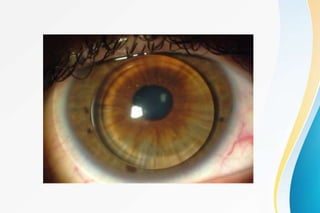
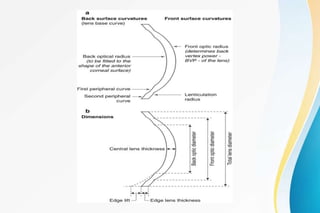
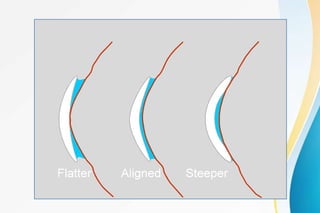
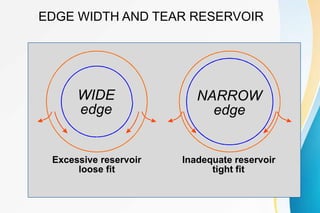
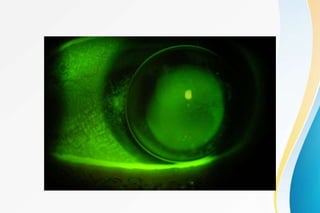
Rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses are rigid plastic lenses that transmit oxygen. They have inherent rigidity like PMMA but are semi-soft due to oxygen permeability. RGP lenses provide clearer vision than soft lenses, are more durable, and less expensive. However, they require an adaptation period and have a higher risk of dislodging than soft lenses. Key design features of RGP lenses include the back surface design, thickness, edge configuration, and diameter, which affect lens fit, movement, comfort, and vision. RGP lenses are used to correct astigmatism and presbyopia and for conditions like keratoconus.