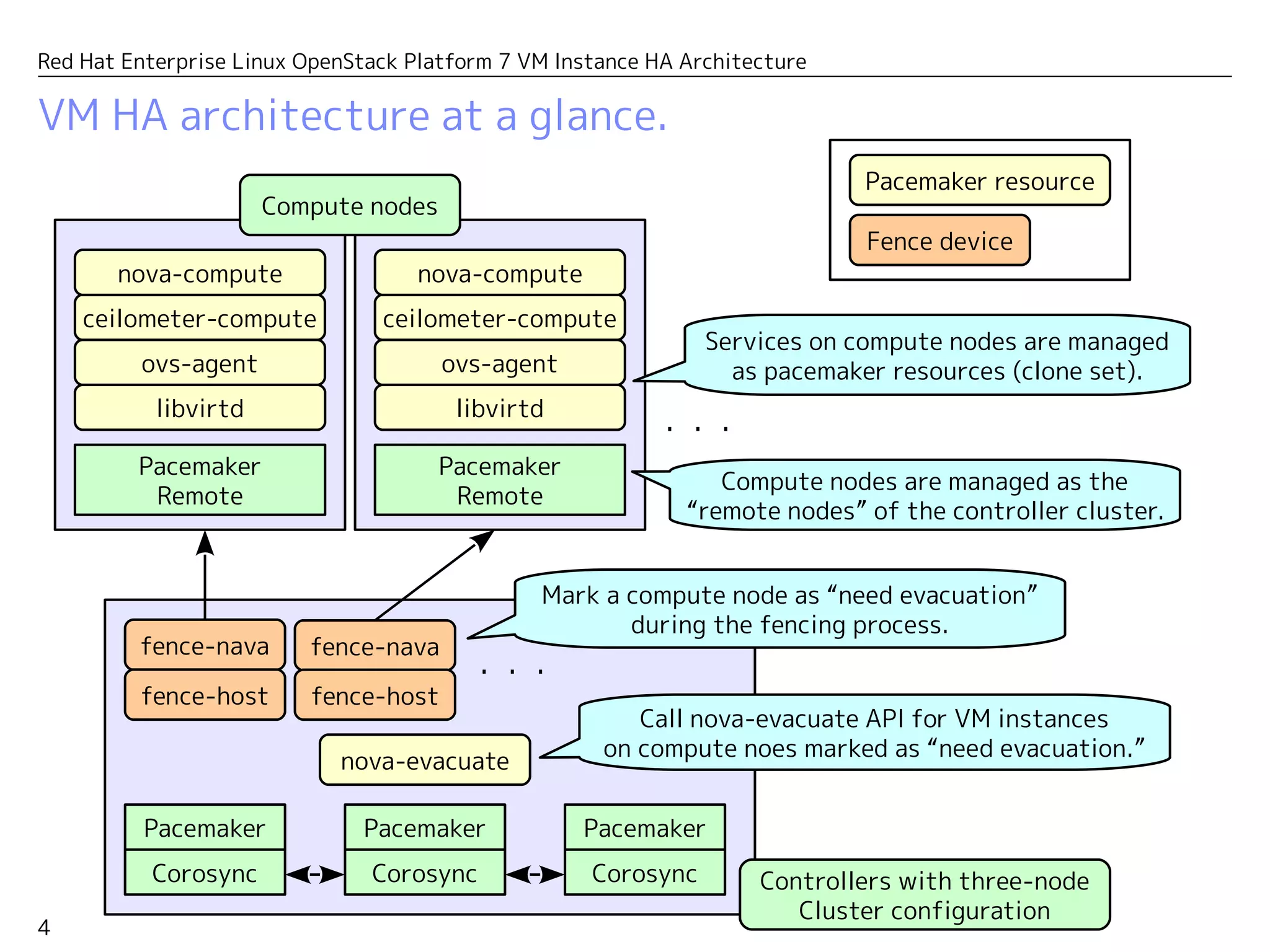
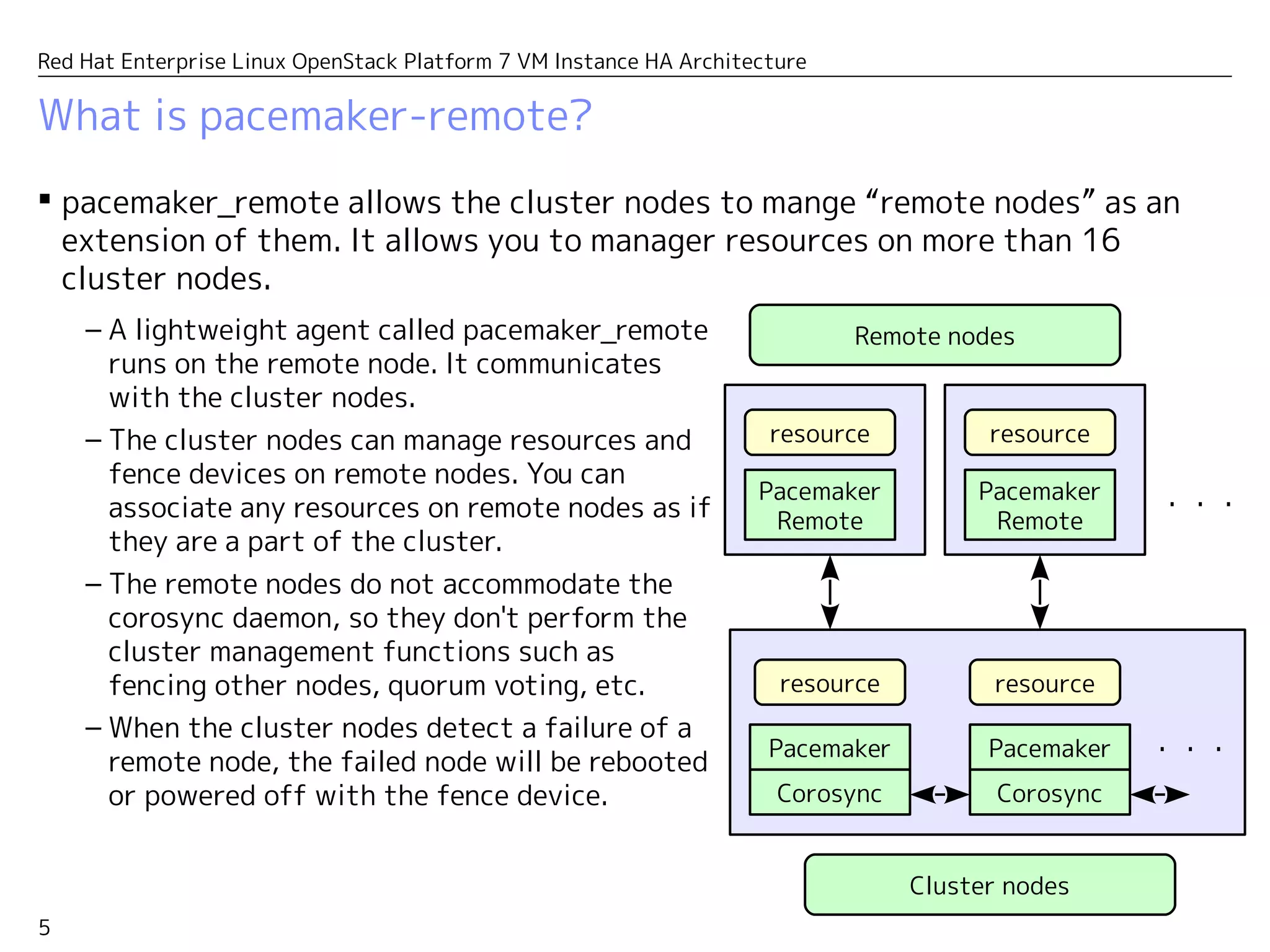
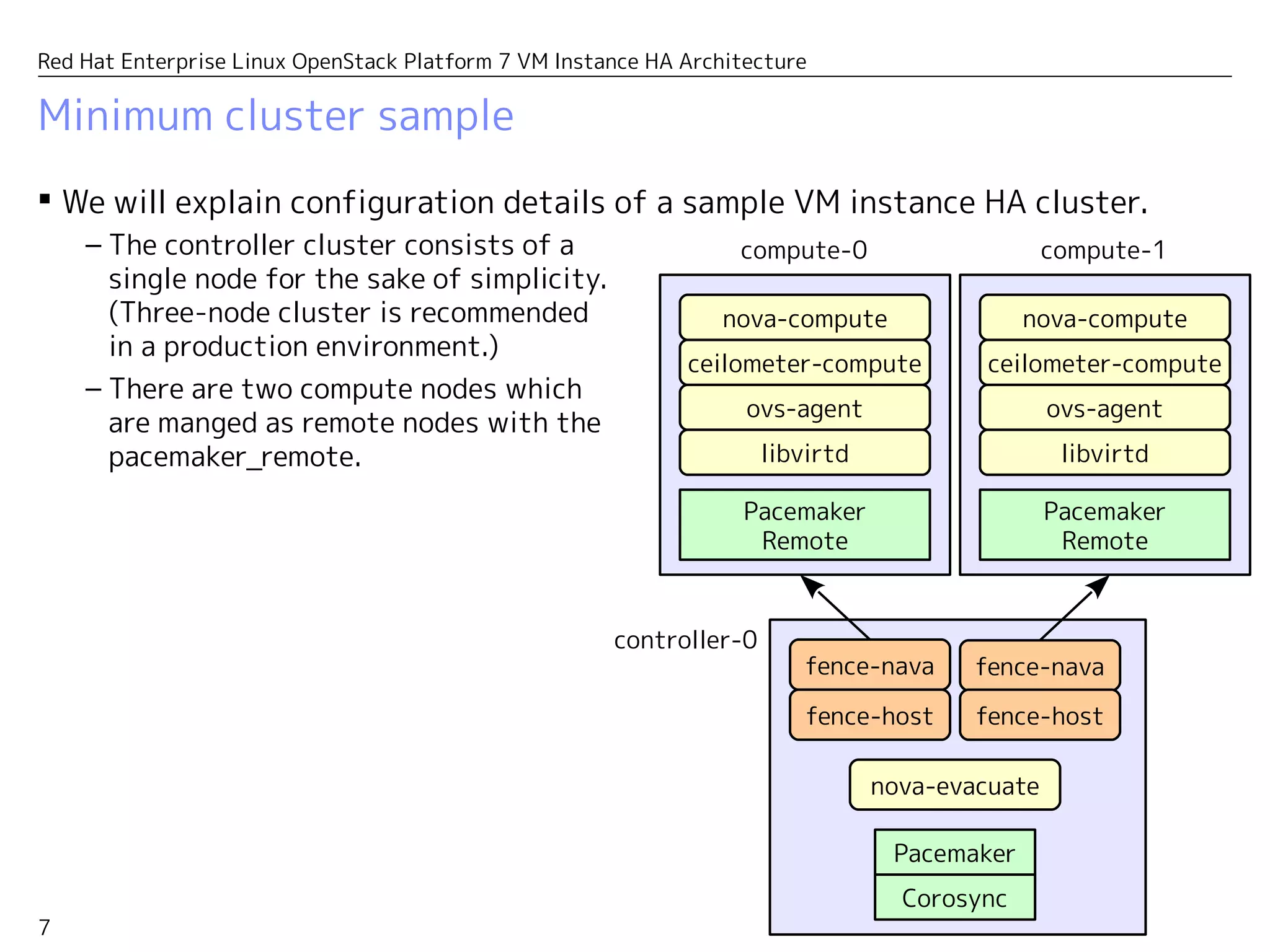
This document presents the high availability (HA) architecture for virtual machines (VM) in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform 7. It details the operational components, including the roles of pacemaker, corosync, and nova-evacuate in managing VM instances across clustered compute nodes. Additionally, it outlines configuration specifics, evacuation processes, and resource management to ensure service continuity during failures.




![8
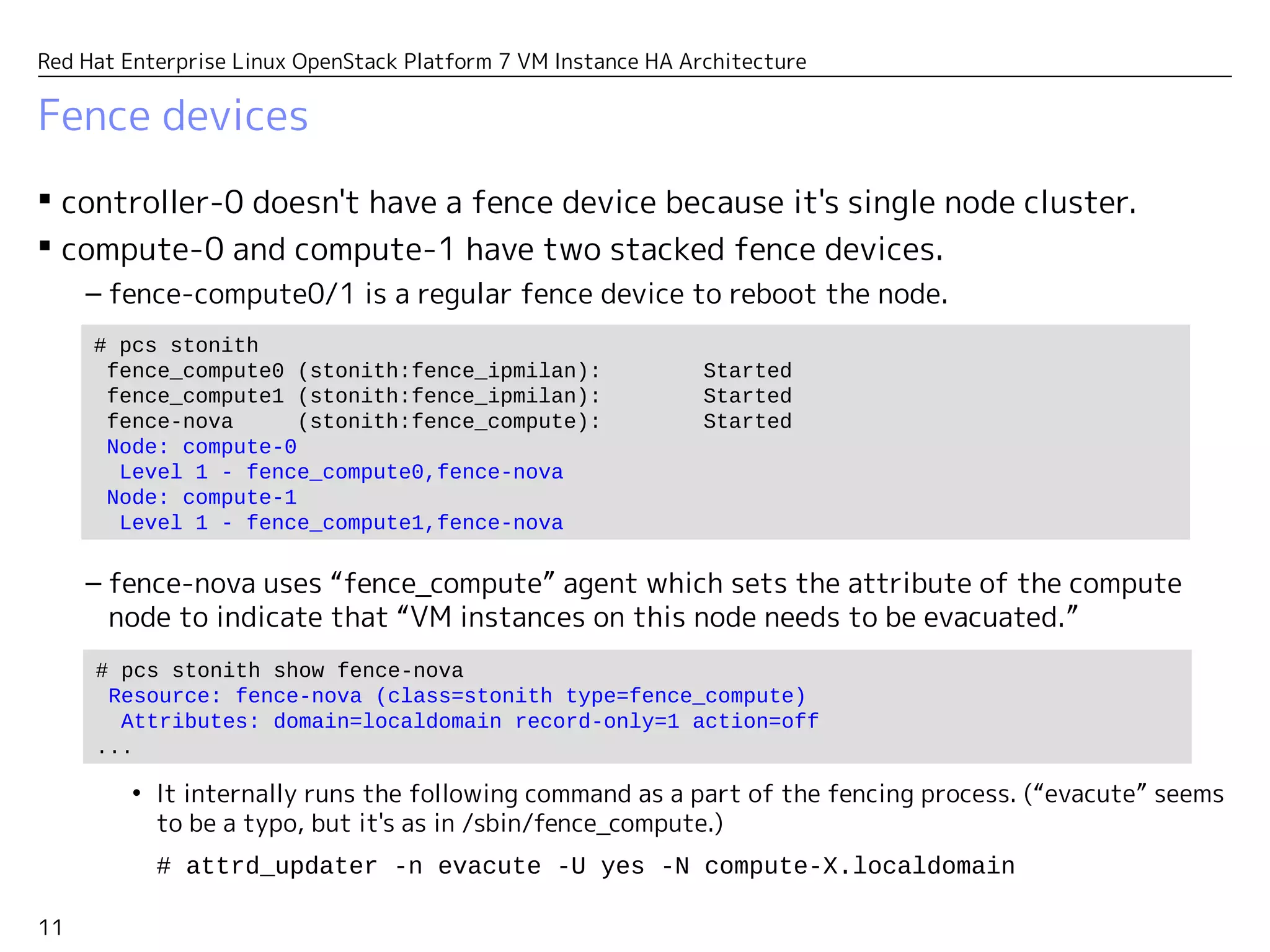
Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform 7 VM Instance HA Architecture
Cluster definition
controller-0 is defined as a cluster node while compute-0 and compute-1 are
defined as remote nodes.
– Only controller-0 has the quorum vote. So from the corosync's viewpoint, it's just a
single node cluster.
# pcs cluster status
Cluster Status:
Last updated: Sun Nov 22 03:16:01 2015 Last change: Sat Nov 21 02:40:39 2015
by root via cibadmin on controller-0
Stack: corosync
Current DC: controller-0 (version 1.1.13-a14efad) - partition with quorum
3 nodes and 126 resources configured
Online: [ controller-0 ]
RemoteOnline: [ compute-0 compute-1 ]
PCSD Status:
controller-0: Online](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rhel-osp7-vmhav10-151122131532-lva1-app6891/75/Red-Hat-Enterprise-Linux-OpenStack-Platform-7-VM-Instance-HA-Architecture-8-2048.jpg)
![9
Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform 7 VM Instance HA Architecture
Resource definition
OpenStack services on compute nodes are started as managed resources.
– In this example, neutron-ovs-agent, libirtd, ceilometer-compute and nova-compute
are defined as managed resources with clone type. (The clone type resources are
enabled on multiple nodes in parallel.)
# pcs resource
...
nova-evacuate (ocf::openstack:NovaEvacuate): Started
Clone Set: neutron-openvswitch-agent-compute-clone [neutron-openvswitch-agent-compute]
Started: [ compute-0 compute-1 ]
Stopped: [ controller-0 ]
Clone Set: libvirtd-compute-clone [libvirtd-compute]
Started: [ compute-0 compute-1 ]
Stopped: [ controller-0 ]
Clone Set: ceilometer-compute-clone [ceilometer-compute]
Started: [ compute-0 compute-1 ]
Stopped: [ controller-0 ]
Clone Set: nova-compute-clone [nova-compute]
Started: [ compute-0 compute-1 ]
Stopped: [ controller-0 ]
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rhel-osp7-vmhav10-151122131532-lva1-app6891/75/Red-Hat-Enterprise-Linux-OpenStack-Platform-7-VM-Instance-HA-Architecture-9-2048.jpg)