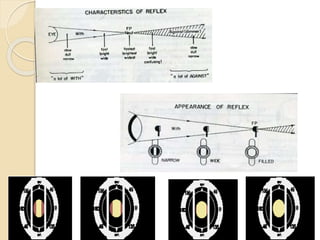
Retinoscopy is the primary objective method for determining a patient's refractive error. It involves using a retinoscope to illuminate the retina and observe the movement of the reflected light. For myopic patients, the light moves in the opposite direction of the retinoscope's movement, while for hyperopic patients it moves in the same direction. The goal is to find the neutralization point where no movement is seen, indicating the proper refractive correction. Factors like the working distance, type of mirror used, and patient's fixation can impact results. Retinoscopy is useful for initial refractive estimates and screening for ocular conditions.


![Methods for objective
refraction
Keratometry
Ophthalmoscopy
Optometers
Auto refraction
Photorefraction
&
Retinoscopy [Most important & common
method ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/retinoscopyadnin-141102091708-conversion-gate02/85/Retinoscopy-adi-3-320.jpg)



































![Clinical use…
Objective determination of refractive error
Starting point of subjective refraction
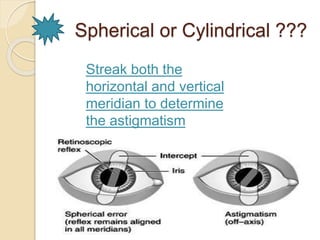
To find out regular & irregular astigmatism
Helpful for non-communicative or non-verbal
pt’s
Screening for ocular disorders [keratoconus,
media opacities]
Some special assessments can be
determined [Accommodation
stability,Accommodative lag]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/retinoscopyadnin-141102091708-conversion-gate02/85/Retinoscopy-adi-42-320.jpg)


