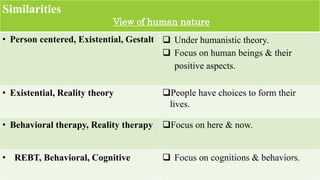
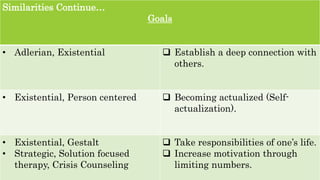
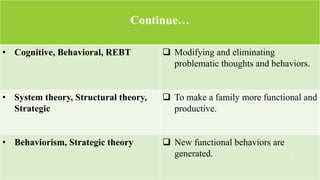
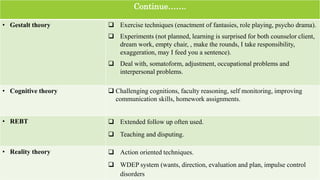
This document compares and contrasts various psychotherapies. It discusses similarities and differences in their views of human nature, goals, roles of counselors, and techniques. Key similarities include a focus on human beings' positive aspects, cognitions and behaviors, psychological needs, and building rapport. Differences include views on the role of biology, unconsciousness, free will and the environment in human development. Goals and roles of counselors also vary between insight-focused versus action-oriented approaches. Techniques range from interpretation to homework assignments depending on the theory.