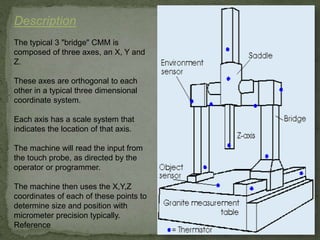
A coordinate measuring machine is a device used to precisely measure the geometry of physical objects using probes attached to three orthogonal axes. It works by probing points on an object placed on the machine table and mapping their x, y, z coordinates, which are then uploaded to computer software for analysis and quality inspection. Common components include a main structure with three motion axes, a probing system, and a data collection system with controller and software.