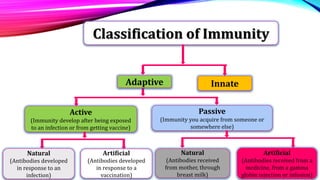
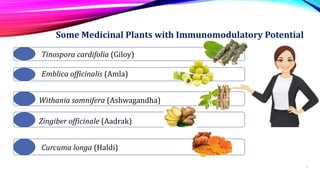
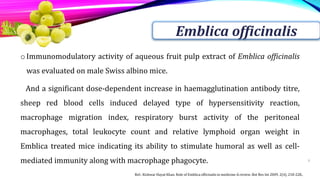
This document discusses the immunomodulatory potential of various medicinal plants, highlighting their ability to enhance immune functions without significant side effects, unlike conventional immunomodulating drugs. It presents a classification of immunity, the workings of the immune system, and the effects of specific plants such as Tinospora cordifolia, Emblica officinalis, and Withania somnifera on immune responses. The conclusion emphasizes the need for further research to optimize the use of these plants in treating illnesses that are challenging for allopathic medicine.