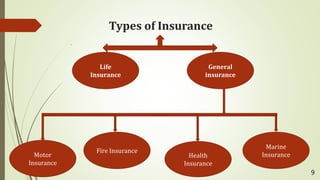
The document defines business as activities involving the purchase, production, and sale of goods and services for profit. It categorizes services into business, social, and personal services, detailing types of each and their characteristics. Key examples of business services include banking, insurance, and transportation, while social services target societal improvement and personal services focus on individual customer experiences.