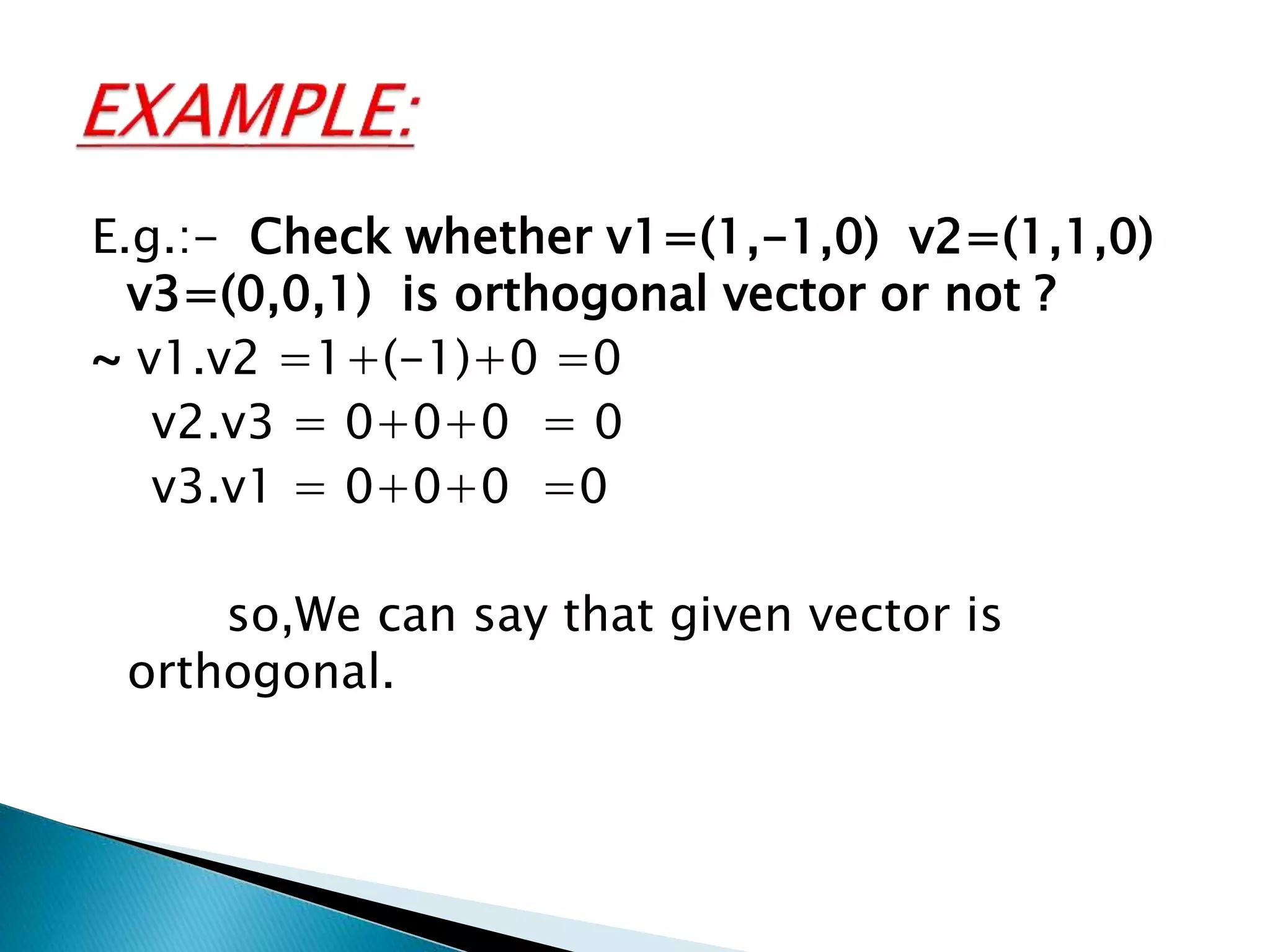
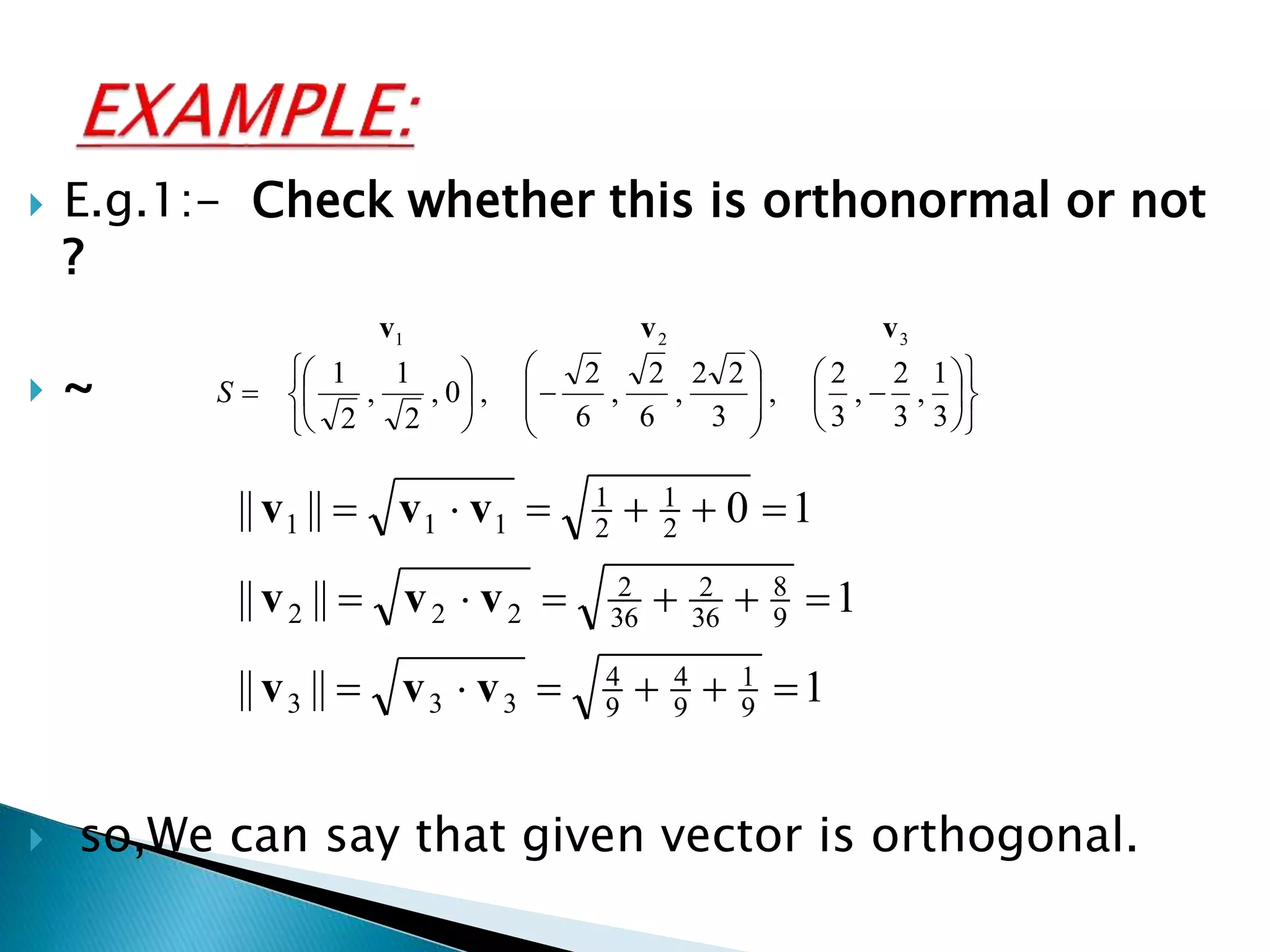
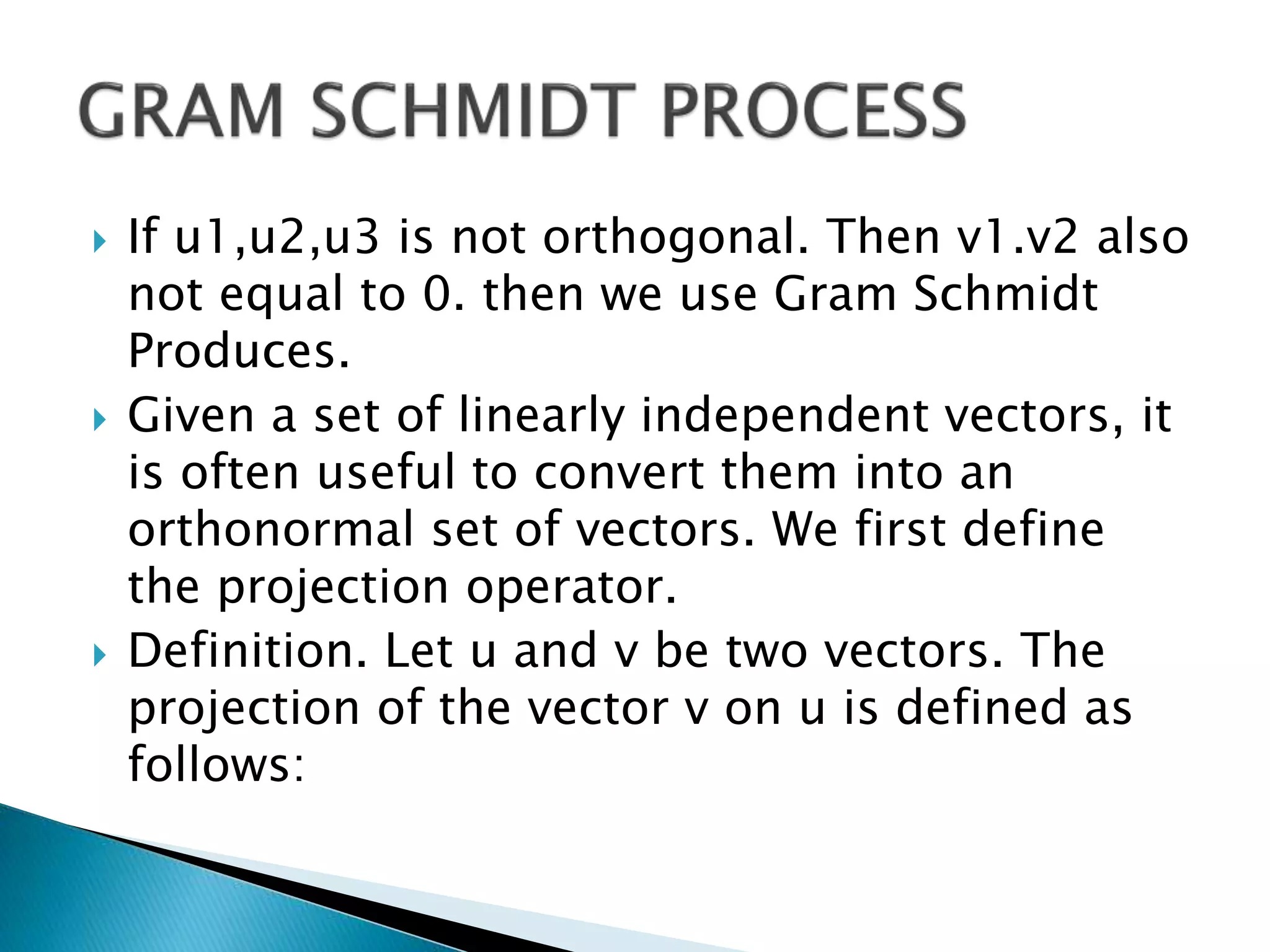
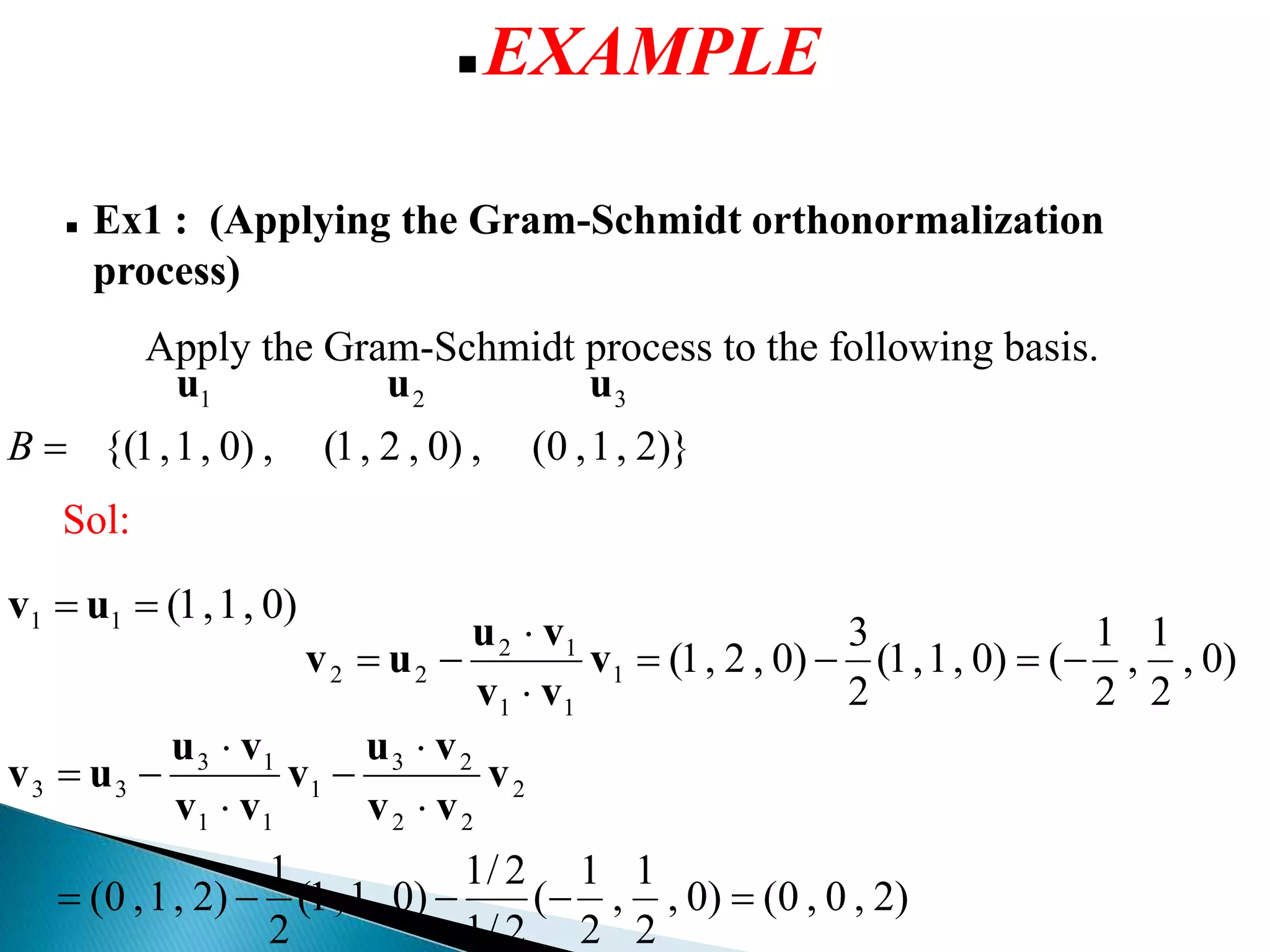
The document discusses concepts related to orthogonal and orthonormal vectors, including definitions and examples such as the Gram-Schmidt process for orthogonalization. It outlines the procedure for converting linearly independent vectors into an orthonormal set and explains orthogonal diagonalization of matrices. Key steps involve finding eigenvalues, eigenvectors, and applying the Gram-Schmidt process to achieve orthonormal vectors.




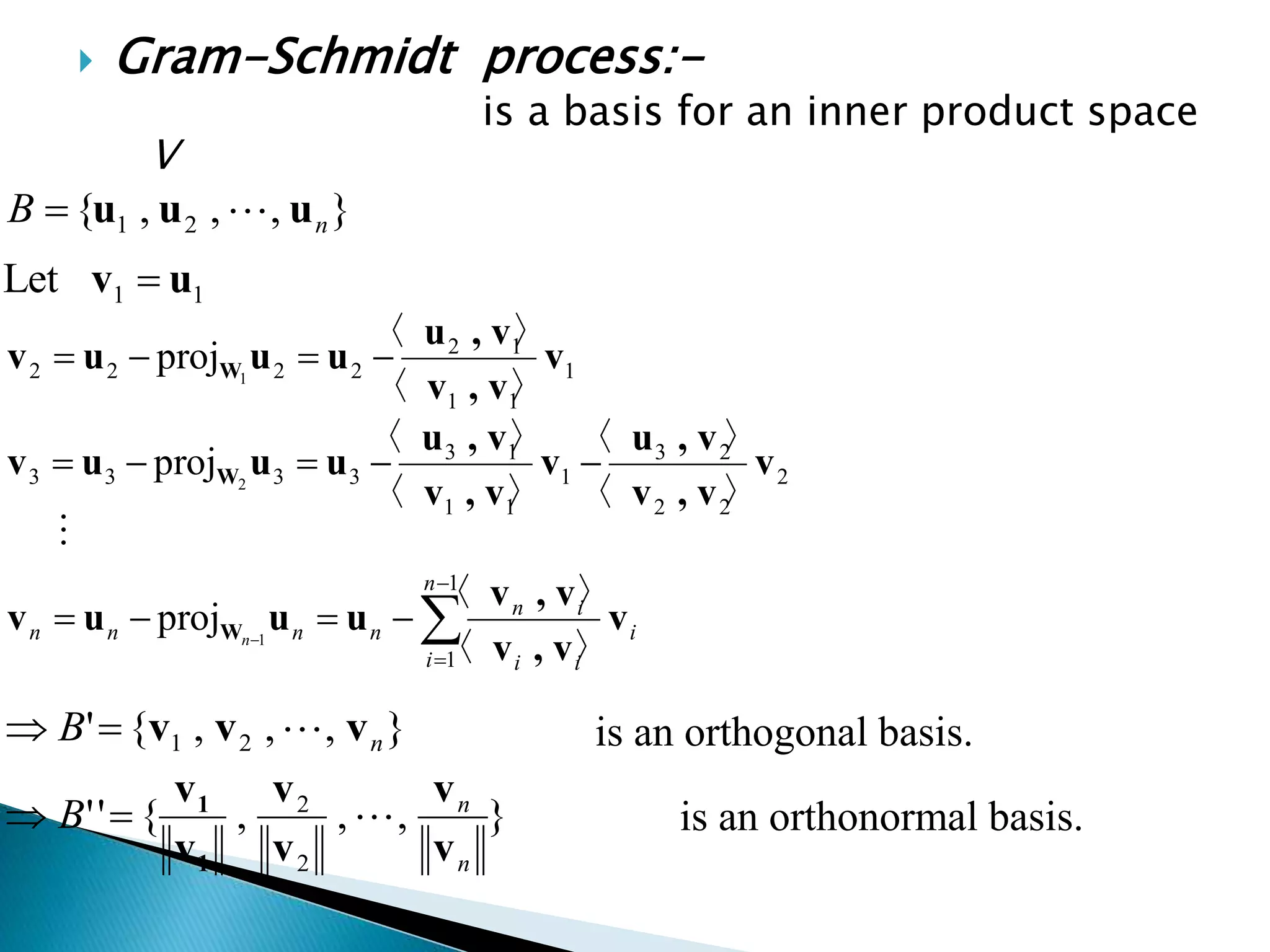


![ STEP 1. find out eigen values.
STEP 2. Find out eigen vectors.
STEP 3. say eigen vectors as a u1,u2,u3…..
STEP 4. convert in a ortho normal vector
q1,q2,q3….using gram schmidt process.
STEP 5. find matrix p=[ q1,q2,q3]
STEP 6.find p^-1 A P= P^T A P=[ λ1 0 0 ]
[ 0 λ2 0 ]
[ 0 0 λ3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalvcla-151006172920-lva1-app6892/75/ORTHOGONAL-ORTHONORMAL-VECTOR-GRAM-SCHMIDT-PROCESS-ORTHOGONALLY-DIAGONALIZATION-12-2048.jpg)




