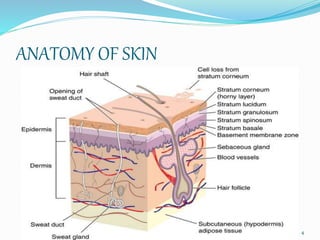
This document discusses pharmaceutical creams. It defines what a cream is and describes the anatomy of skin. It outlines different types of creams including cleansing, vanishing, foundation, night, massage, hand, body, and all-purpose creams. It discusses the components and manufacturing processes of creams and provides examples of formulations. Finally, it covers the uses of creams and some novel advances in cream technology.