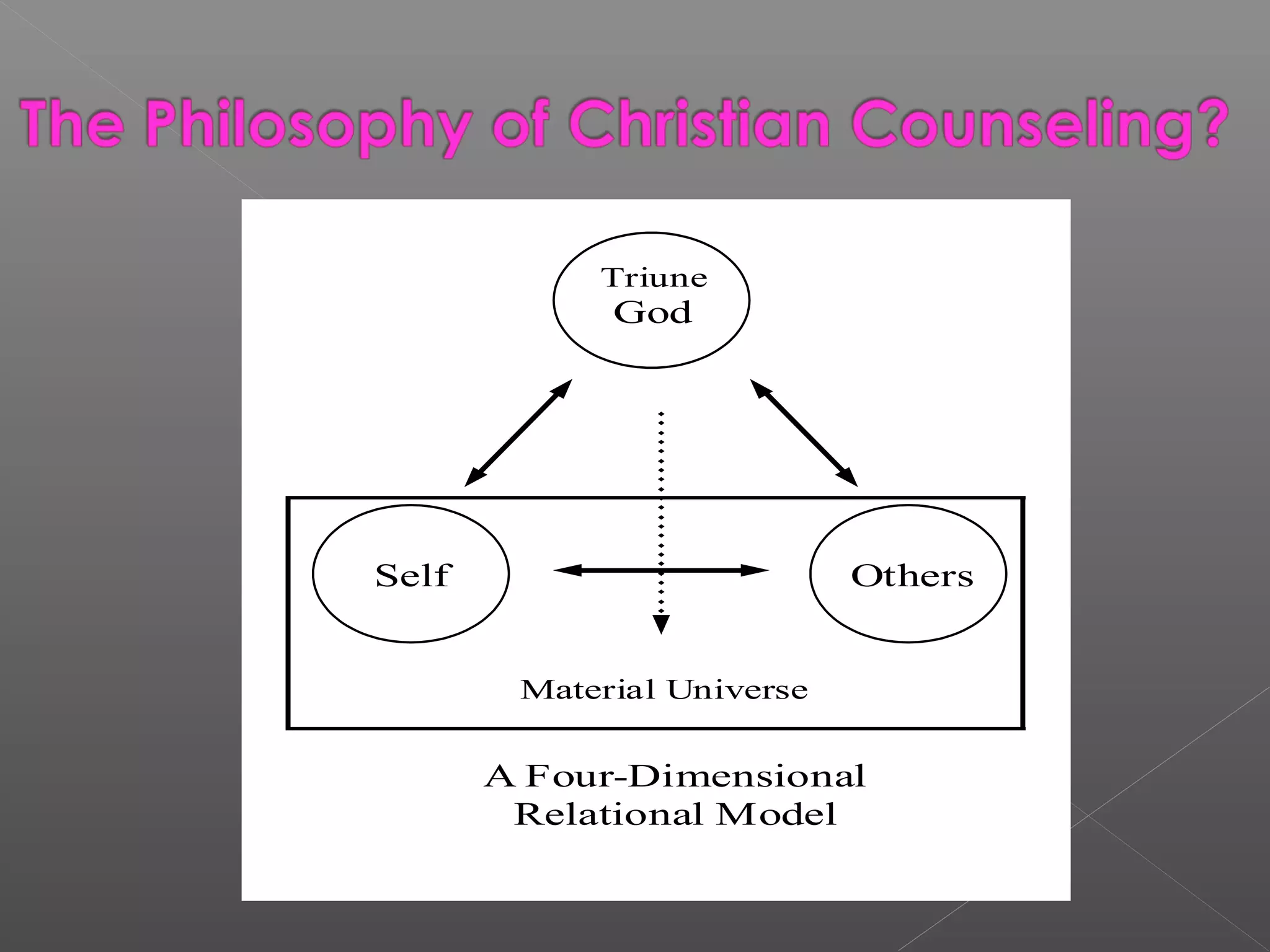
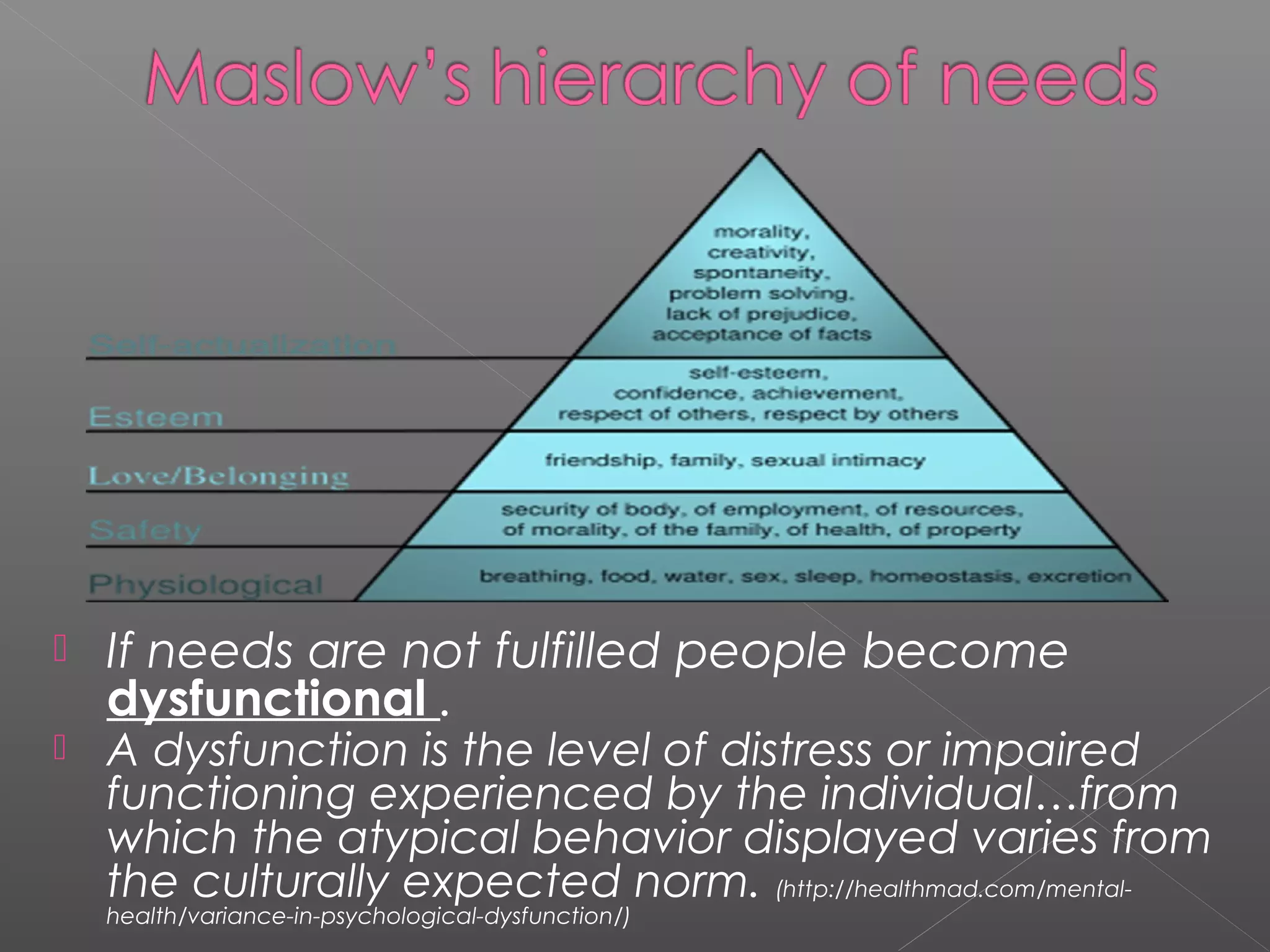
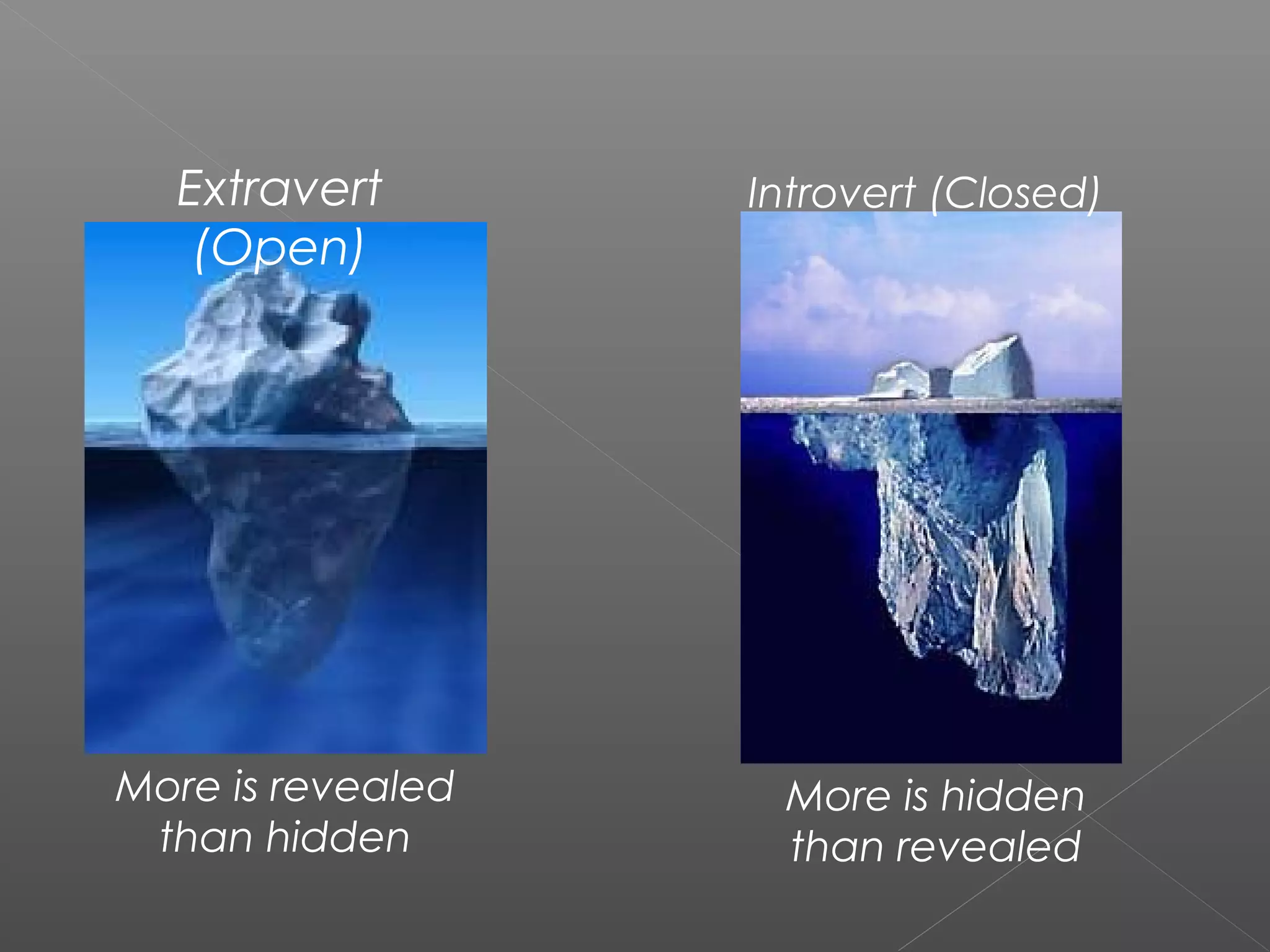
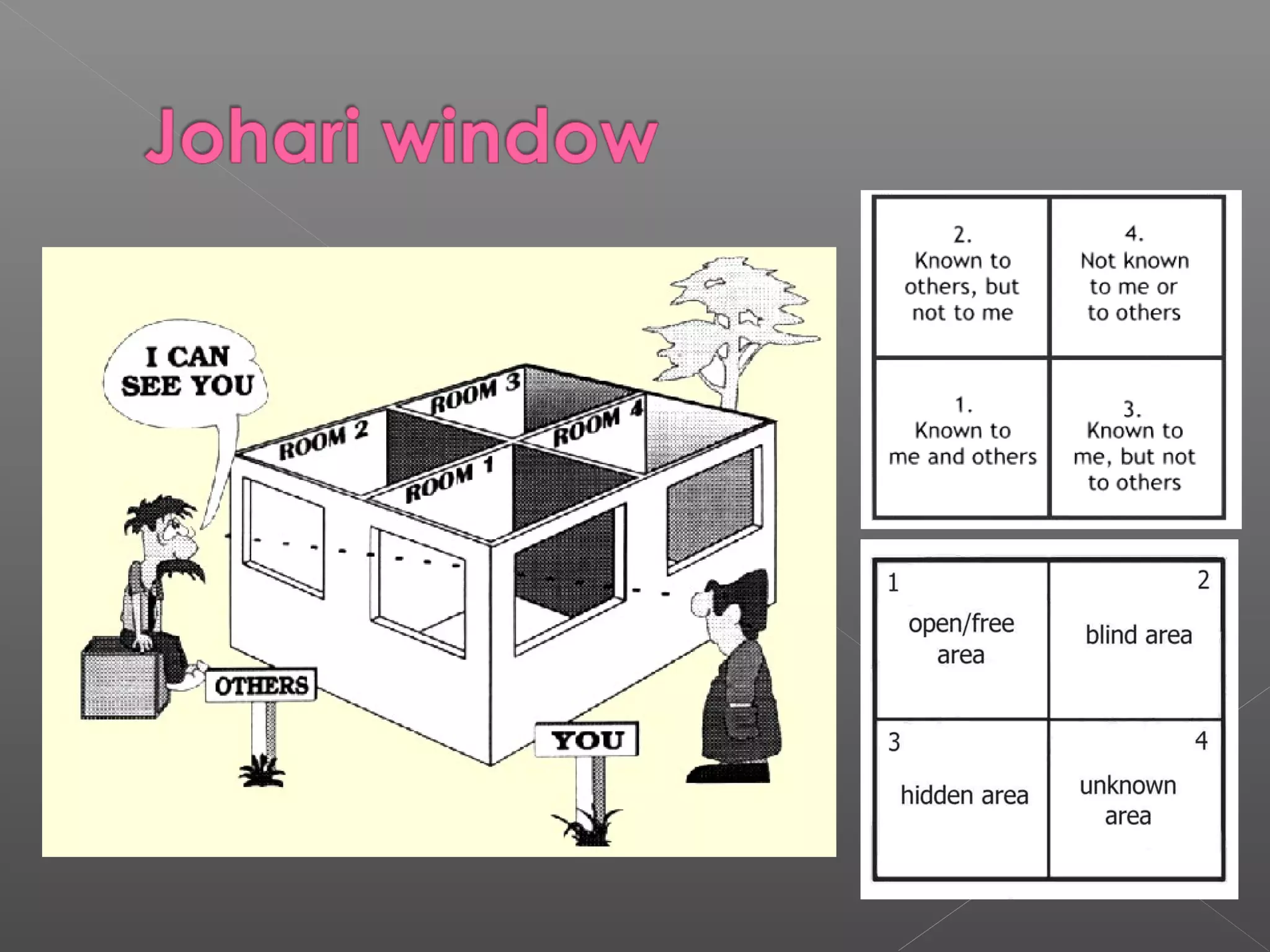
Counseling is both a science and an art that aims to help clients understand themselves and their situations in order to solve problems and facilitate personal growth and change. It involves a professional relationship between a trained counselor and client to clarify the client's perspective and resolve emotional or interpersonal issues. Christian counseling specifically applies biblical principles using professional counseling techniques to treat clients' issues and stimulate their spiritual growth. The goals of counseling include facilitating behavior change, improving relationships and coping skills, and promoting overall development, including spiritual transformation through salvation.