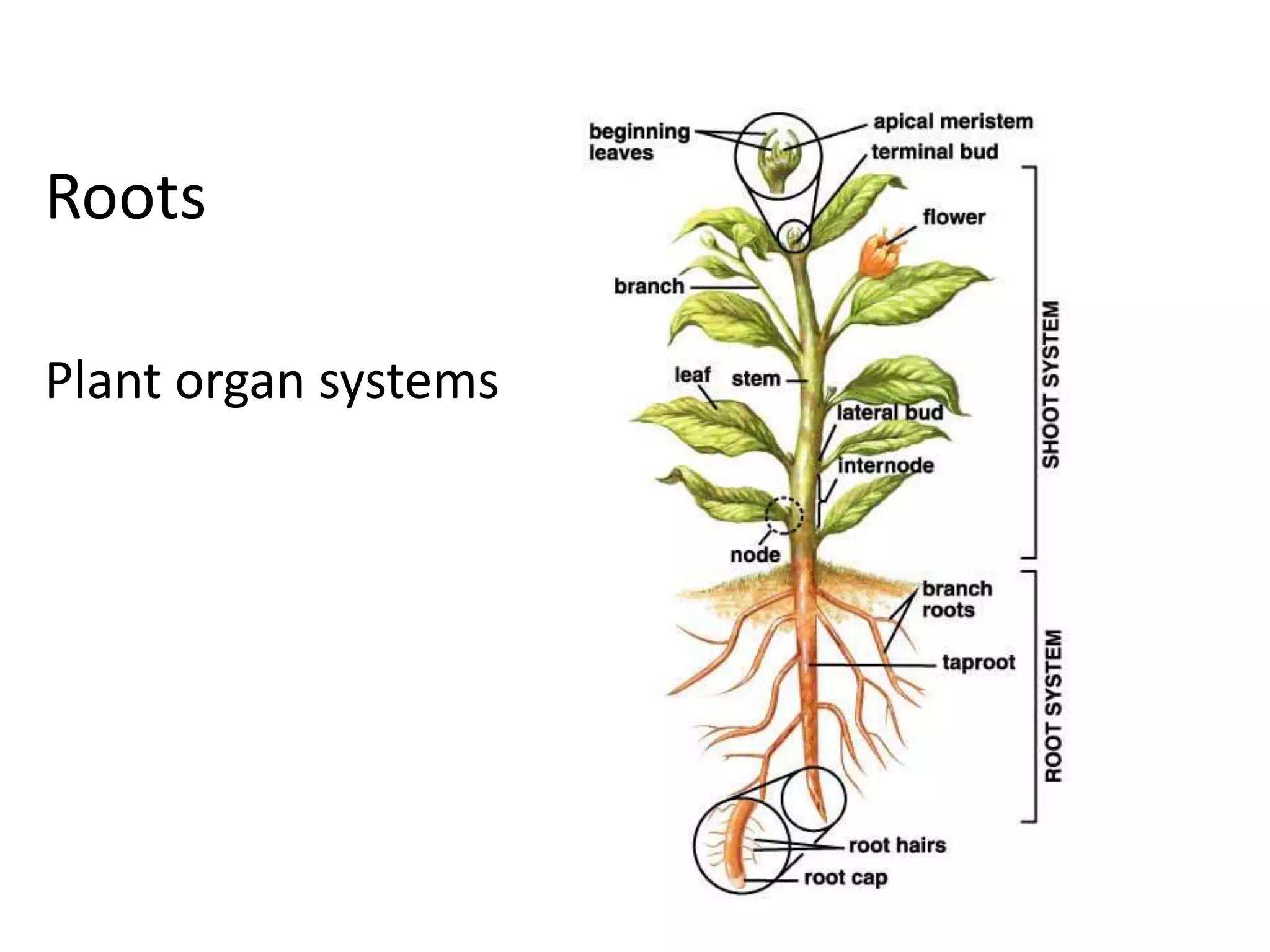
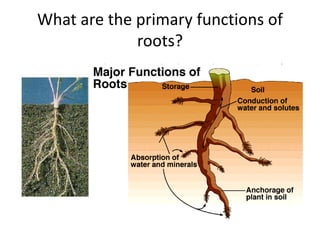
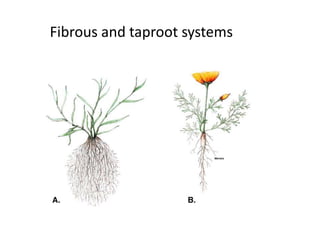
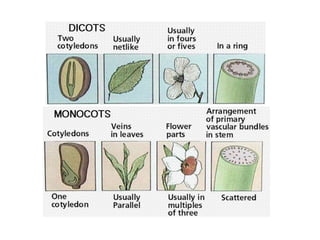
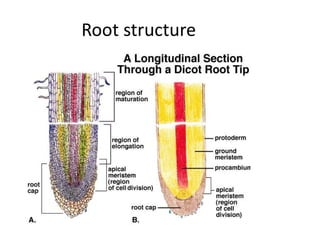
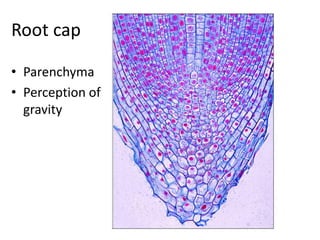
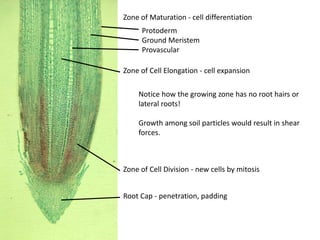
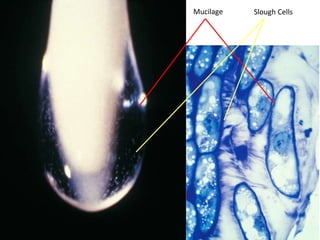
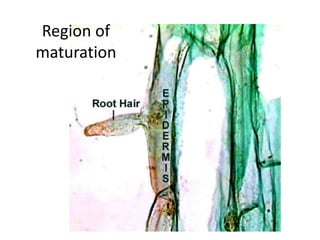
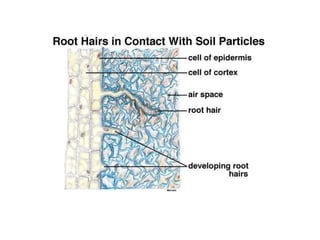
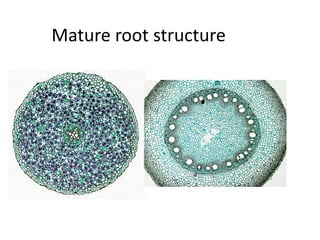
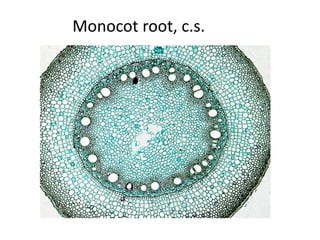
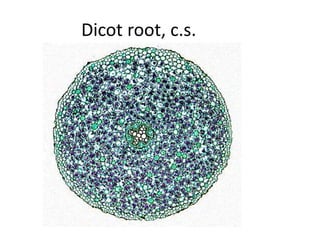
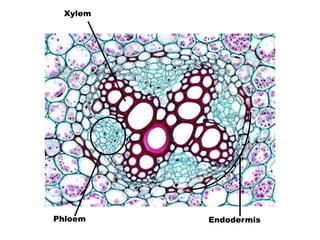
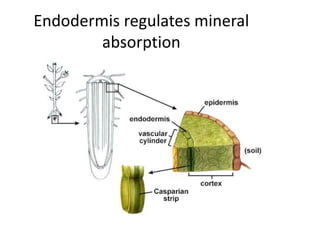
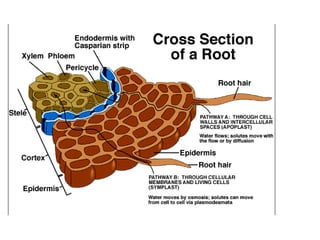
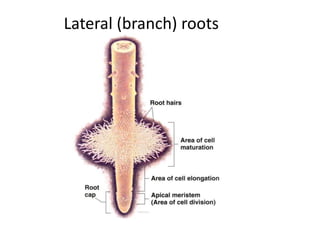
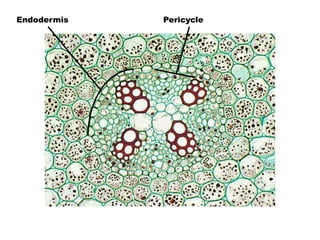
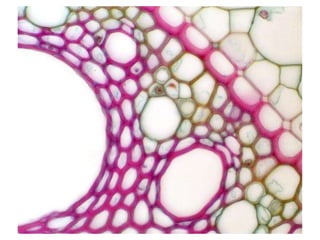
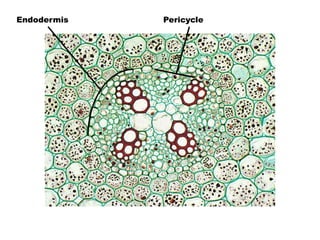
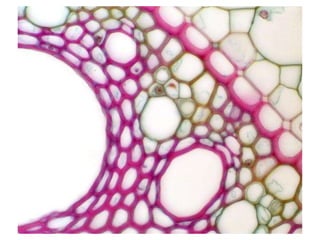
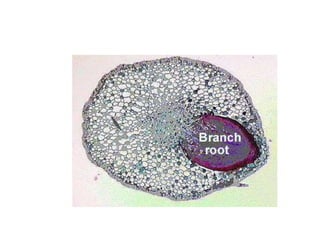
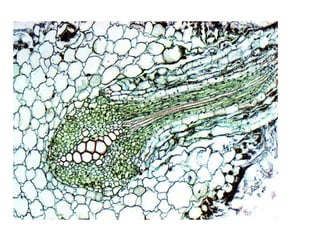
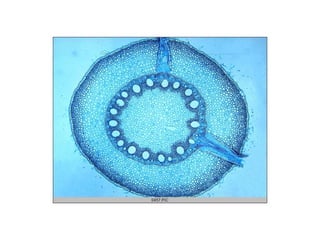
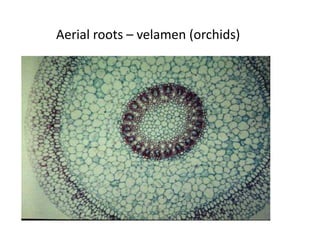
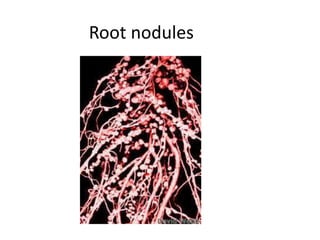
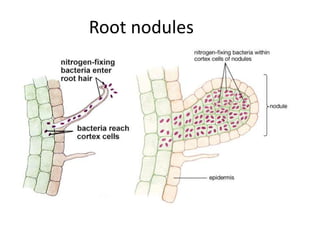
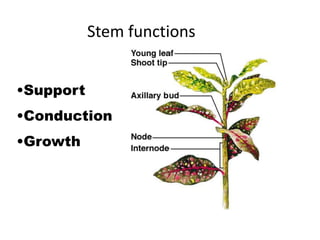
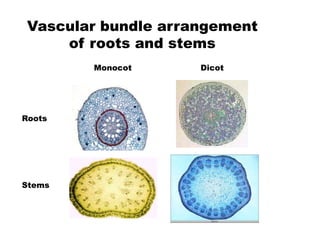
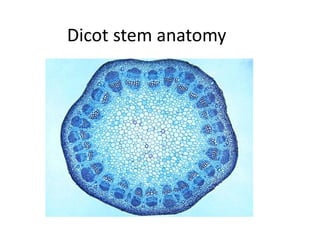
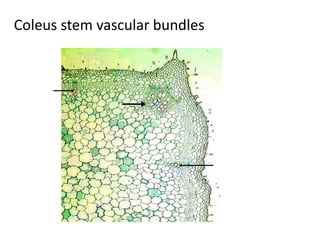
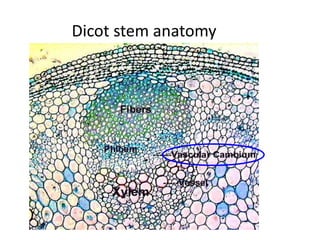
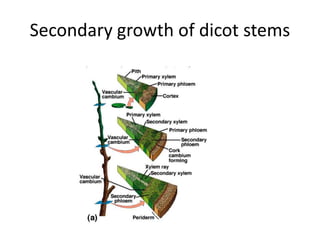
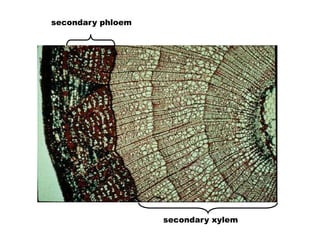
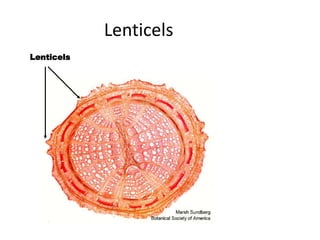
This document summarizes the structure and functions of plant roots. It describes the major zones of a root including the root cap, zone of cell division, zone of elongation and zone of maturation. It explains how roots uptake water and minerals through root hairs, and how roots sense gravity through auxin hormone distribution, allowing roots to grow downward. The document also briefly discusses root types such as storage roots, aerial roots, and root nodules. Additionally, it compares monocot and dicot root anatomy.