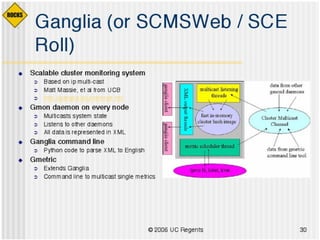
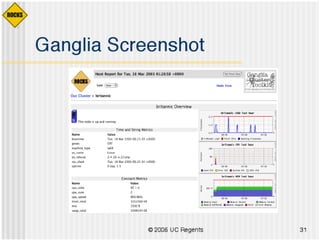
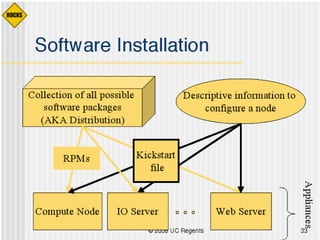
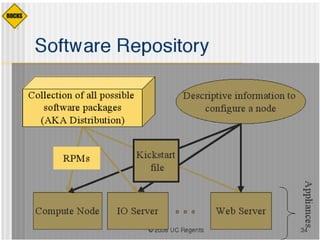
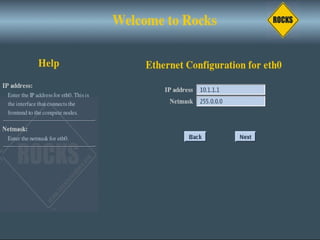
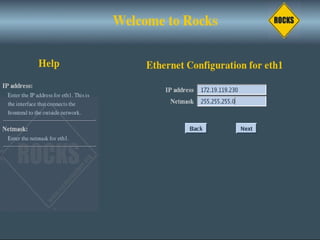
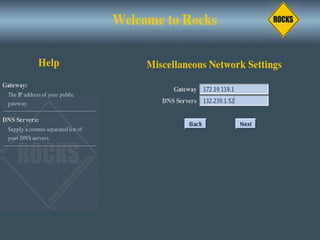
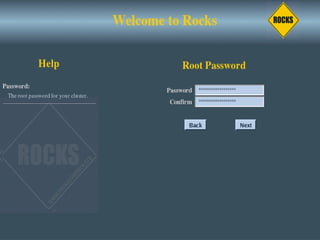
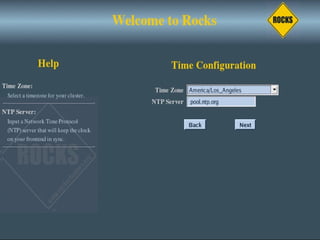
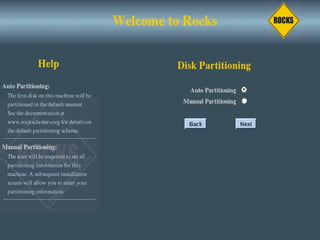
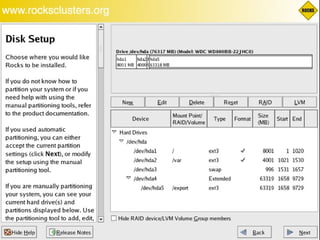
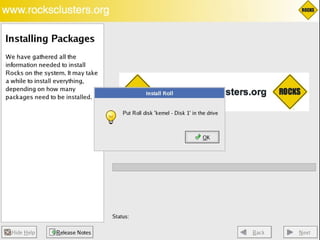
This document discusses various options for building and managing computer clusters, including do-it-yourself (DIY) clusters, pre-configured solutions like OSCAR and Rocks, and Microsoft solutions. It provides overviews of the software and processes for setting up and maintaining these different types of clusters.




















![Example c3 configuration # /etc/c3.conf ## # describes cluster configuration ## cluster gcb { gcb.fiu.edu #head node dead placeholder #change command line to 1 indexing compute-0-[0-8] #first set of nodes exclude 5 #offline node in the range (killed by J. Figueroa) } -------](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-4-clustercomputing-090811073537-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-Cluster-Computing-23-320.jpg)