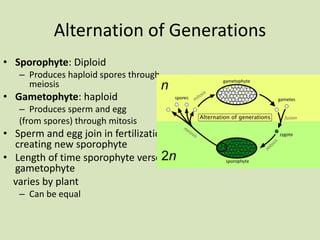
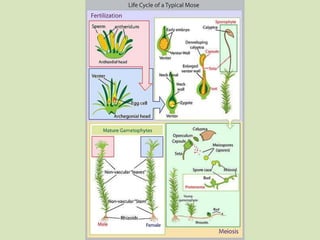
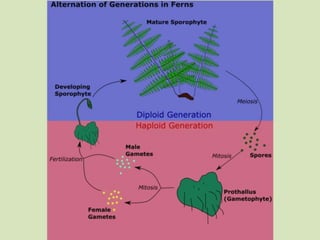
This document summarizes key characteristics of seedless plants, including their alternation of generations life cycle and reproduction processes. It discusses nonvascular plants like mosses which have separate male and female gametophytes and how seedless vascular plants like ferns are adapted to land with vascular tissue and windblown spores. The fern life cycle is specifically outlined, noting terms like prothallus, sporangia, sorus, and fronds.