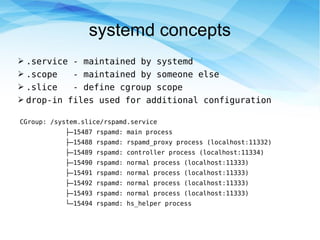
This document discusses using systemd to manage control groups (cGroups) and set resource limits for processes and services. It describes how systemd simplified cGroup management by creating a cGroup for each service and allowing configuration via service files and drop-in files. Specific configuration options like memory and CPU limits can be set directly in the service file, via a slice file that multiple services reference, or using systemctl commands. Systemd provides unified management of cGroups and services.











![Manually editing the .service files
➢ Get the service file location:
root@mailme:~# systemctl status rspamd
● rspamd.service - rapid spam filtering system
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rspamd.service;
enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
➢ Setting the memory limit:
[Service]
MemoryMax=2G
➢ Apply changes:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart rspamd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlyourserviceresourceswithsystemd-210806002033/85/Control-your-service-resources-with-systemd-13-320.jpg)
![Manually editing the .service files
➢ Get the service file location:
root@mailme:~# systemctl status rspamd
● rspamd.service - rapid spam filtering system
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rspamd.service;
enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
➢ Setting the memory limit:
[Service]
MemoryMax=2G
➢ Apply changes:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart rspamd
For full list of the options refer to:
man systemd.resource-control](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlyourserviceresourceswithsystemd-210806002033/85/Control-your-service-resources-with-systemd-14-320.jpg)
![Drop-in configuration files
➢ If your service is called: rspamd.service
➢ Create directory to hold specific configs:
mkdir /etc/systemd/system/rspamd.service.d
➢ Then in that directory, create the specific configuration
files, like: memory.conf
[Service]
MemoryAccounting=1
MemoryHigh=1800M
MemoryMax=2100M
MemorySwapMax=2100M
➢ Apply changes:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart rspamd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlyourserviceresourceswithsystemd-210806002033/85/Control-your-service-resources-with-systemd-15-320.jpg)

![slice file
➢ In /etc/systemd/system/new.slice
[Slice]
MemoryAccounting=1
MemoryHigh=1800M
MemoryMax=2100M
MemorySwapMax=2100M
CPUQuota=12%
CPUQuotaPeriodSec=2s
➢ This way you have all of your limits in one file](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlyourserviceresourceswithsystemd-210806002033/85/Control-your-service-resources-with-systemd-17-320.jpg)
![slice file
➢ In /etc/systemd/system/rspamd.service
[Service]
Slice=new.slice
➢ This way you will reference the slice that
you have previously created](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlyourserviceresourceswithsystemd-210806002033/85/Control-your-service-resources-with-systemd-18-320.jpg)


