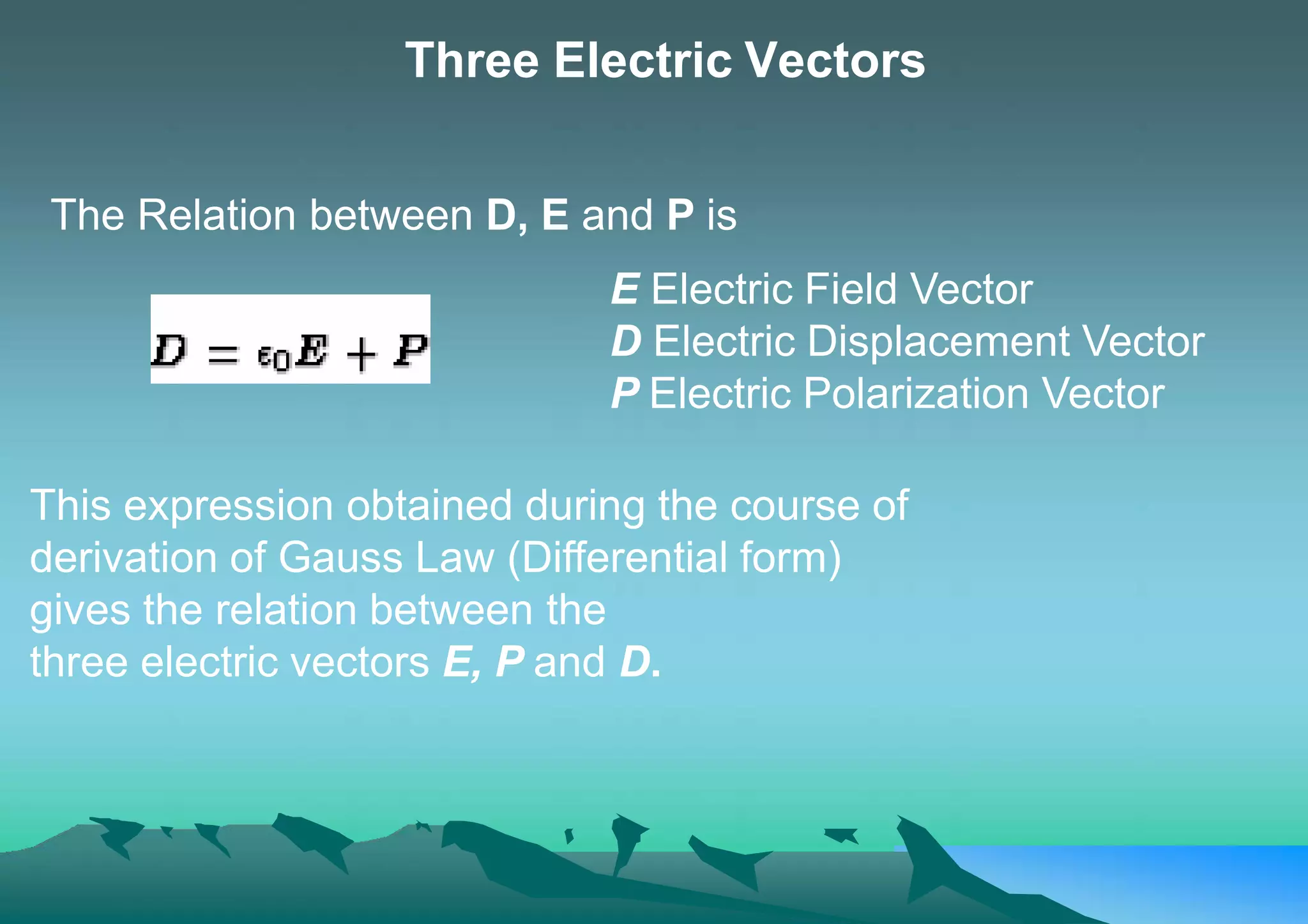
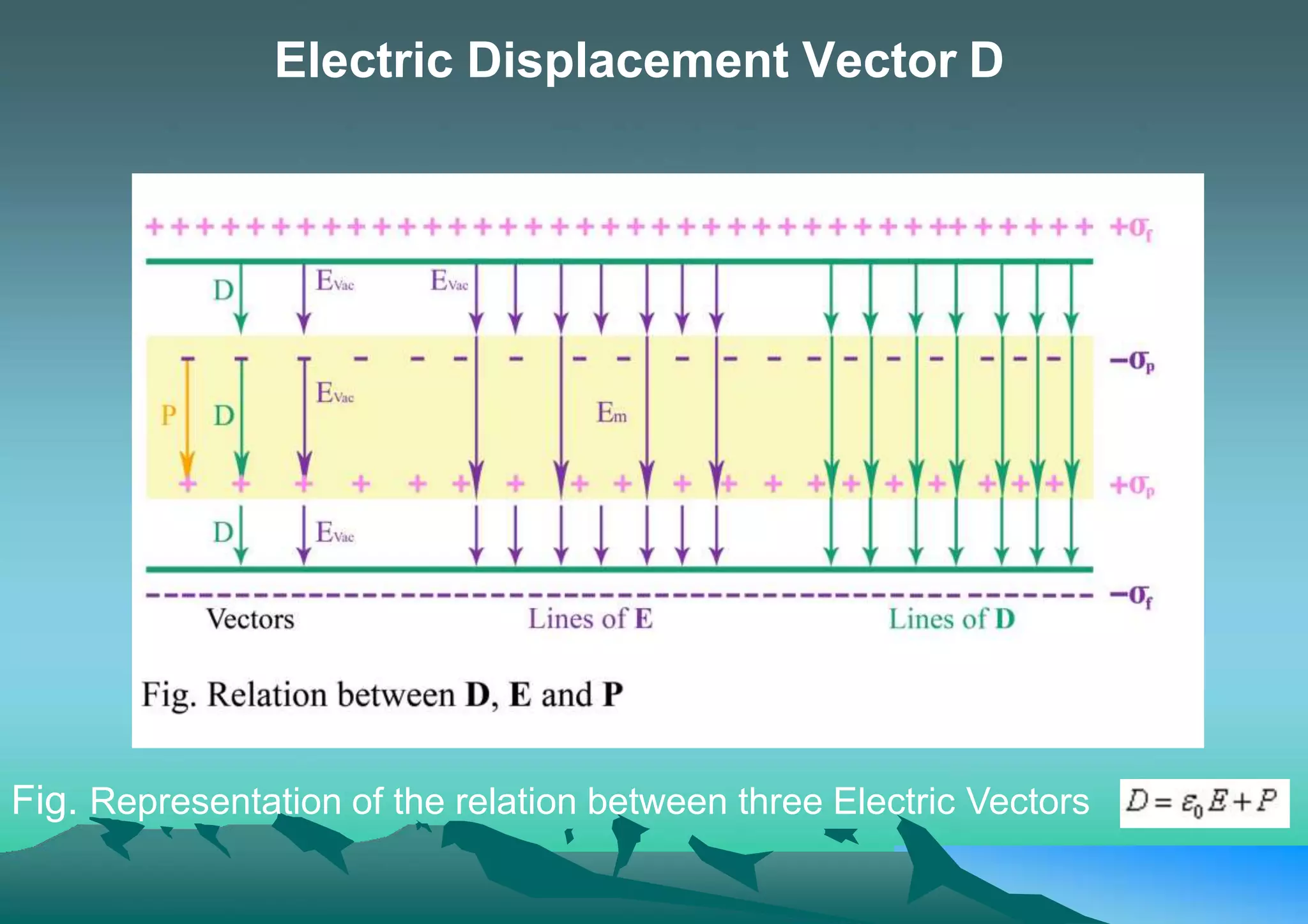
This document discusses the relationship between three electric vectors: the electric field vector E, the electric displacement vector D, and the electric polarization vector P. It states that D is equal to E plus 4πP, meaning D accounts for both the applied electric field E and the effect of electric polarization P inside a dielectric material. The electric displacement vector D is useful for calculations involving dielectric materials, as it enables the use of Gauss's law. P represents the polarization charge in a material and is the difference between the induced electric field D and the imposed field E.