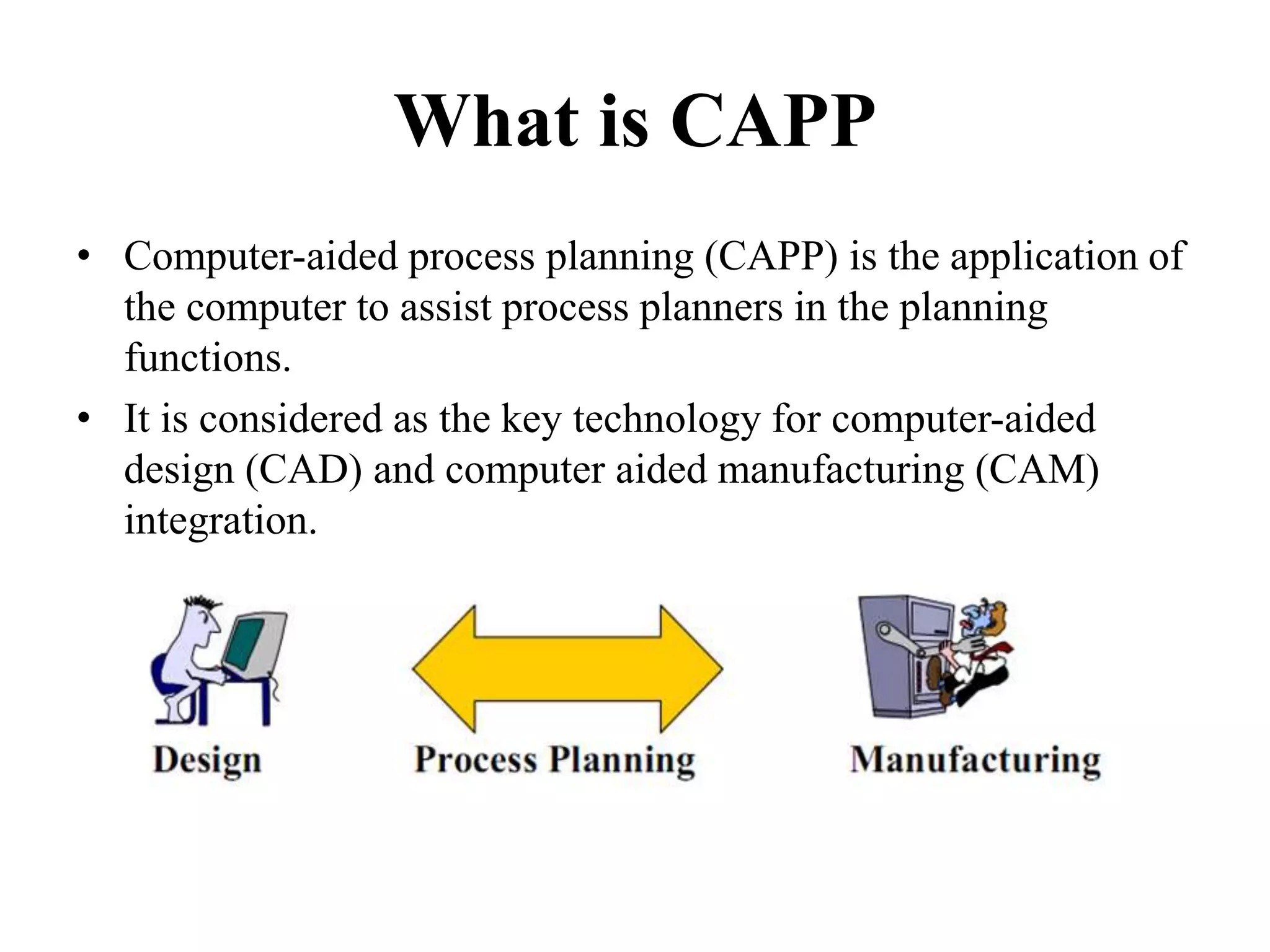
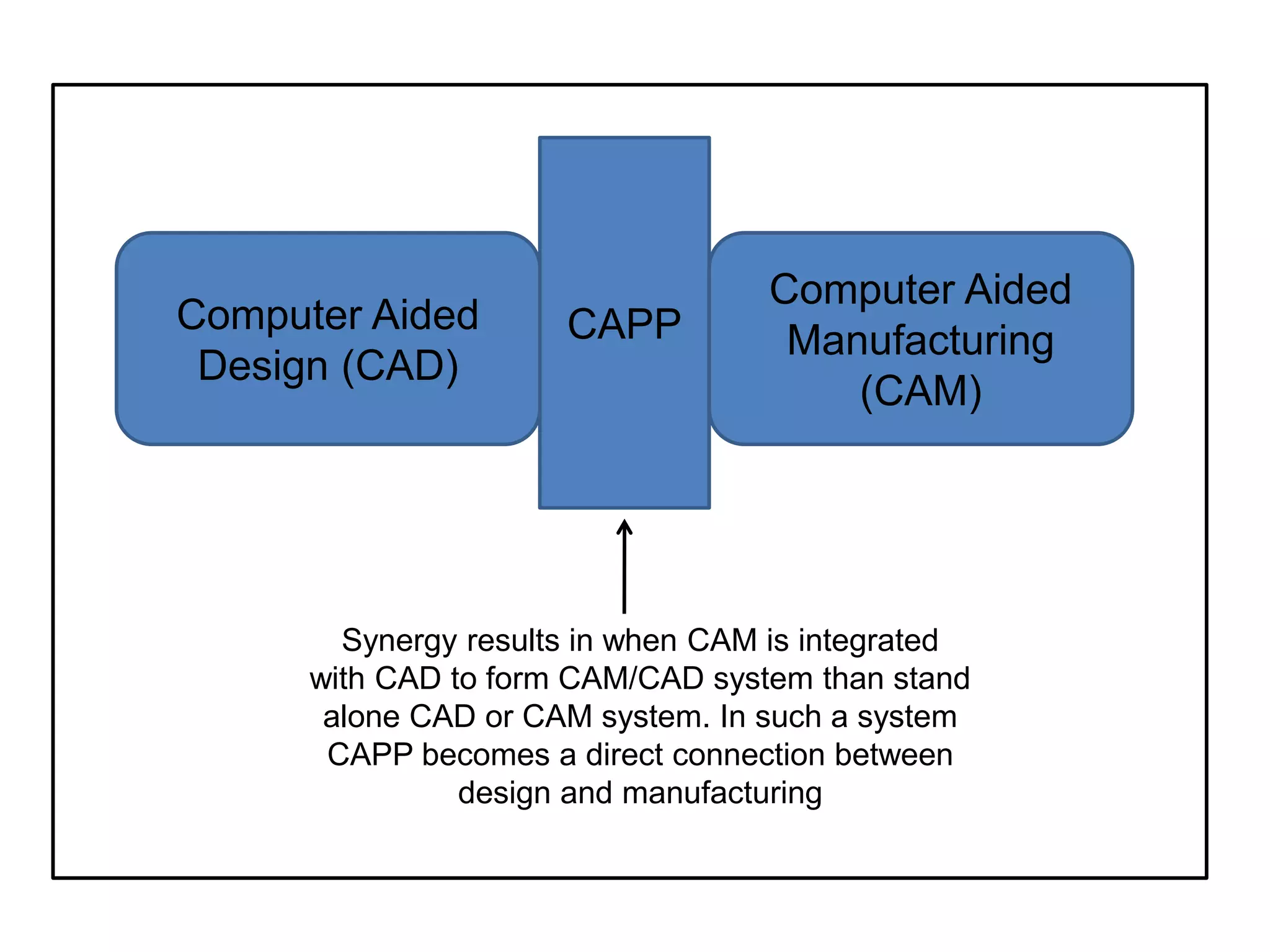
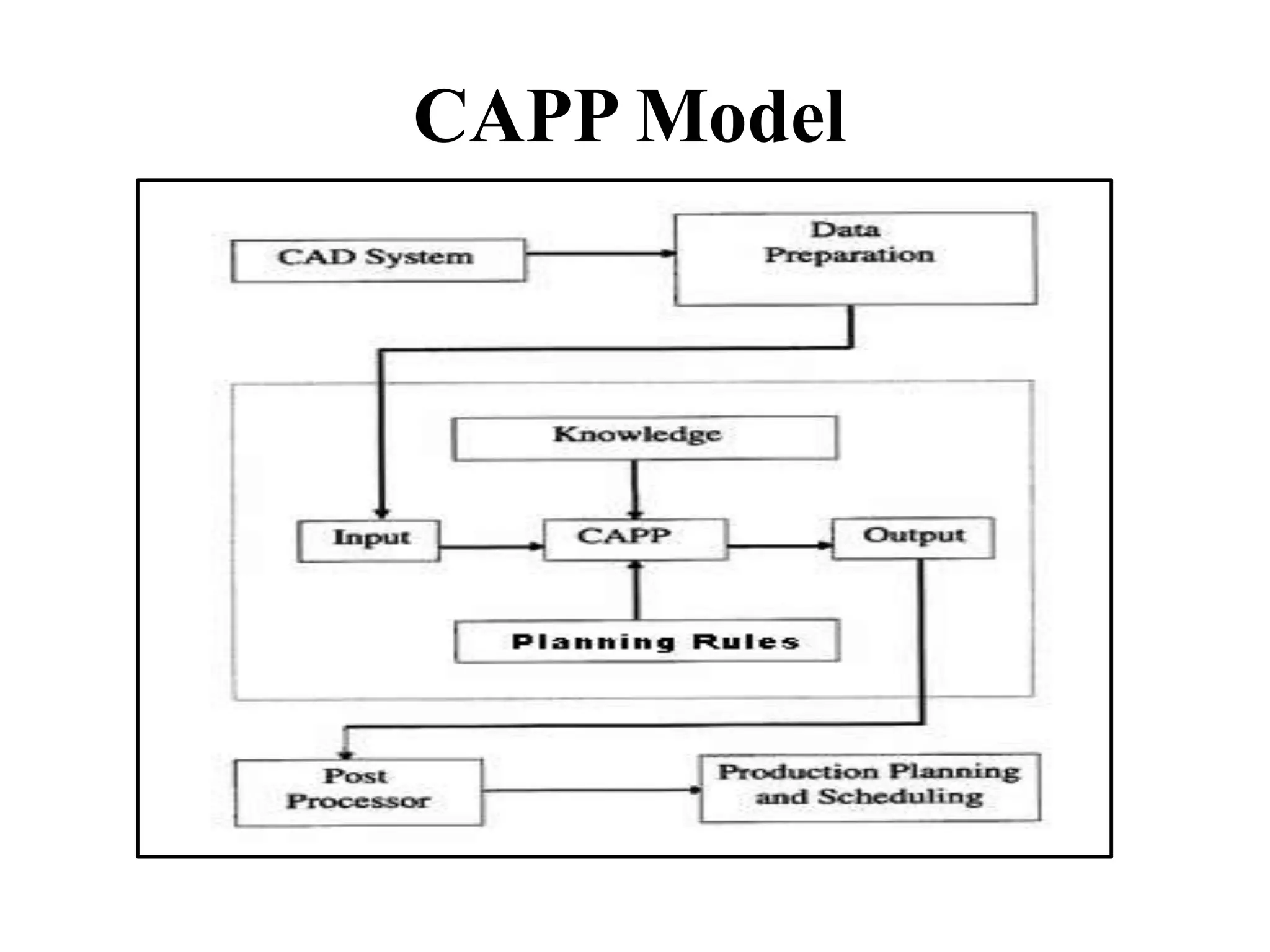
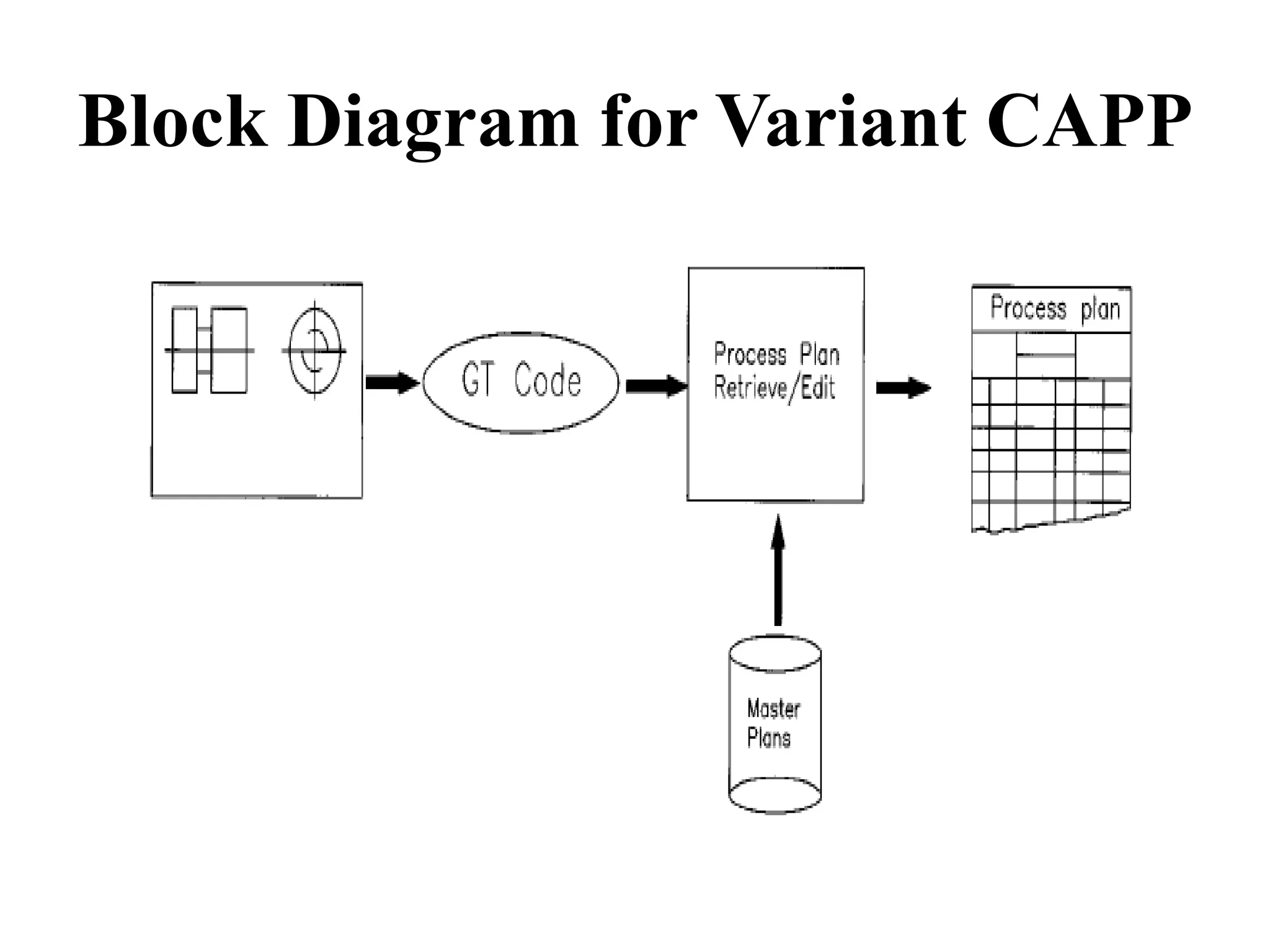
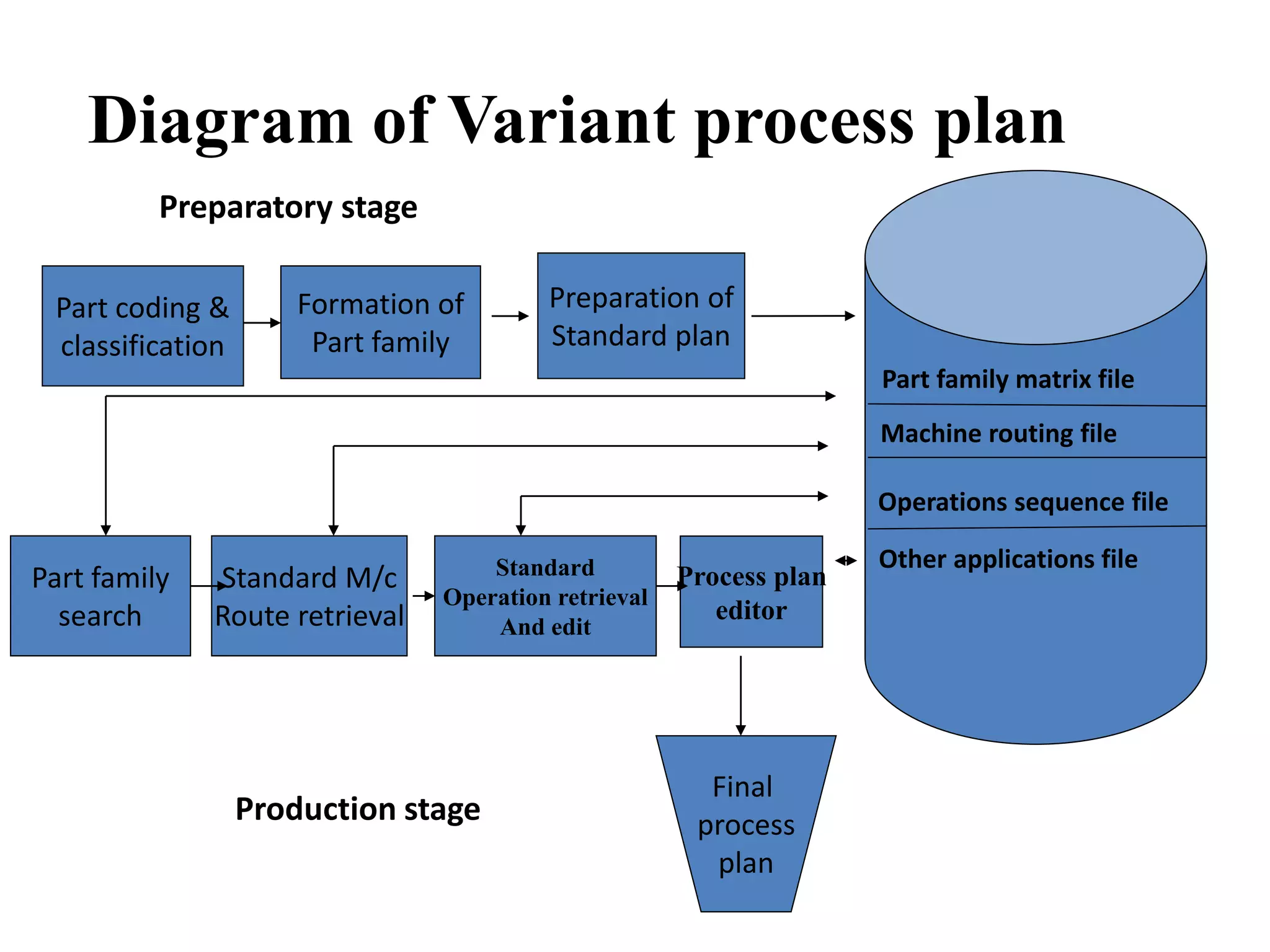
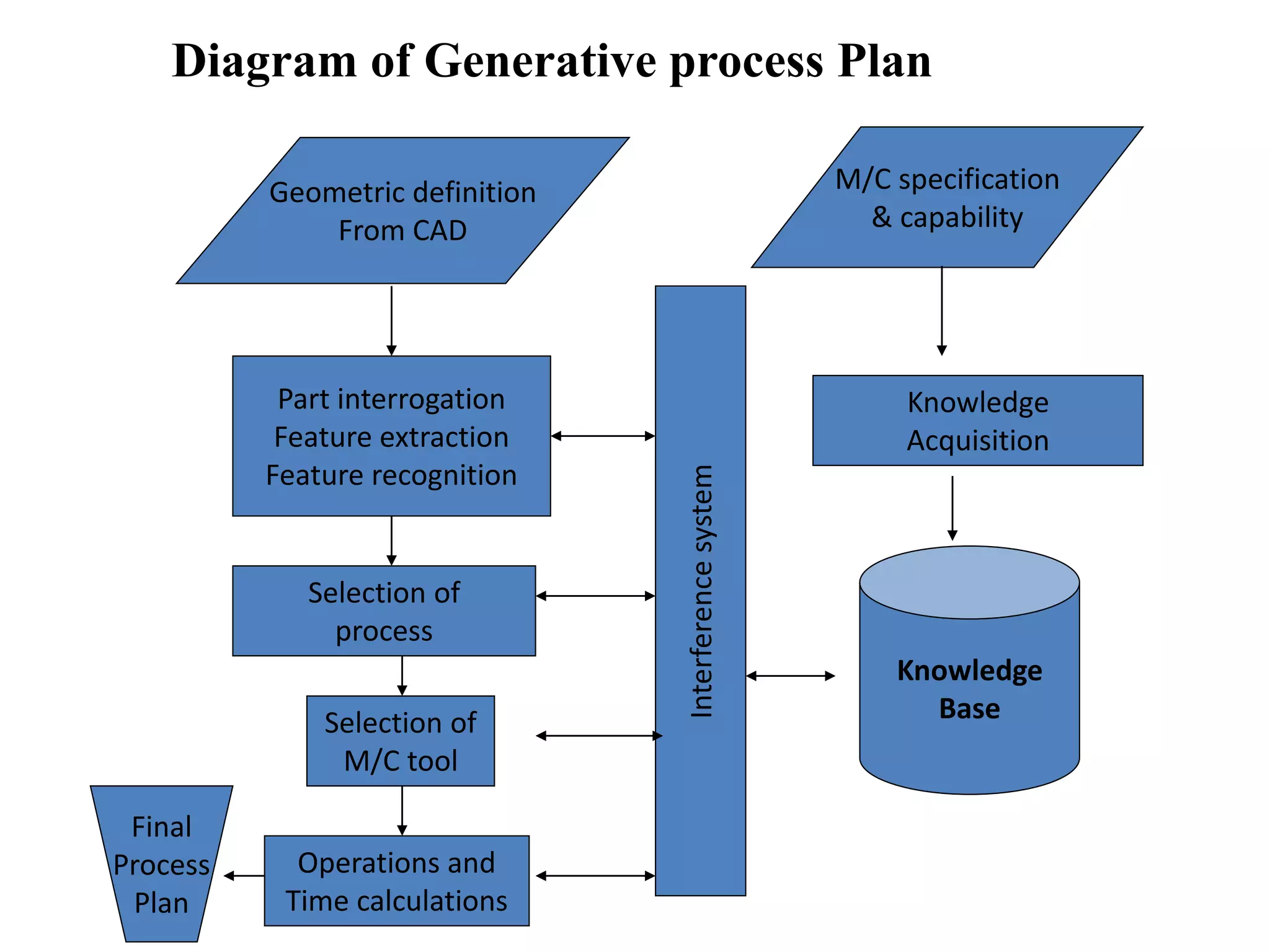
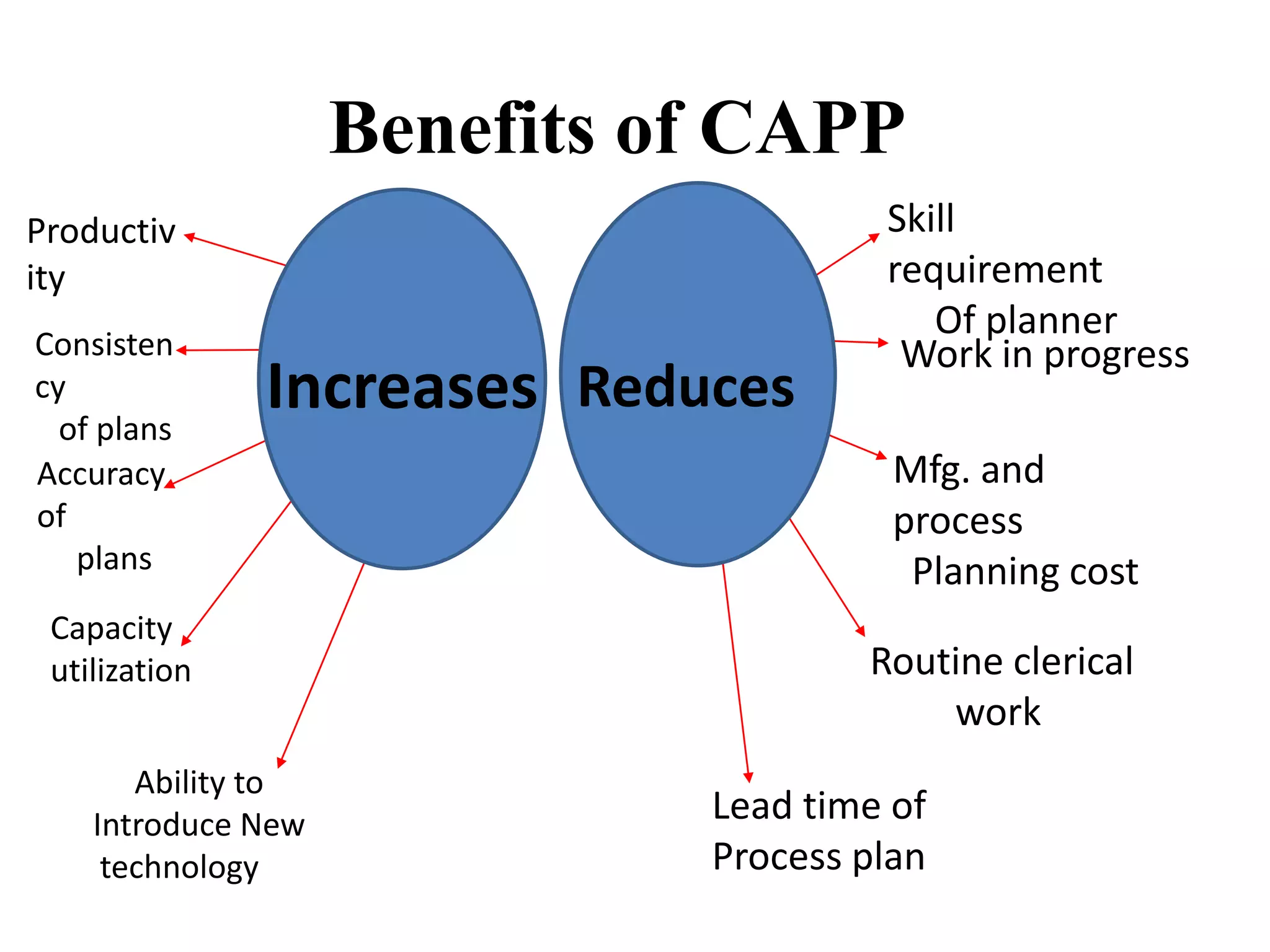
Computer-aided process planning (CAPP) is the application of computers to assist process planners in planning functions. CAPP integrates computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) by providing a direct connection between design and manufacturing. There are two main approaches to CAPP: variant process planning and generative process planning. Variant process planning retrieves and modifies standard process plans from a database, while generative process planning creates customized process plans using decision logic and part geometry data without predefined plans. CAPP provides benefits like increased productivity, consistency of plans, accuracy of plans, and reduced costs.