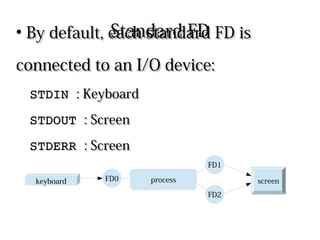
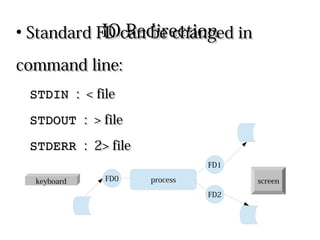
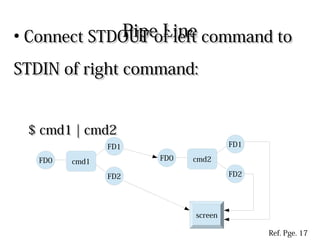
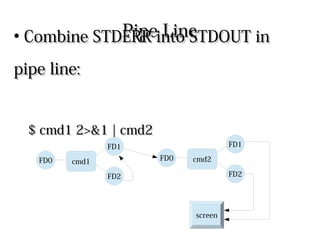
Processes use file descriptors (FDs) to perform input/output operations. The first 3 FDs - STDIN, STDOUT, and STDERR - are used by default for keyboard, screen, and screen respectively. Standard FDs can be redirected using operators like <, >, 2> to redirect input, output, and errors. Pipelines connect the STDOUT of one command to the STDIN of another to pass output as input between commands.