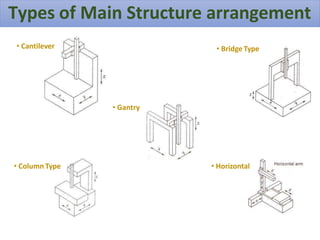
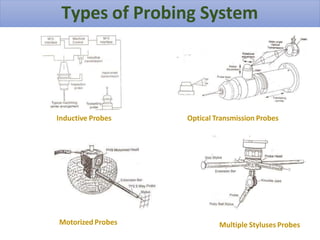
A Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) is a device used to measure the geometrical characteristics of objects, employing various probing systems to collect data in three-dimensional space. Key components include a structure with three axes of motion, a probing system, and a data collection system, which together ensure precision in measuring and inspecting parts across various industries. CMMs offer advantages like flexibility, reduced setup times, and improved productivity, making them vital in fields such as aerospace, automotive, and medical technology.