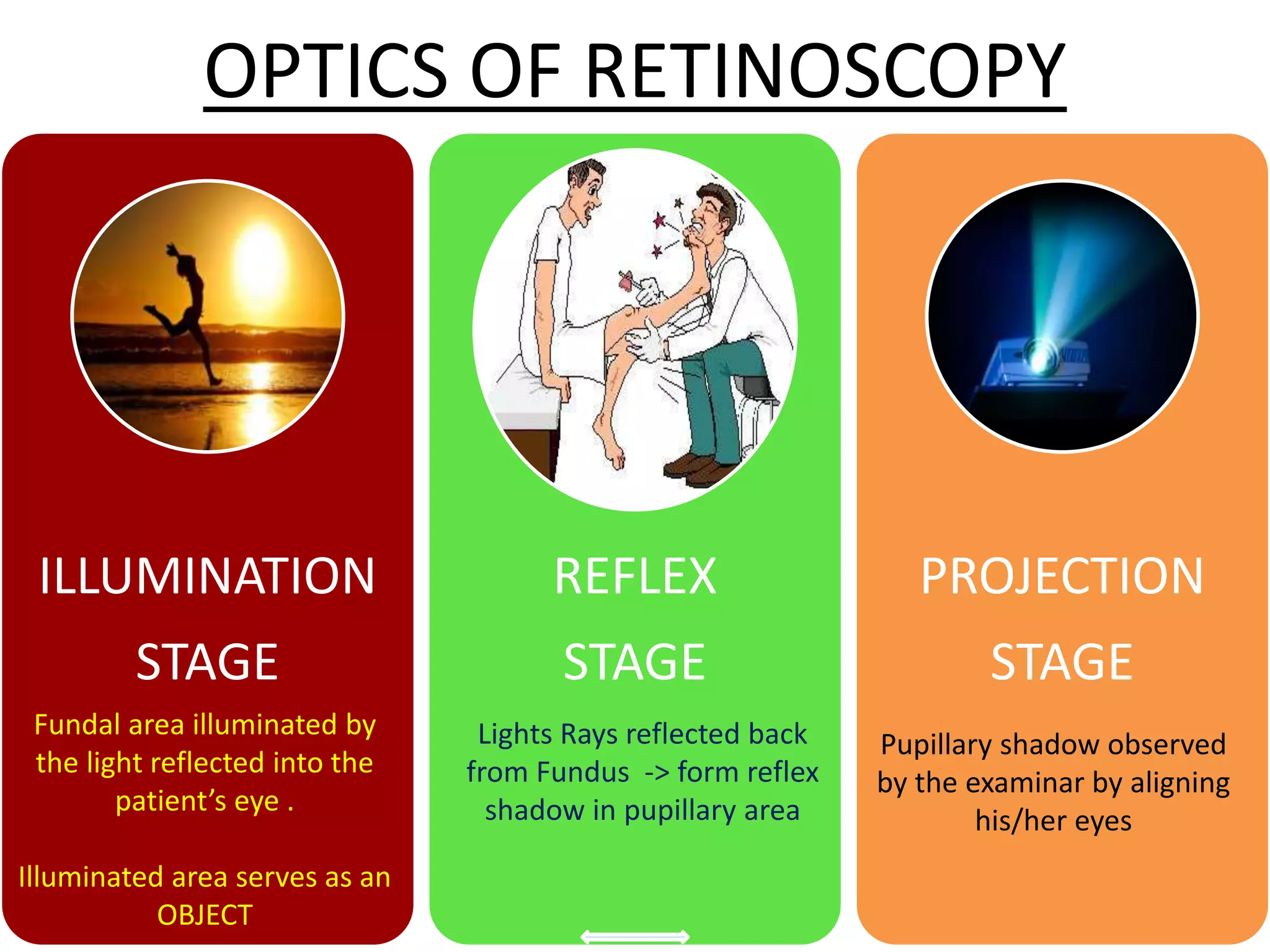
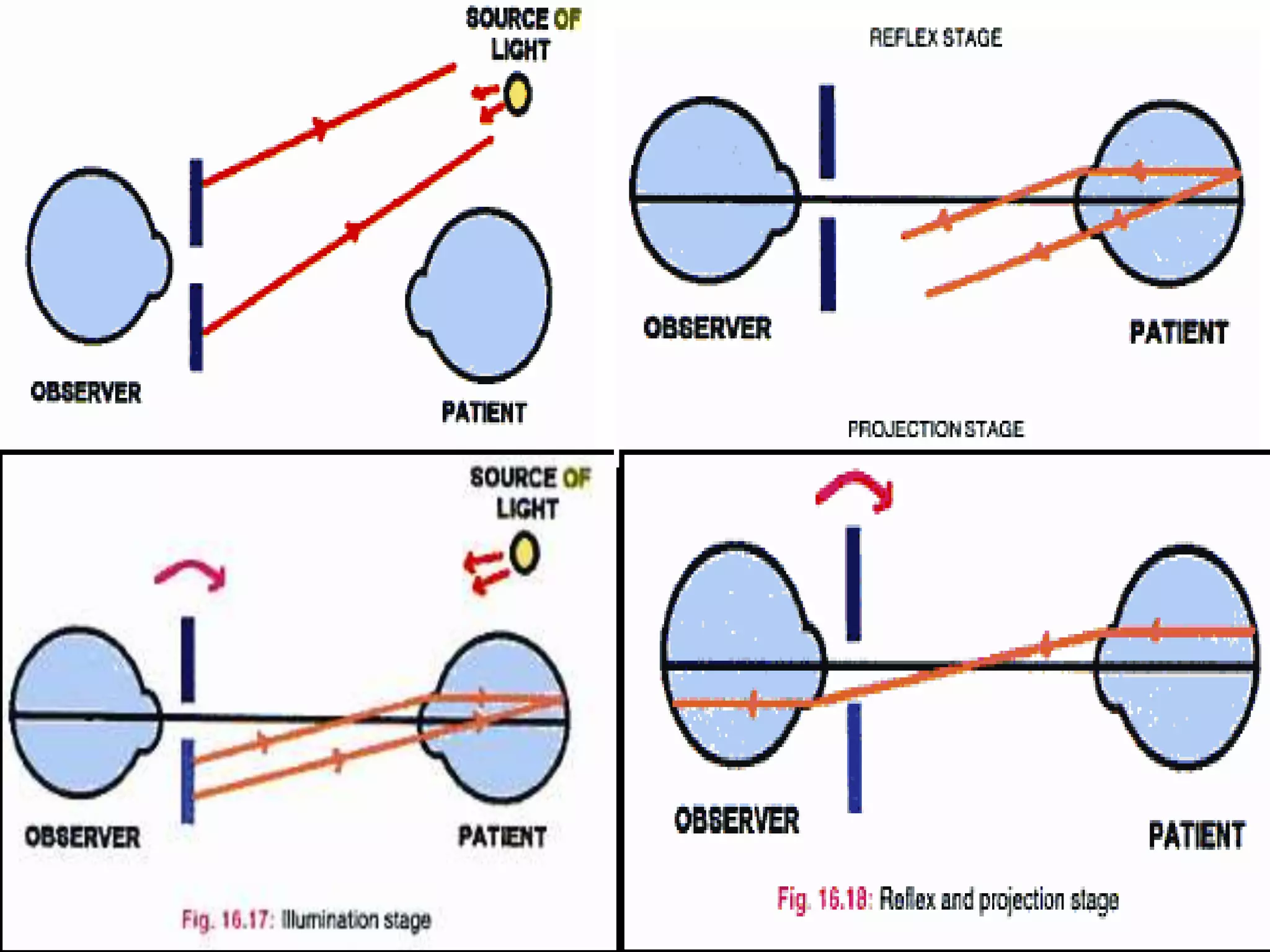
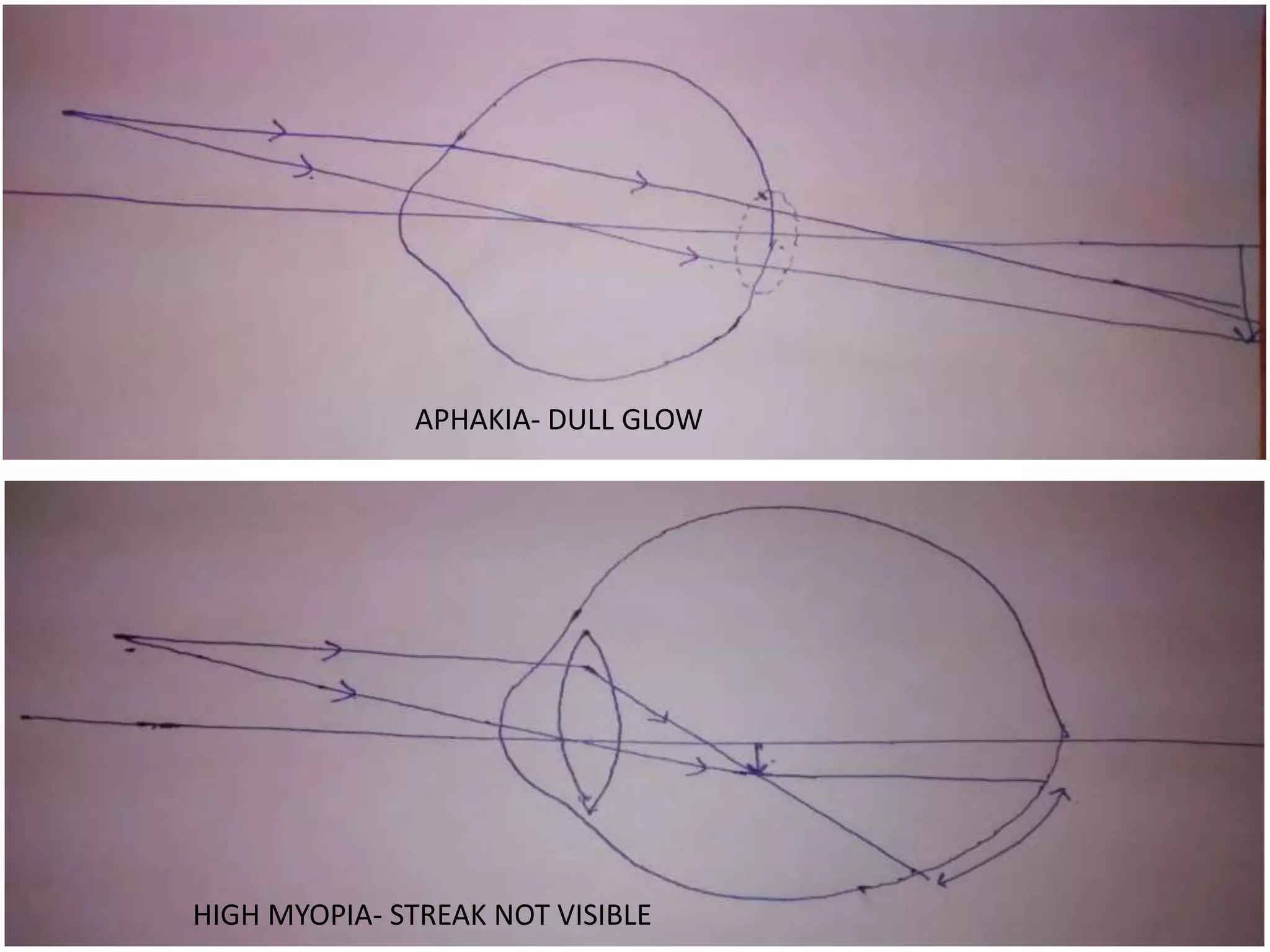
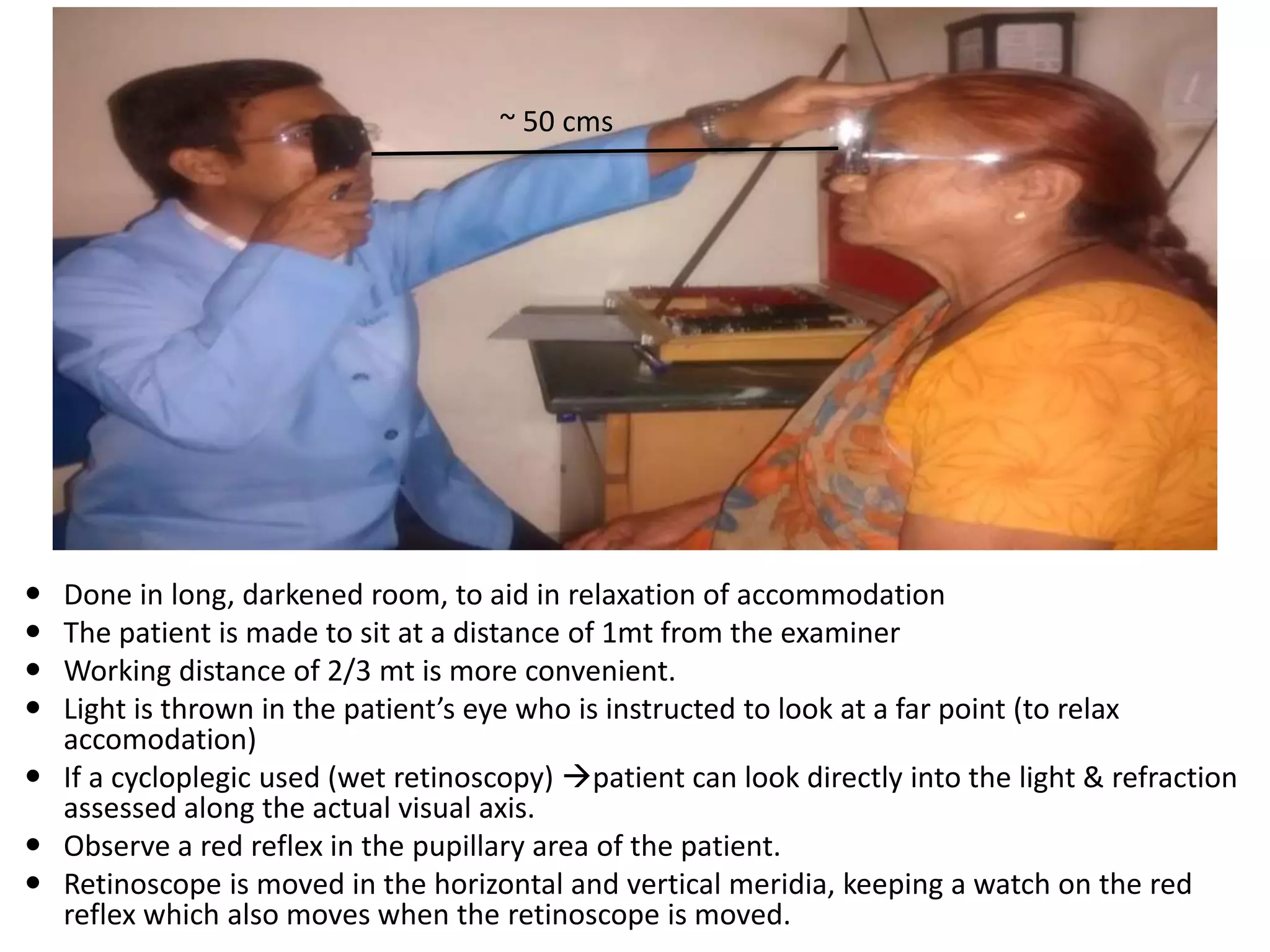
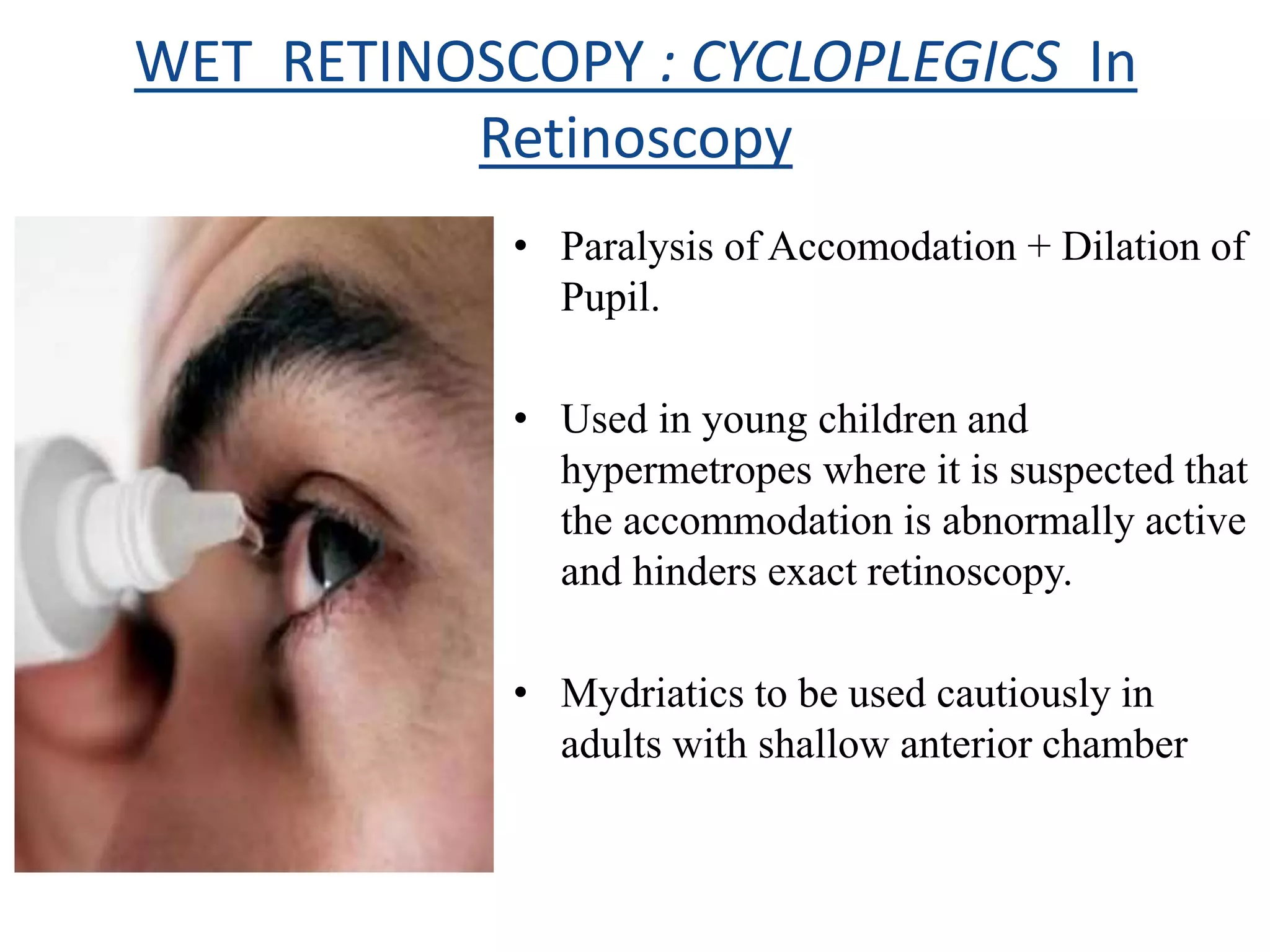
Dr. Pushkar Dhir gave a seminar on retinoscopy. He discussed how retinoscopy works by illuminating the retina and observing the light reflex. It can be used to objectively measure refractive error in infants and others who cannot communicate. Both dry and wet retinoscopy were explained. Challenges like an unclear red reflex due to media opacity or high refractive error were addressed. Subjective refinement using techniques like the Jackson Cross Cylinder was also covered. The seminar provided an in-depth overview of the retinoscopy procedure and techniques.