This document summarizes Linux control groups (cgroups) and their capabilities for limiting and accounting for CPU, memory, block I/O, networking, and freezing processes. It describes the general cgroup structure and available controllers for CPU, CPU accounting, CPU scheduling, memory limits and accounting, block I/O statistics and limiting, network classification and prioritization, freezing processes, and checkpoint/restore with CRIU. Examples are given for configuring CPU and memory limits on cgroups.



![cpuset
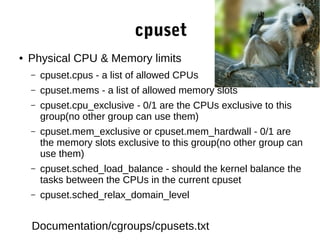
● Physical CPU & Memory limits
– cpuset.sched_relax_domain_level
-1 : no request. use system default or follow request of others.
0 : no search.
1 : search siblings (hyperthreads in a core).
2 : search cores in a package.
3 : search cpus in a node [= system wide on non-NUMA system]
on NUMA systems only
4 : search nodes in a chunk of node
5 : search system wide
Documentation/cgroups/cpusets.txt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-cgroups-140320112716-phpapp01/85/LSA2-02-Control-Groups-5-320.jpg)

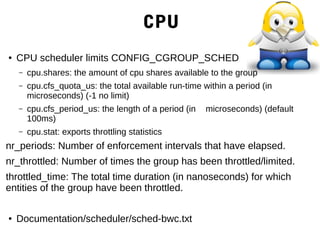
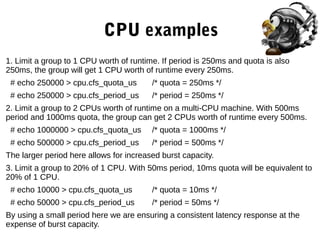



![blkio limiting
● blkio.weight - allowed range 10 - 1000
● blkio.weight_device - weight per device
● blkio.leaf_weight[_device] - when competing with
child cgroups
● blkio.time - disk time allocated in miliseconds
● blkio.throttle.read_bps_device
● blkio.throttle.write_bps_device
● blkio.throttle.read_iops_device](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-cgroups-140320112716-phpapp01/85/LSA2-02-Control-Groups-12-320.jpg)

