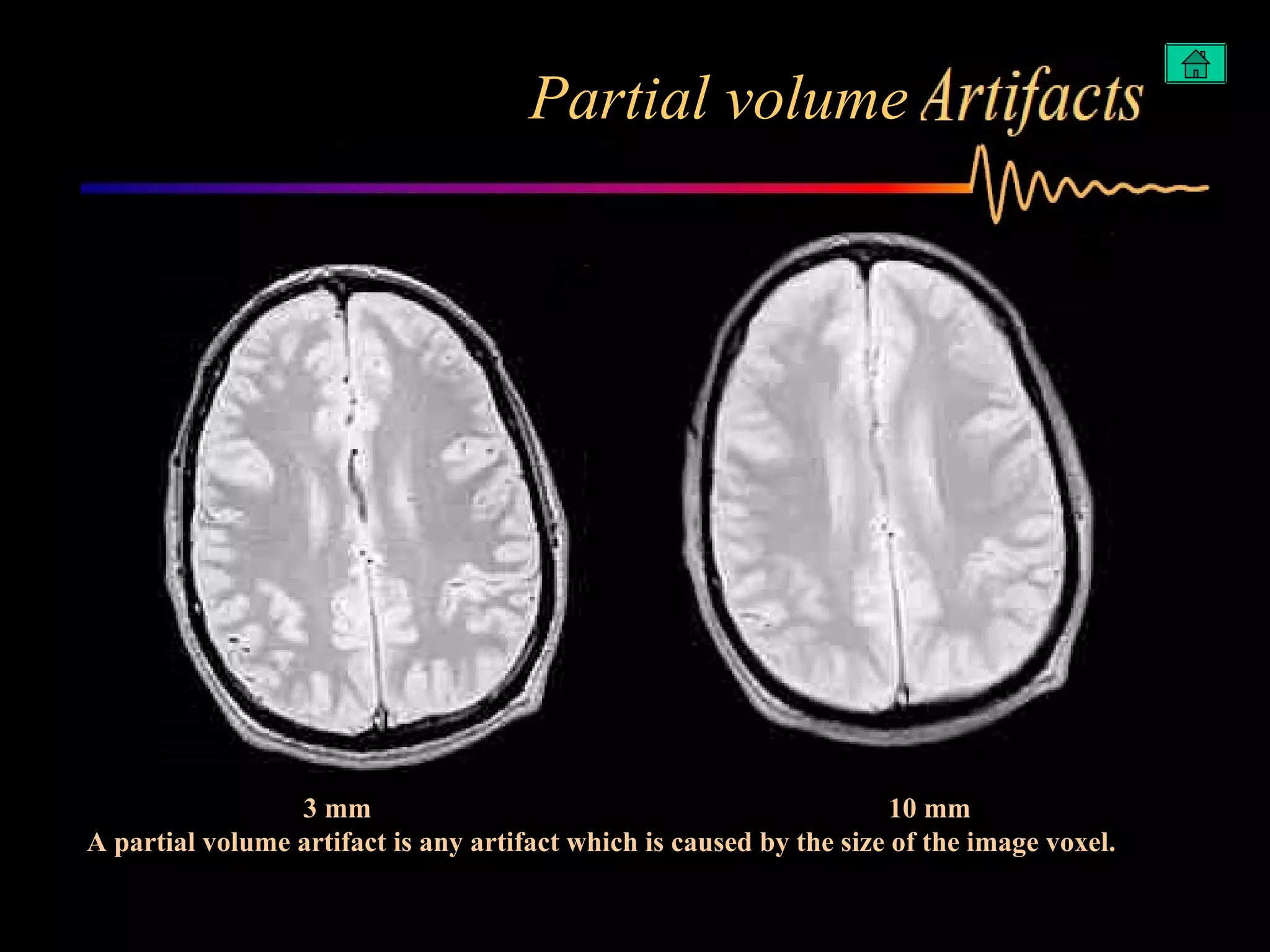
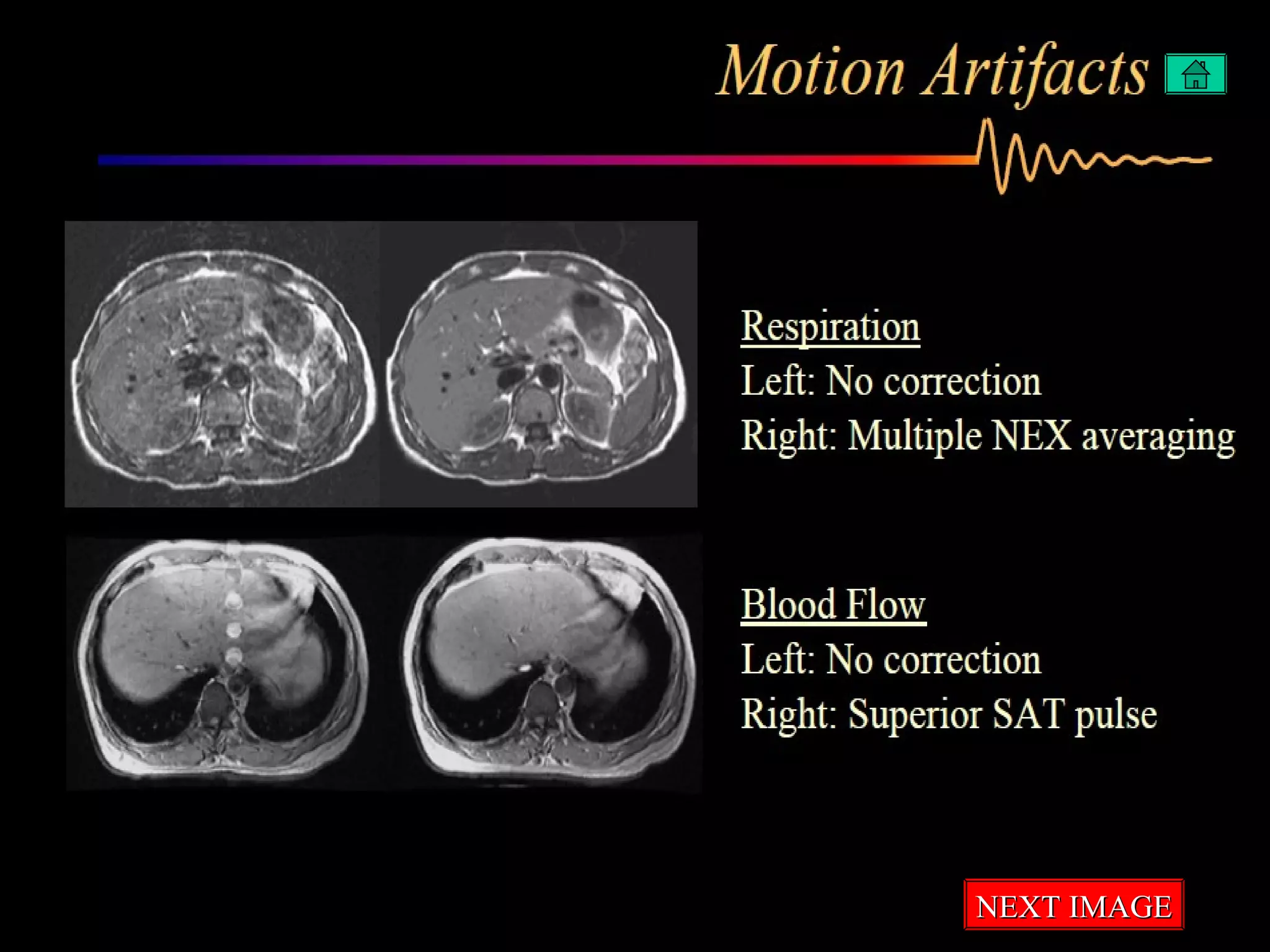
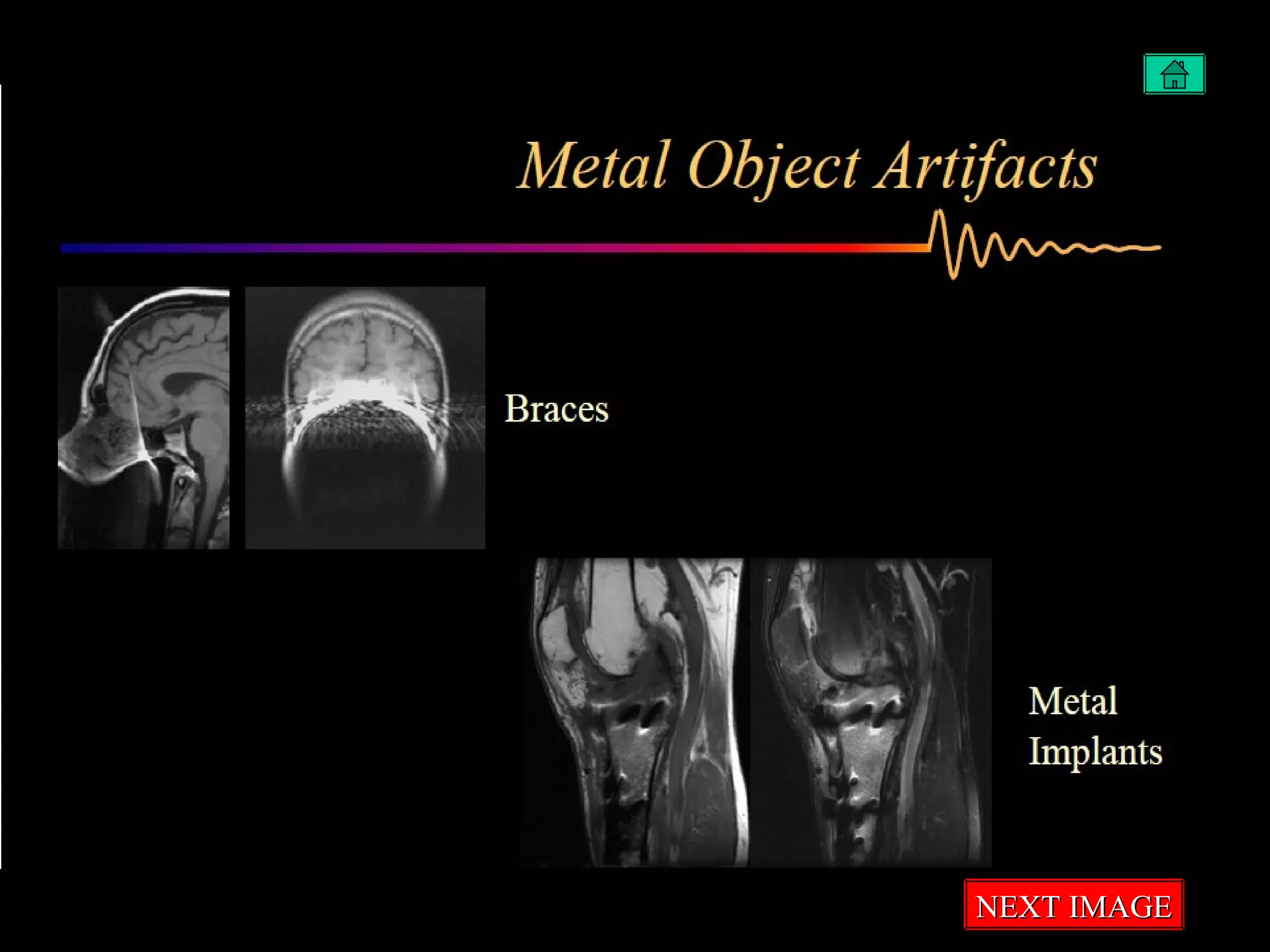
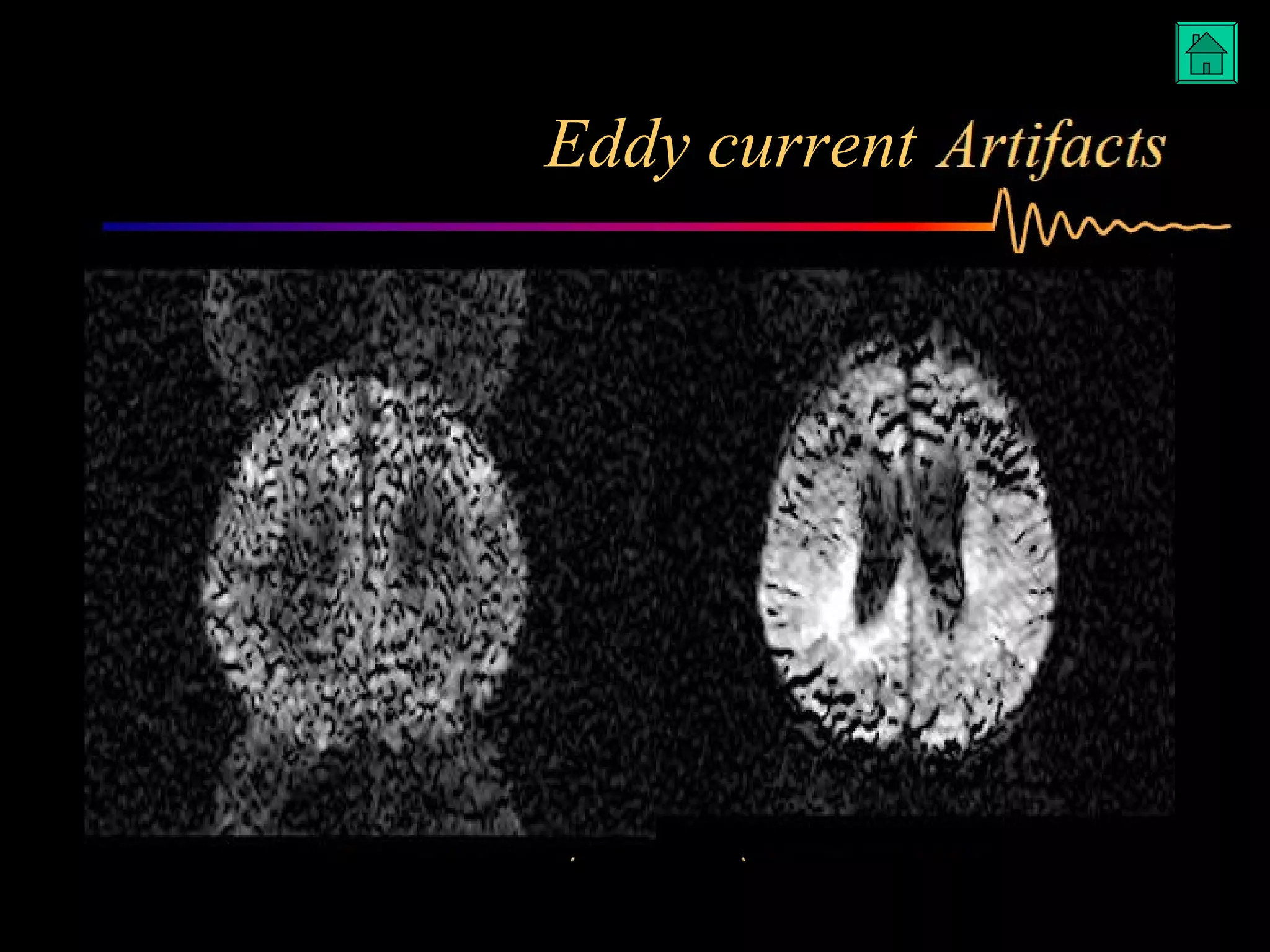
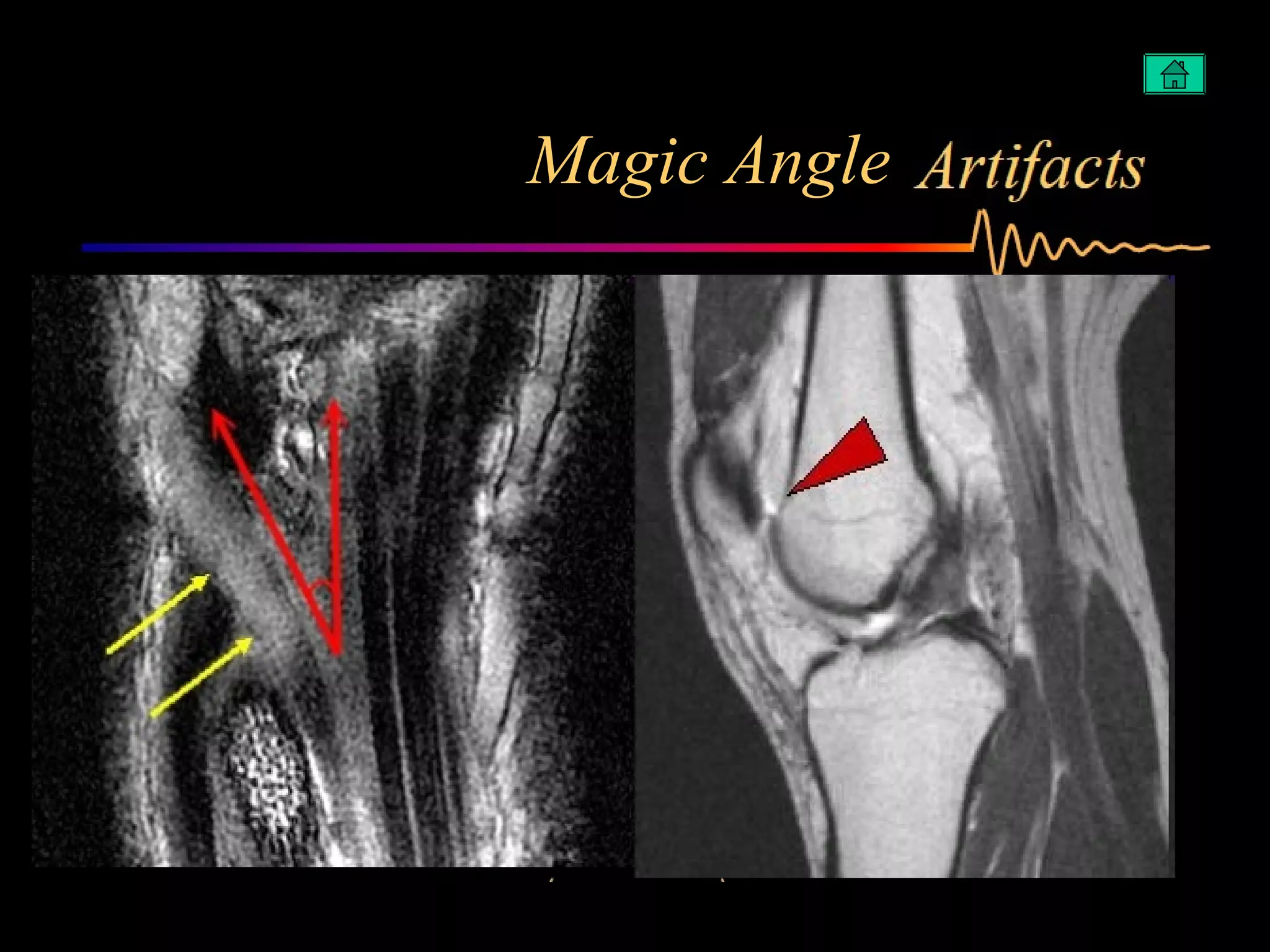
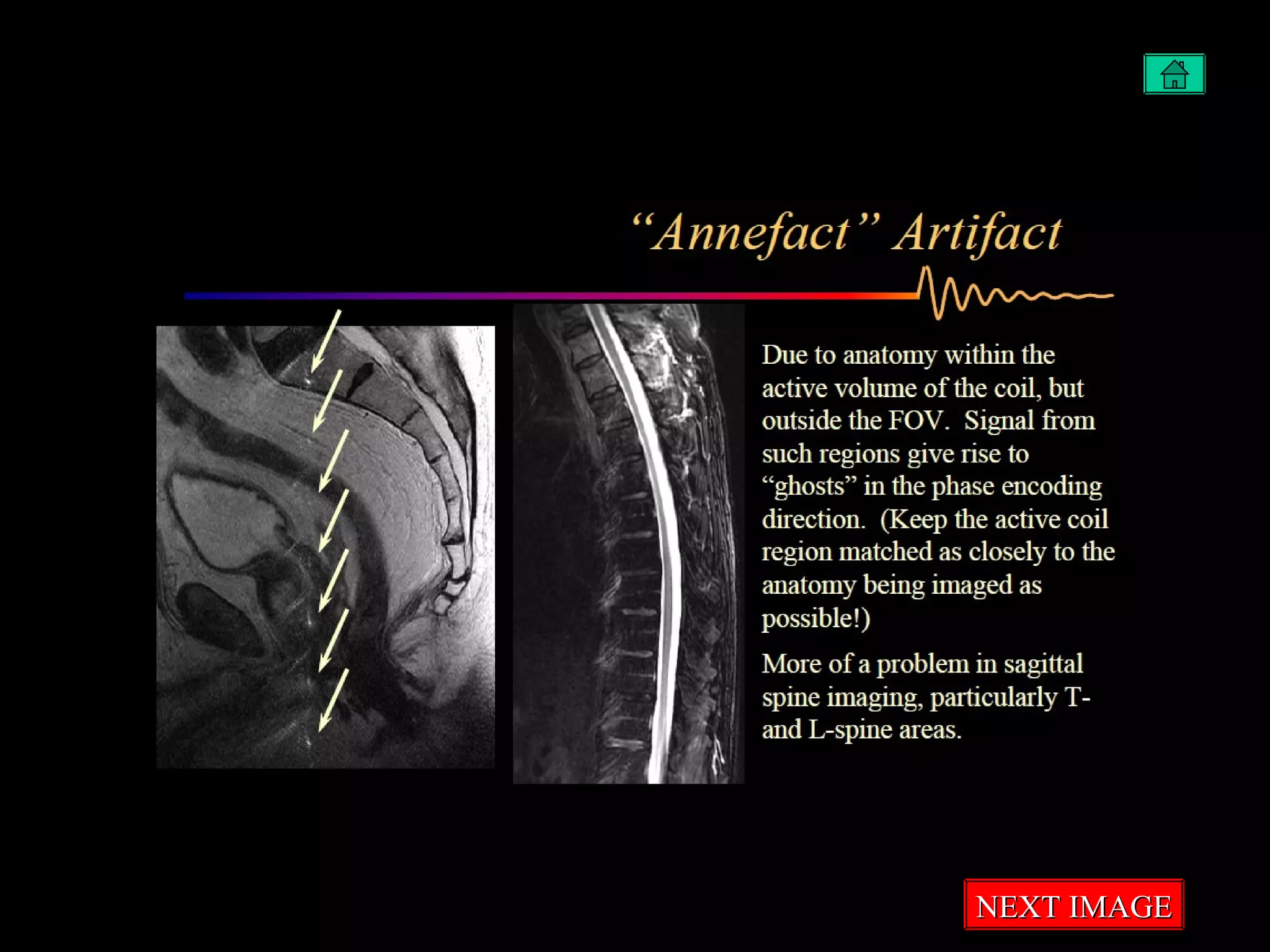
The document summarizes common artifacts seen in MRI imaging including wrap around artifacts caused by a small field of view, partial volume artifacts from thick slices, chemical shift misregistration from misaligned water and fat signals, and motion-induced ghosts from patient movement during scanning. It provides examples and explanations of each artifact type as well as potential corrections.