This document provides an overview of retinoscopy, including:
- Retinoscopy is an objective technique to determine refractive errors by observing the movement of light reflected from the retina.
- The practitioner modifies the movement of the reflected light with trial lenses to find the point of reversal and determine the refractive error.
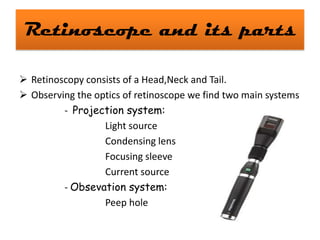
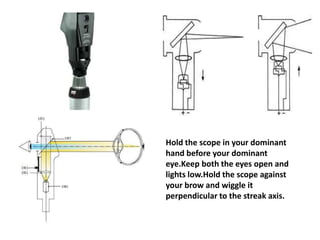
- It describes the parts of the retinoscope and how it works, as well as techniques for static and dynamic retinoscopy to evaluate spherical and cylindrical refractive errors.
- The document outlines the procedure for retinoscopy, including controlling accommodation, adding trial lenses to find the point of neutralization or reversal, and determining the final refractive prescription.