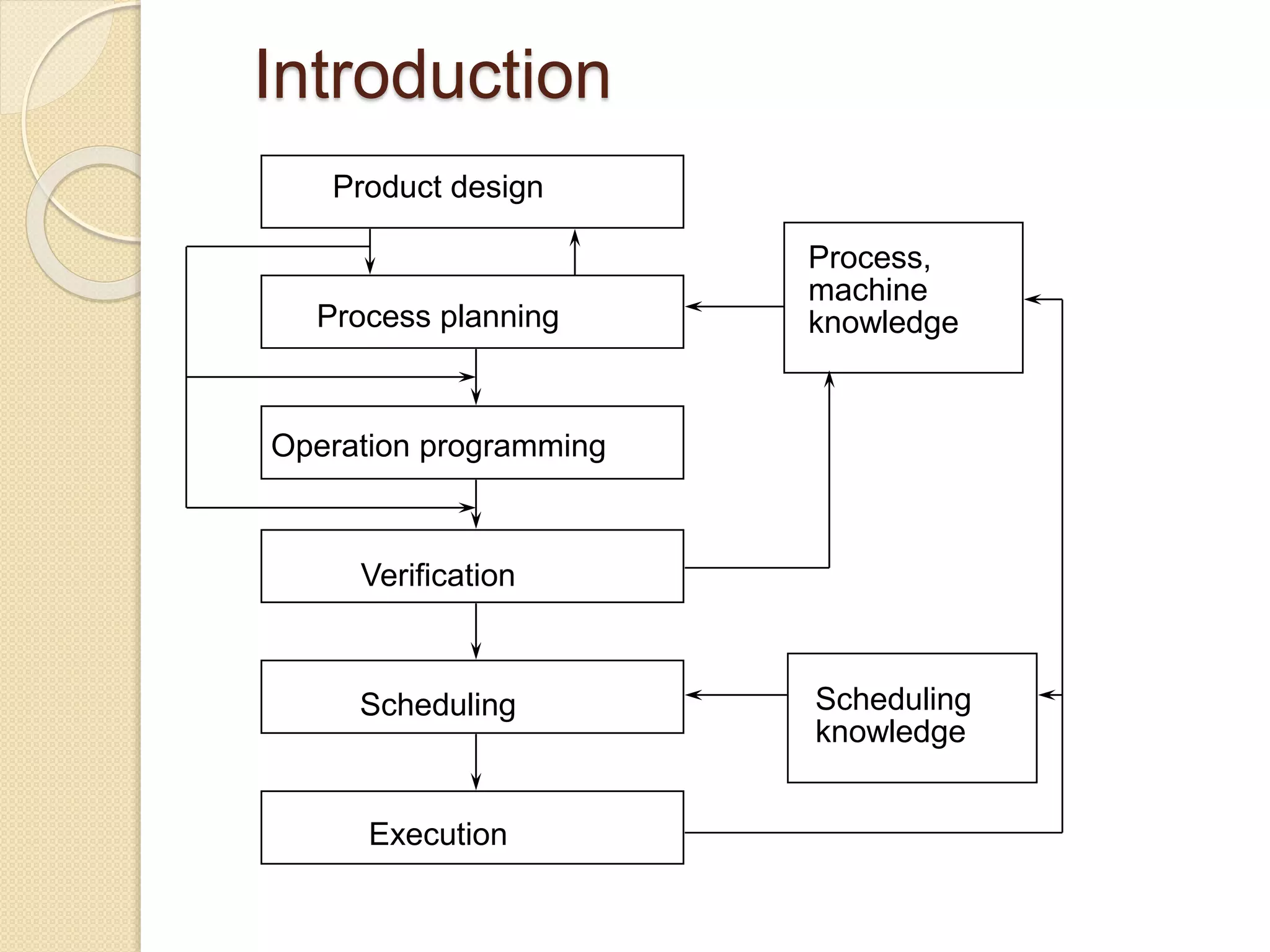
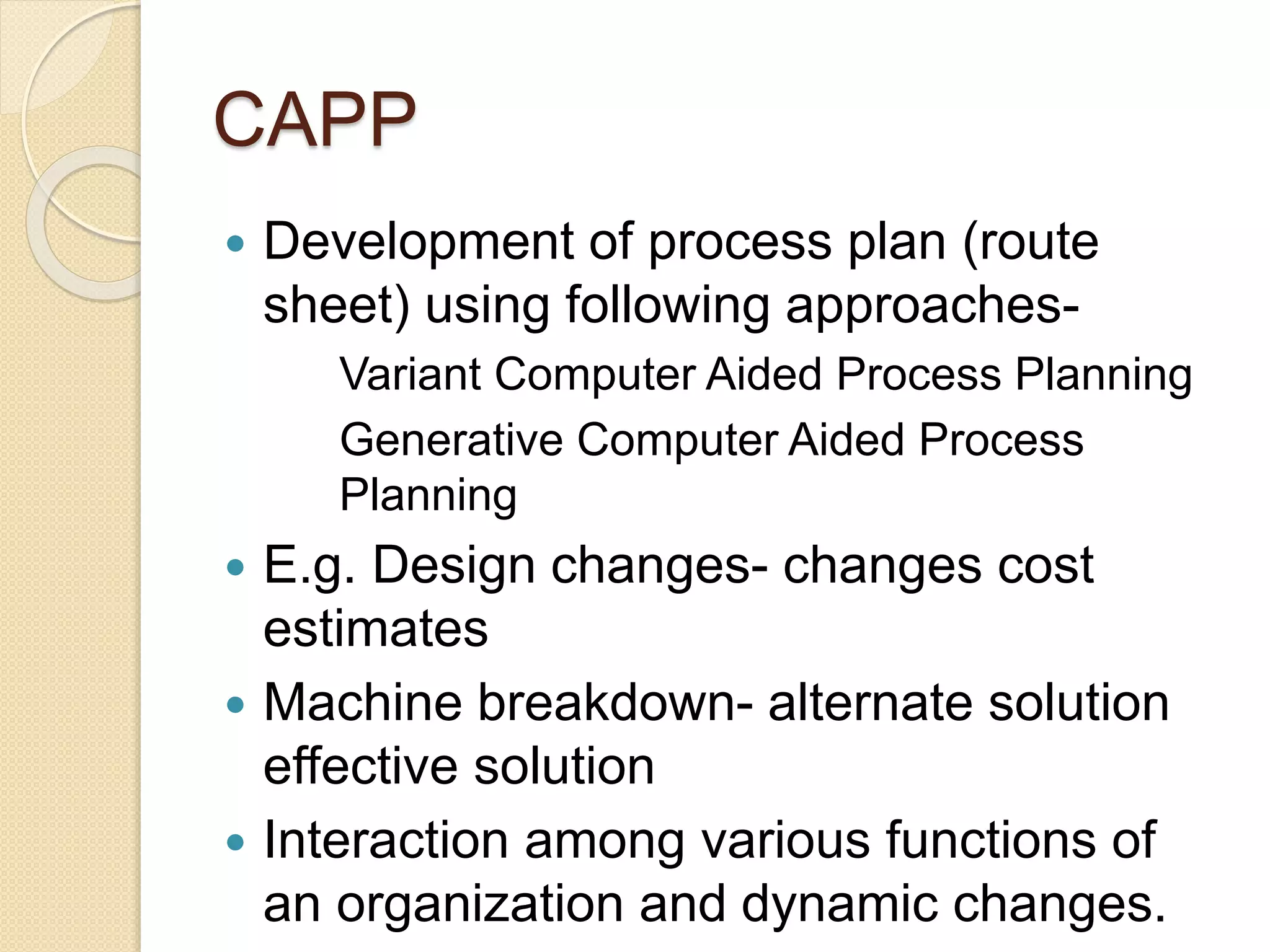
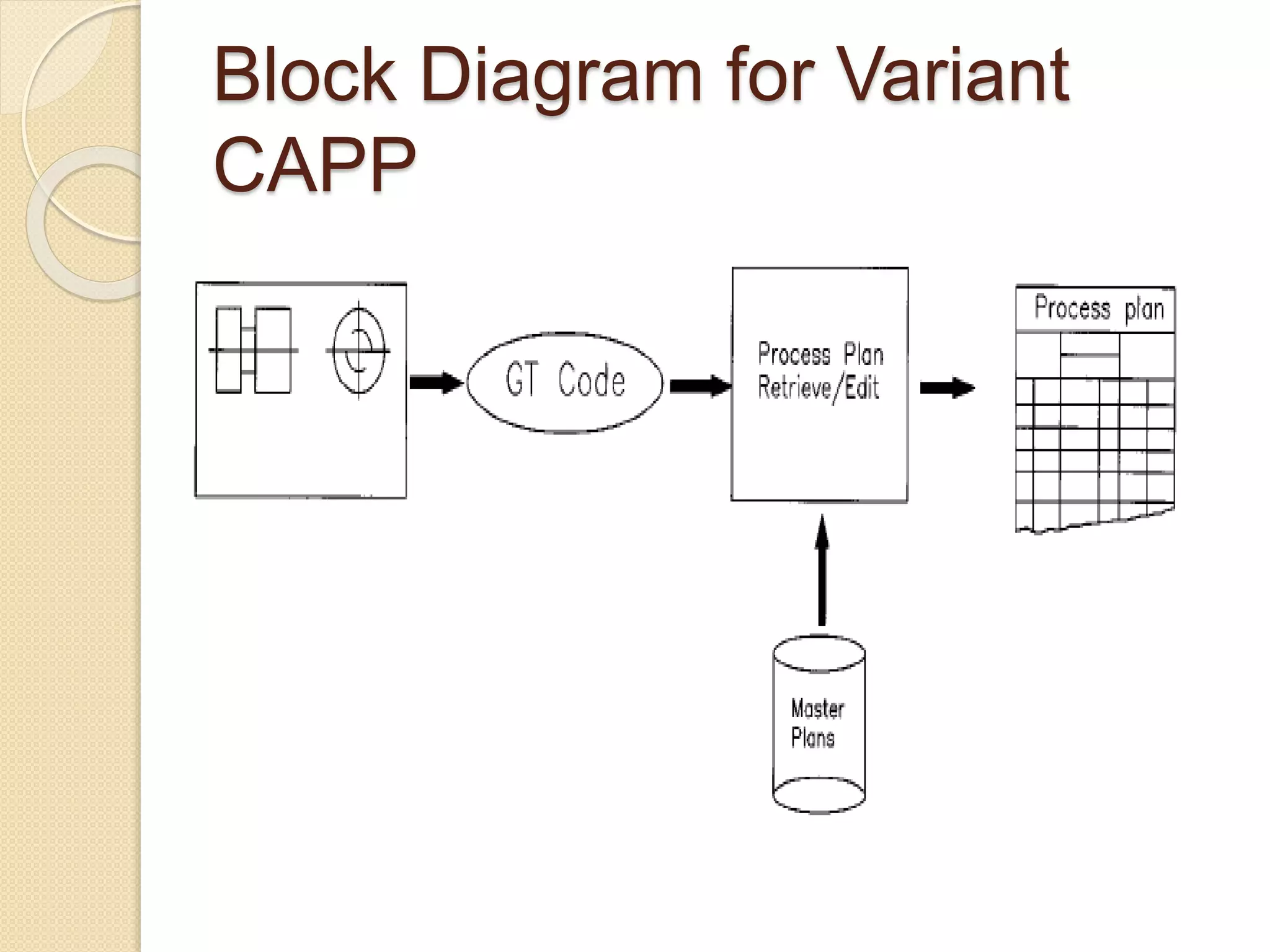
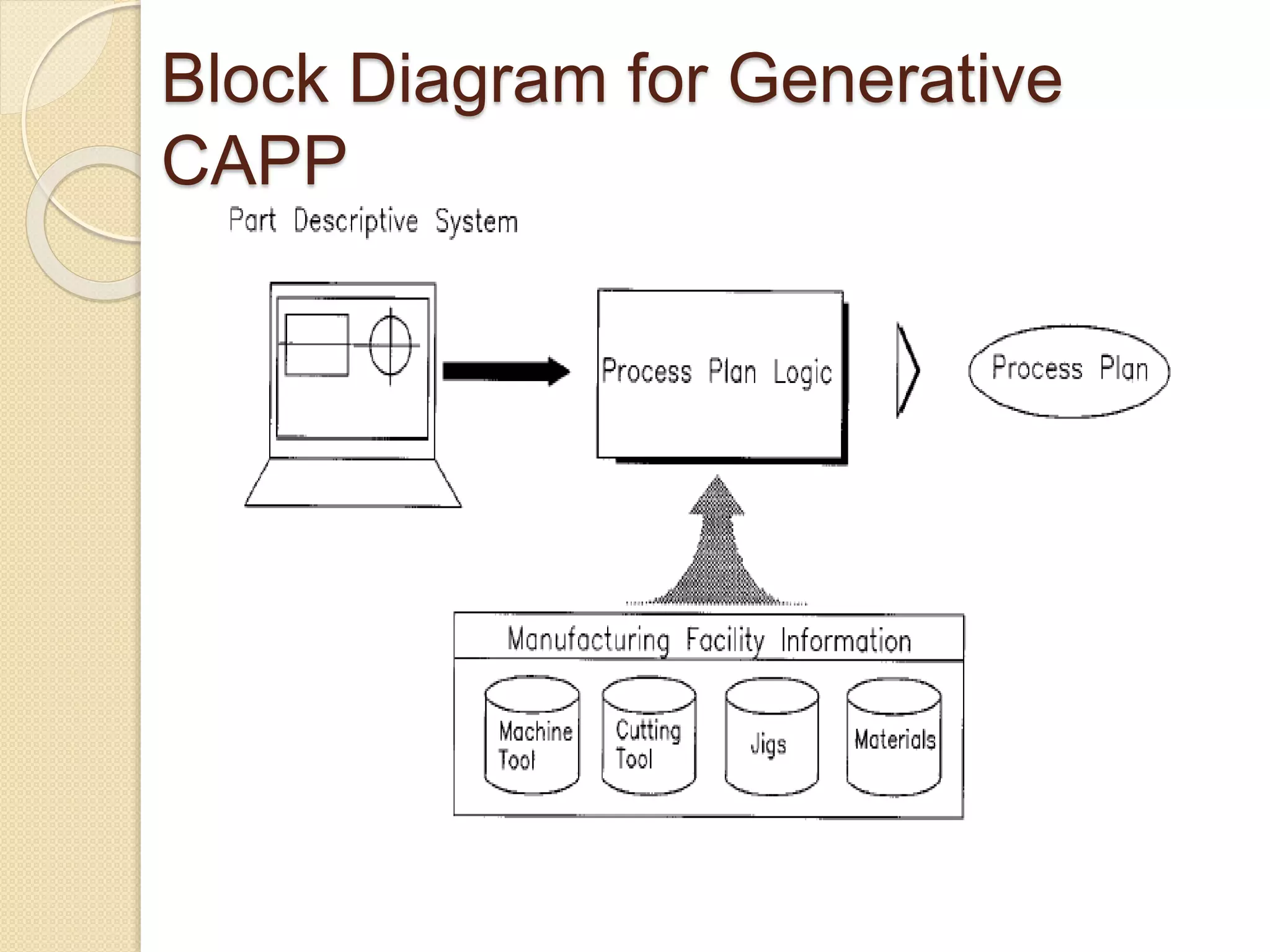
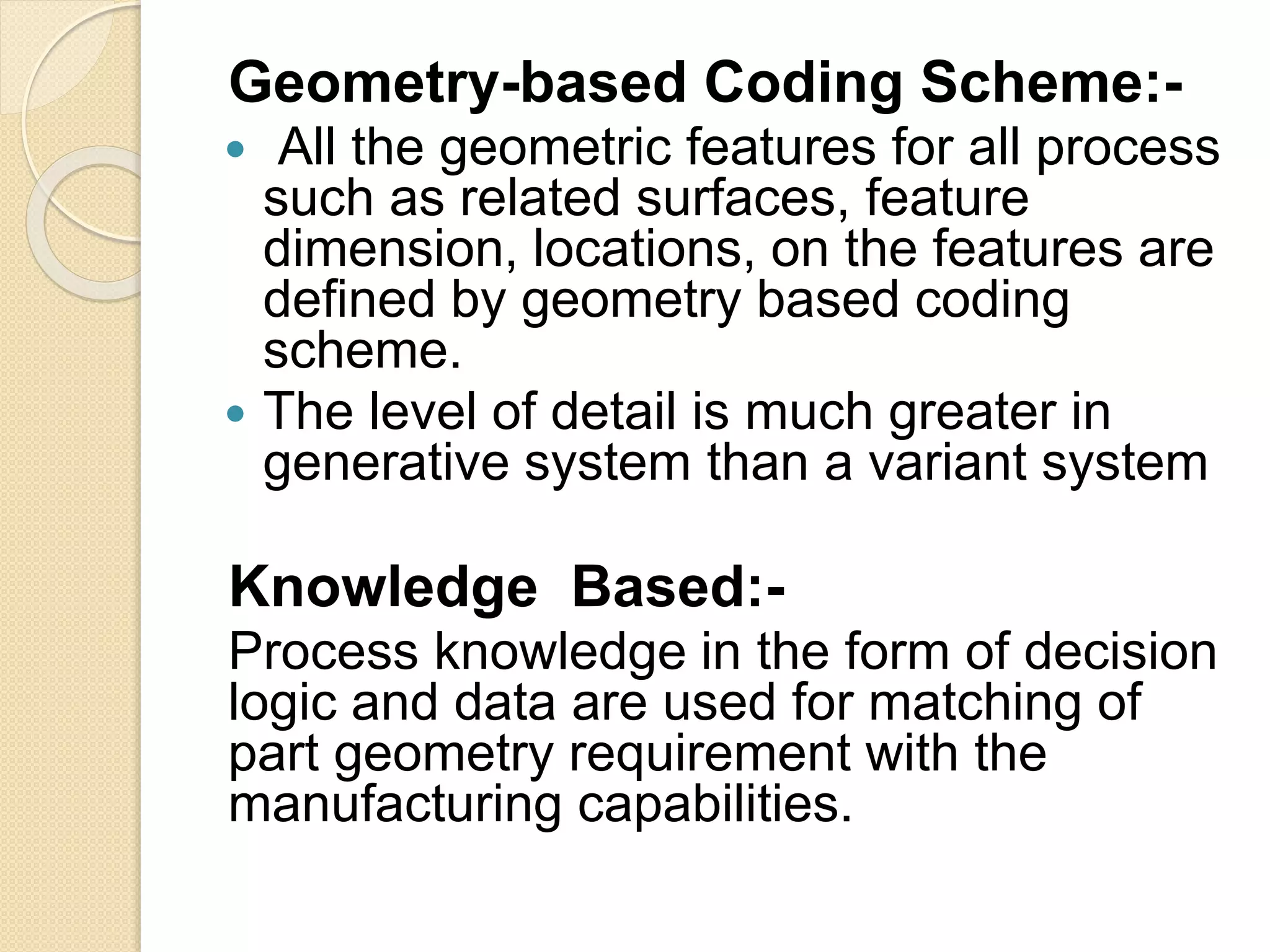
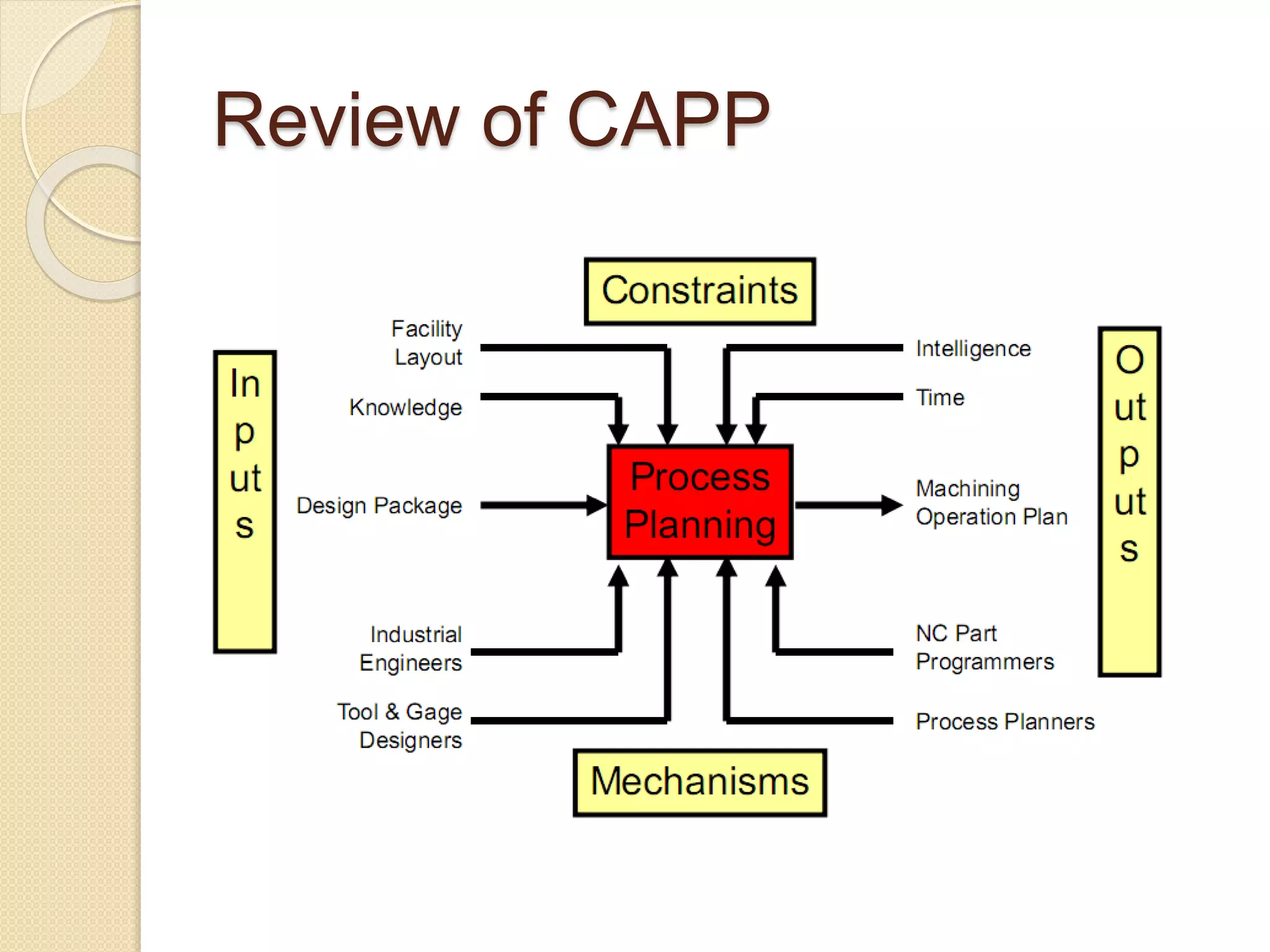
This document provides an overview of Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP). It discusses the general steps in CAPP, including design input, material selection, and cost estimation. It describes two main approaches to CAPP: variant CAPP, which retrieves and modifies existing process plans; and generative CAPP, which generates new plans using decision logic and algorithms. The advantages of CAPP are reducing time/costs and increasing consistency and productivity. The disadvantages include difficulty maintaining consistency and accounting for all manufacturing factors in variant CAPP, and high initial costs compared to manual planning.