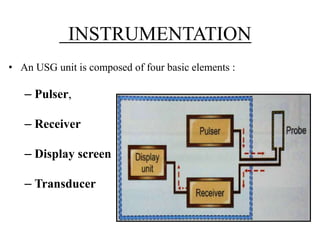
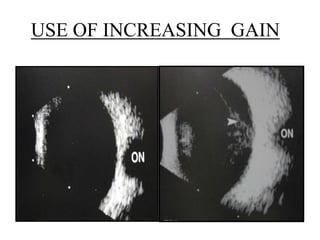
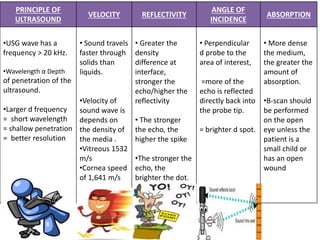
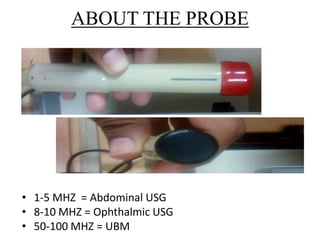
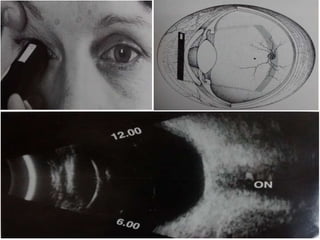
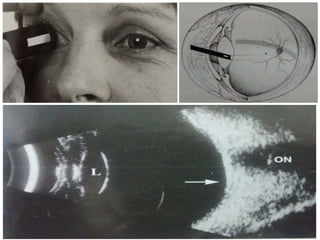
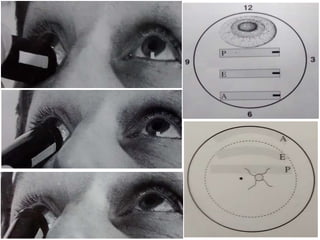
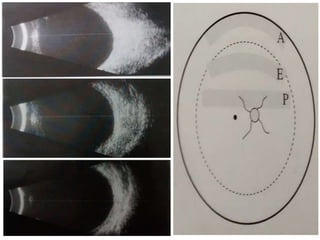
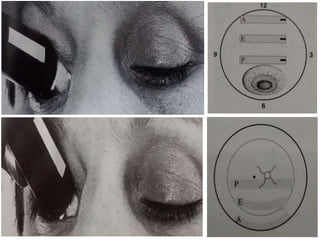
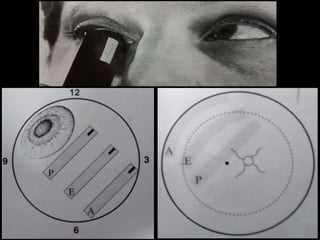
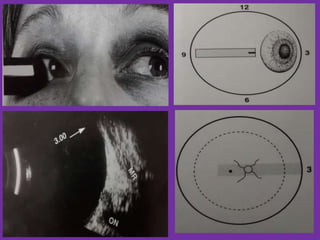
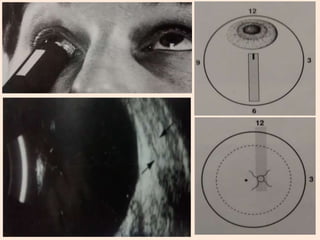
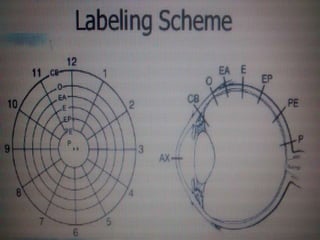
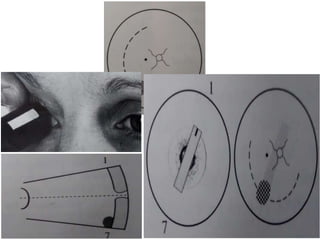
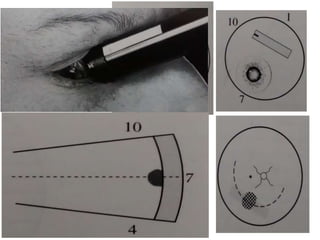
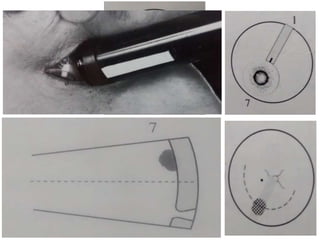
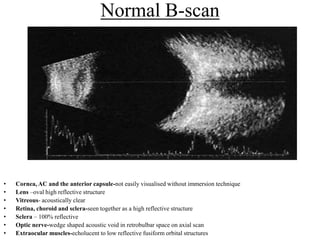
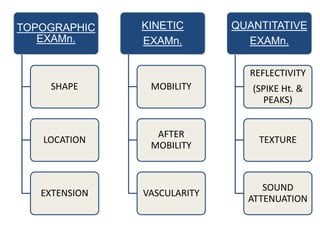
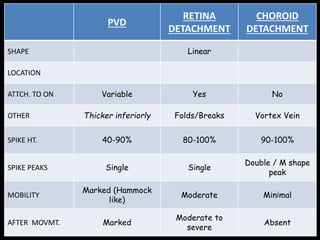
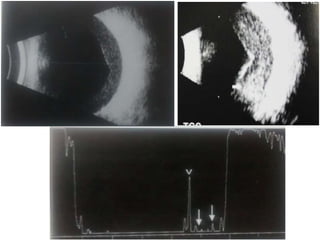
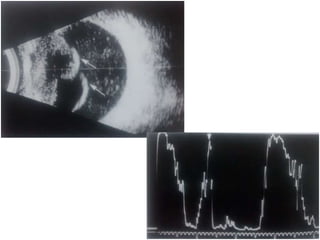
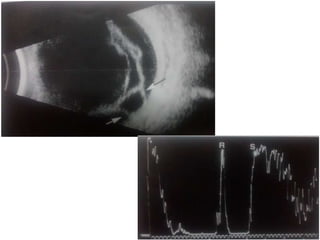
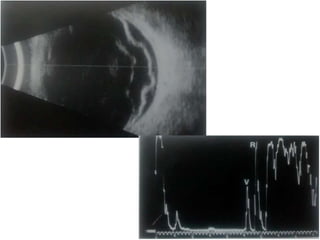
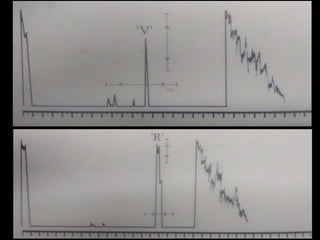
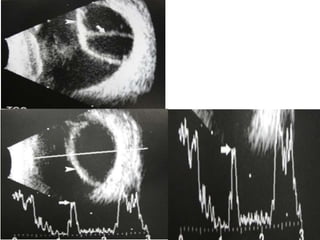
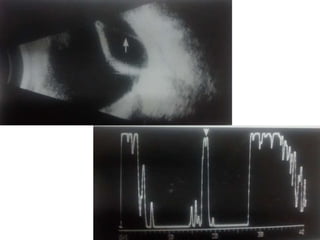
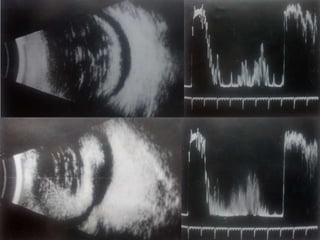
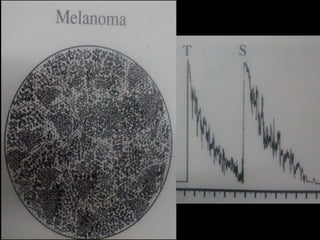
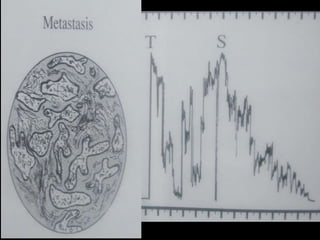
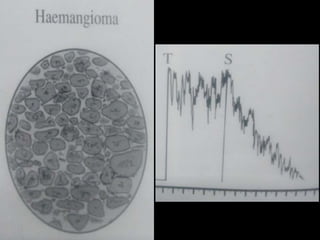
Ultrasonography is a non-invasive imaging technique used to examine the eye. The B-scan was developed in the 1950s and 1960s and allows cross-sectional imaging of the eye. It works by emitting high frequency soundwaves into the eye and receiving echoes to create images. The B-scan examines features such as lesions through their shape, location, texture and mobility. Proper technique is required for high quality images, including centering lesions and using an appropriate probe frequency and gain. B-scans are useful for diagnosing various pathologies by comparing features to normal anatomical structures.