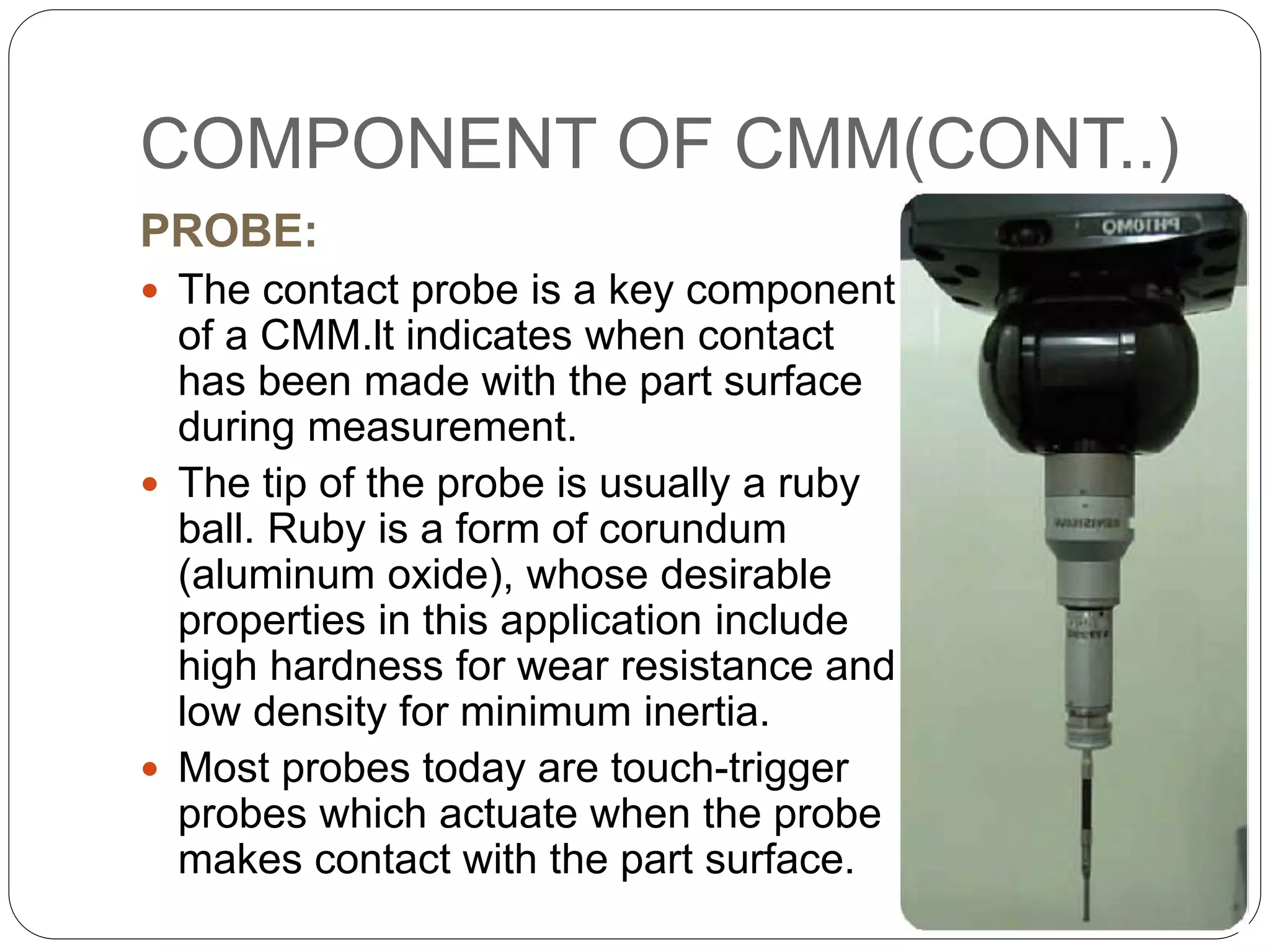
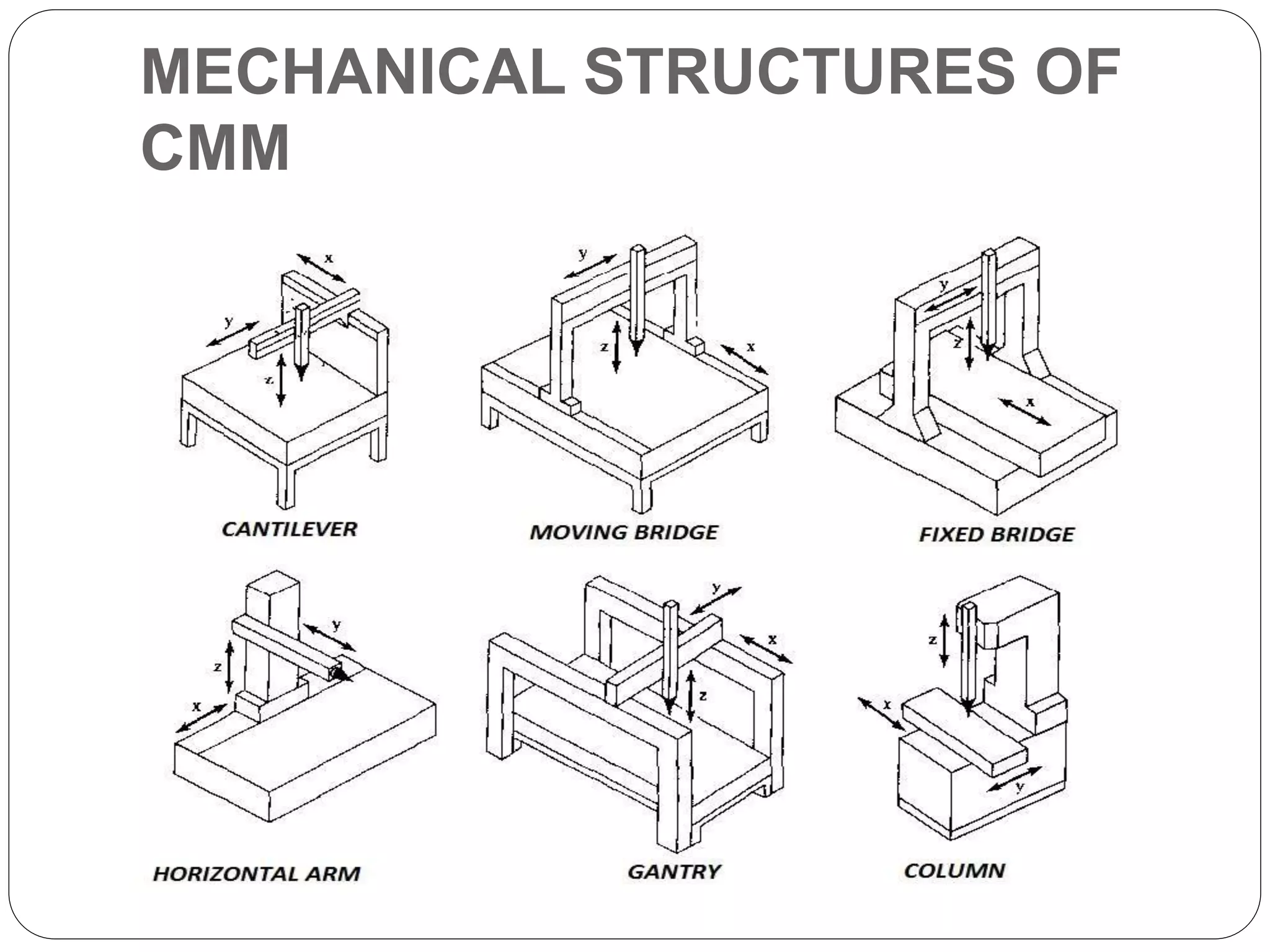
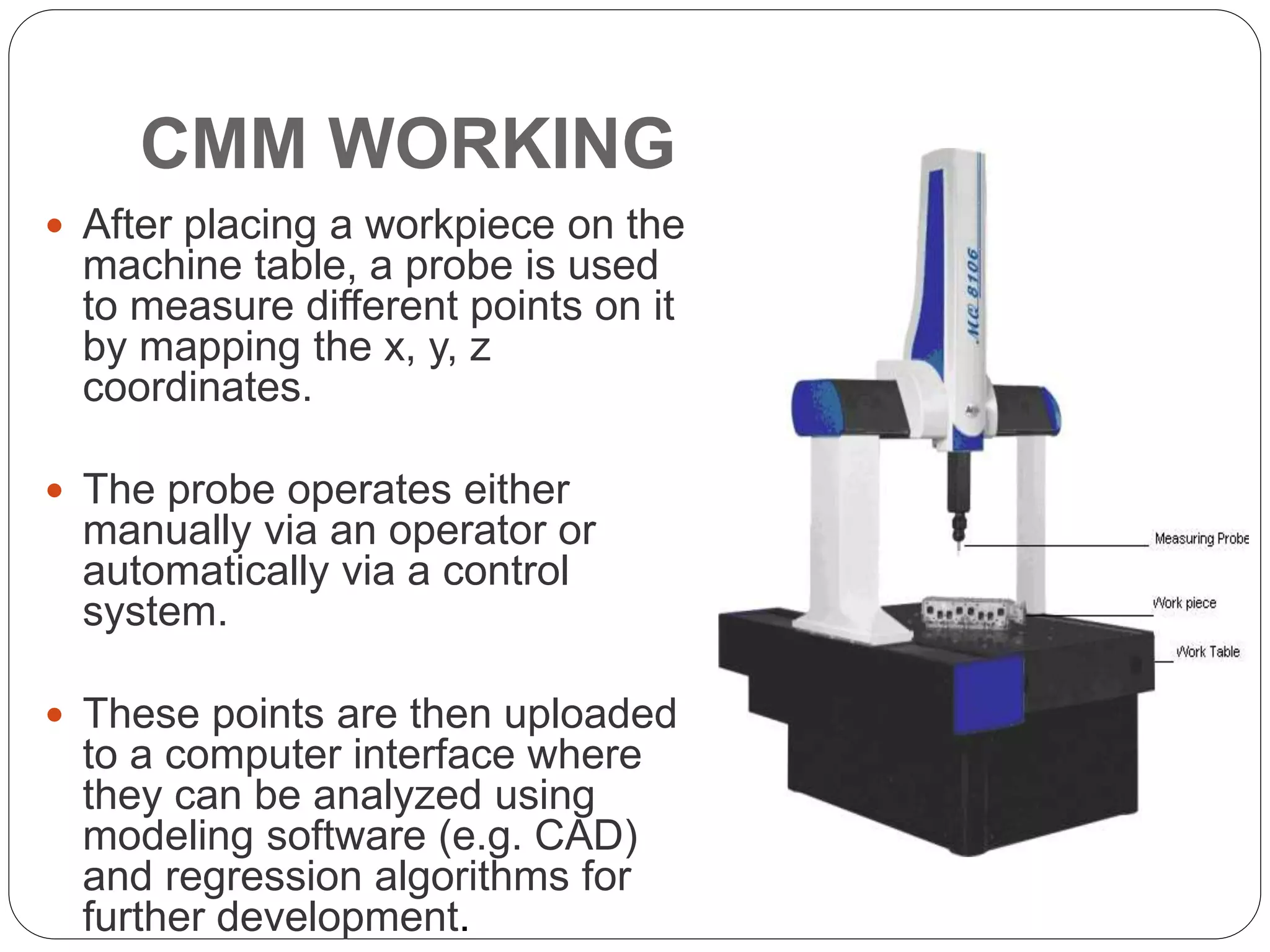
The document discusses coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). CMMs are electromechanical systems used for coordinate metrology that can convert physical measurements into electrical signals. A basic CMM consists of a probe head and probe to contact workpiece surfaces, a mechanical structure that provides motion in three axes, and displacement transducers to measure coordinate values. Modern CMMs also include a drive system and control unit to move each axis. CMMs can precisely measure complex profiles with high sensitivity and speed and are classified based on their mechanical structure.