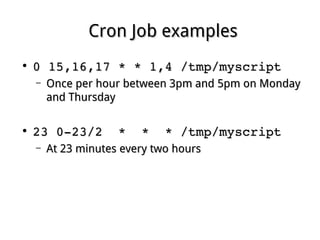
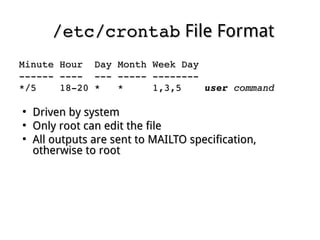
This document discusses different methods for automating system administration tasks by scheduling jobs, including cron, anacron, and at. Cron executes tasks on a recurring schedule, while anacron runs jobs that may have been missed when the system was offline. The at command executes a one-time job at a specified time in the future. Configuration files like cron.allow and cron.deny control which users can schedule jobs with these tools.