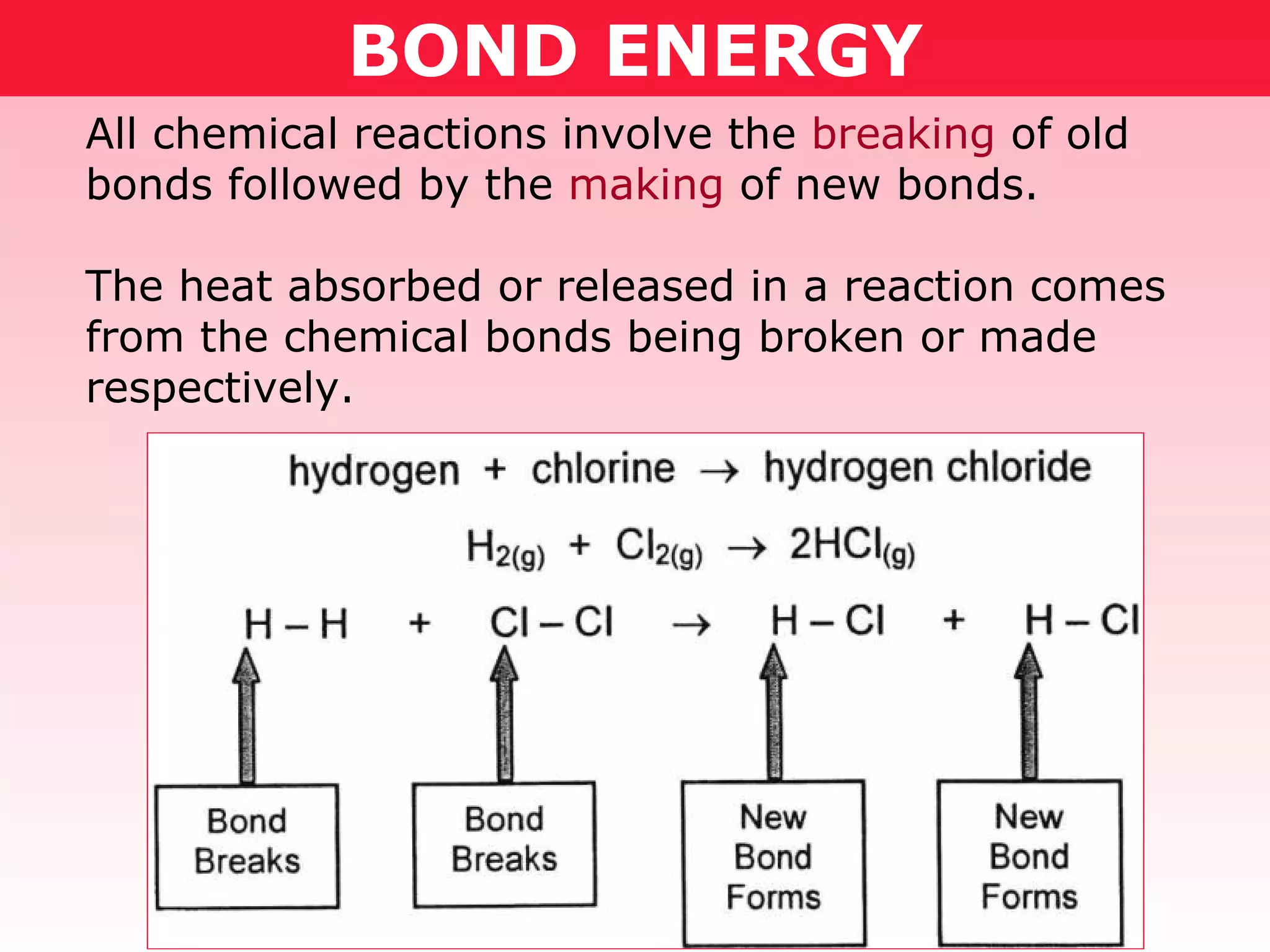
- Chemical reactions involve breaking old bonds and forming new ones. Bond breaking requires energy and is endothermic, while bond formation releases energy and is exothermic.
- The bond energies table lists the average energy required to break common types of bonds. However, bond energies can vary depending on neighboring bonds.
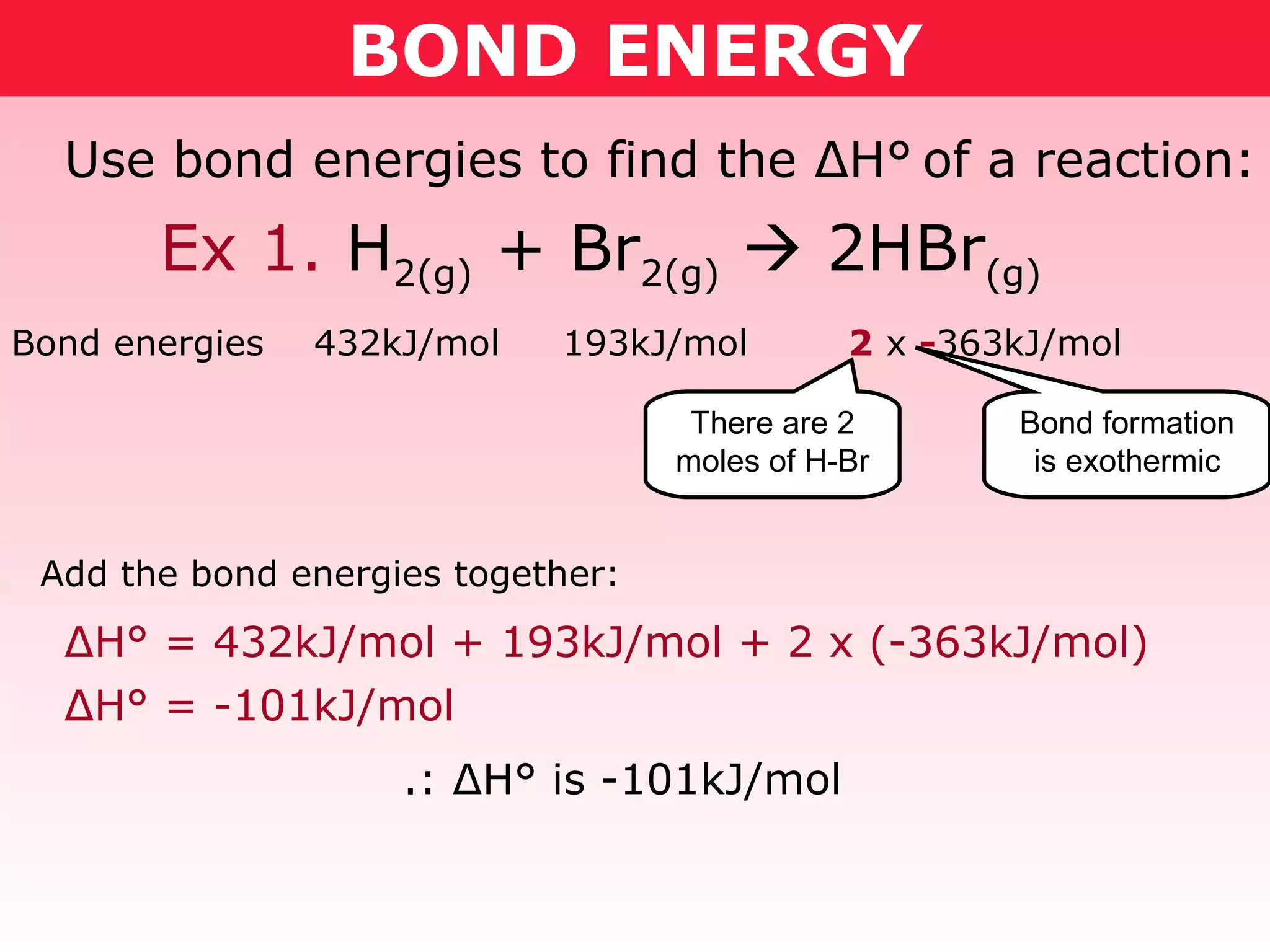
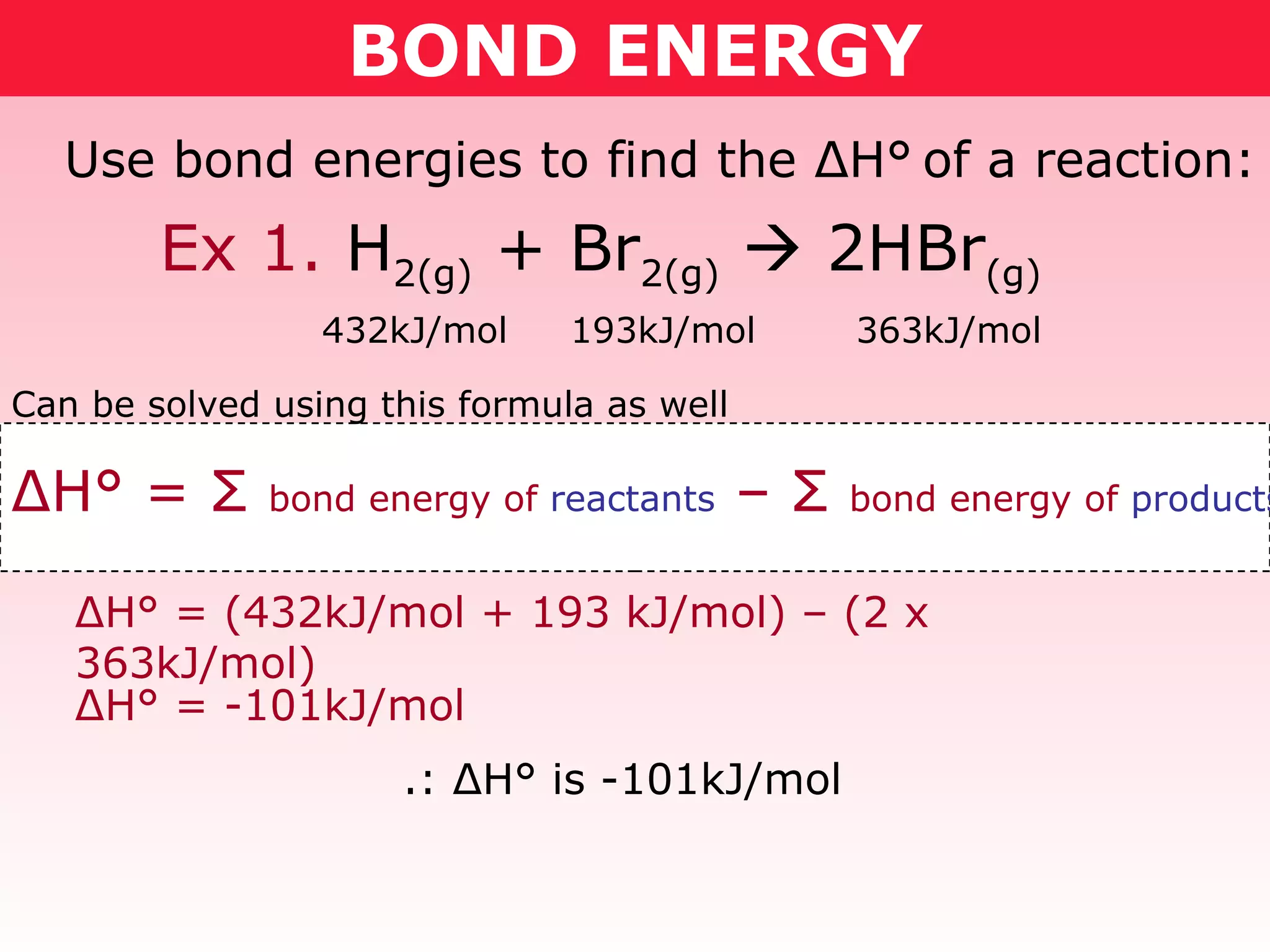
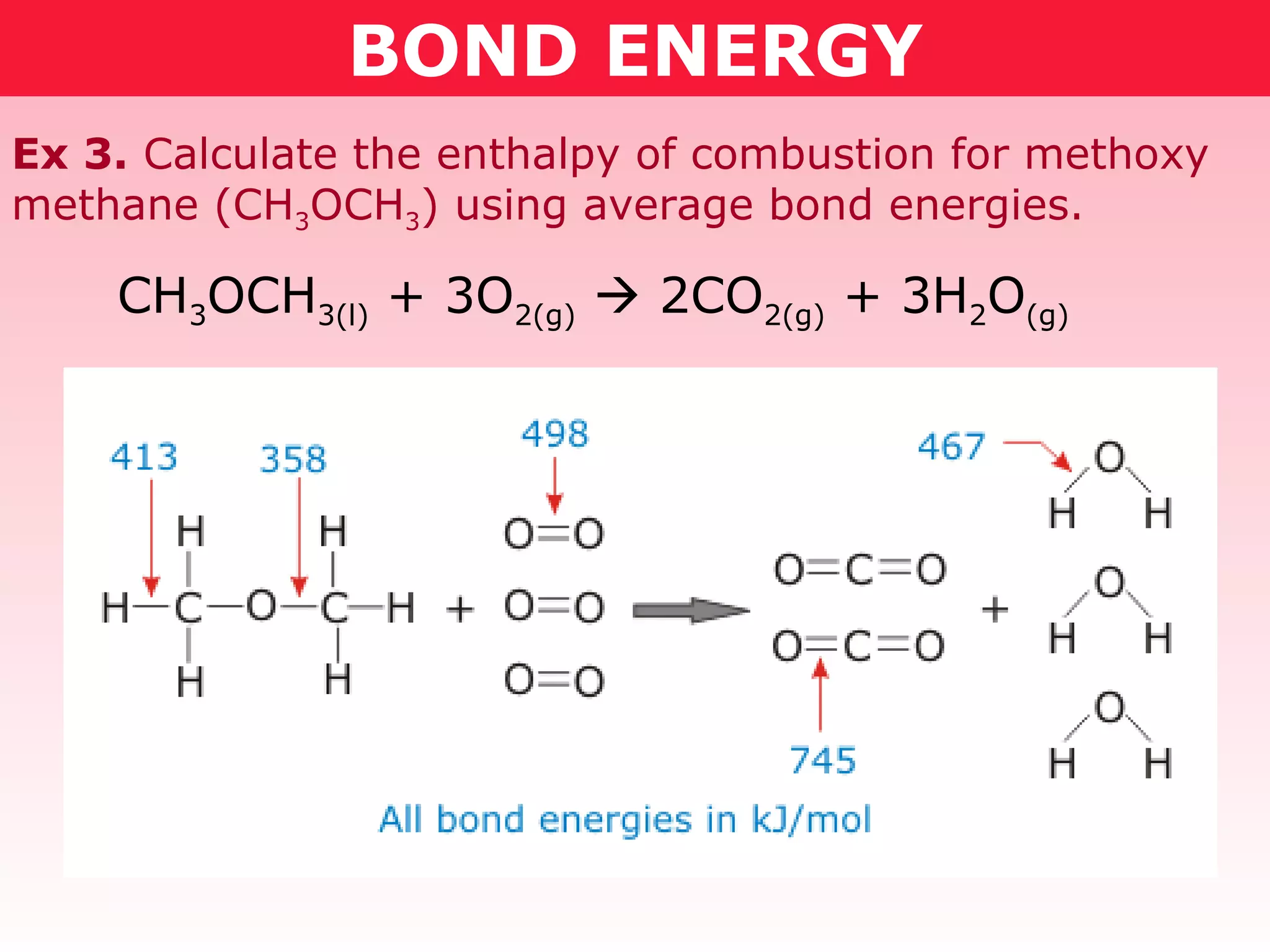
- Reaction enthalpy change (ΔH) can be calculated by adding the bond energies of reactants and subtracting the bond energies of products. This was demonstrated for combustion reactions of ethanol and methoxymethane.