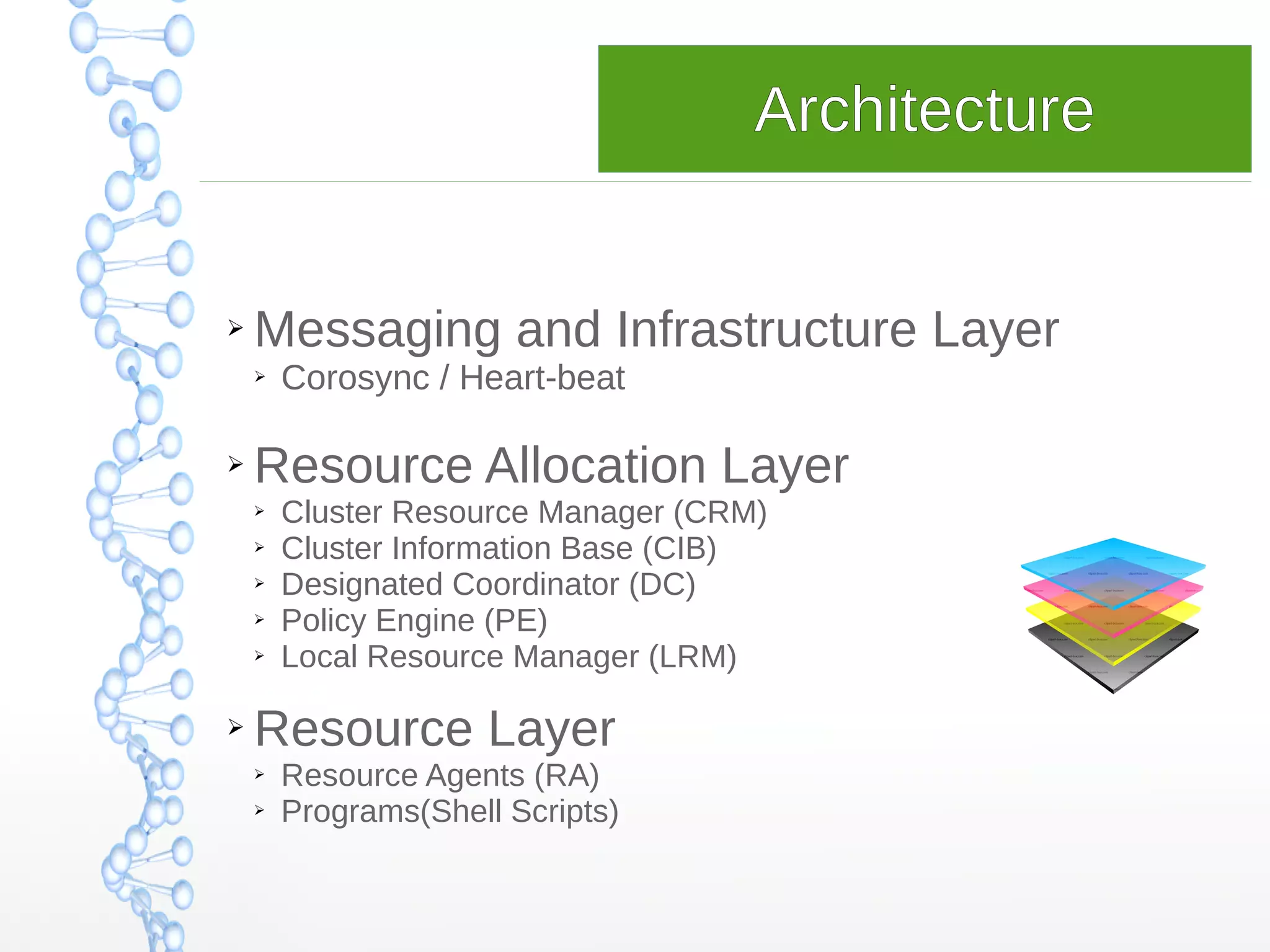
This document provides an overview of HA clustering on OpenSUSE. It discusses key aspects of HA clusters including eliminating single points of failure, reliable crossovers, failure detection, increased availability, improved performance, and scalability. It also describes the typical architecture of an HA cluster including messaging/infrastructure layers, resource allocation layers, resource agents, and more. Tips are provided around configuration, troubleshooting, and references for further information.