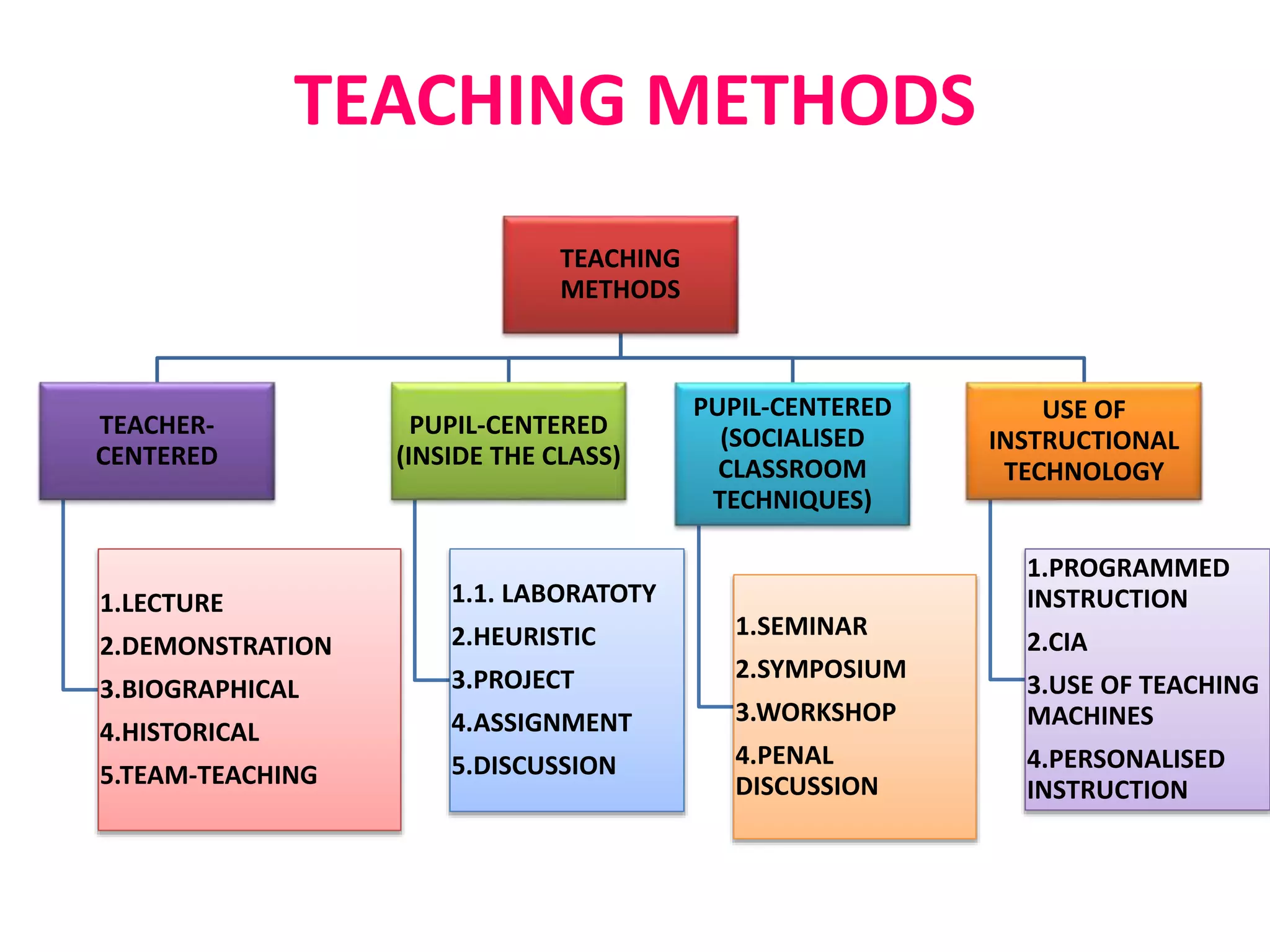
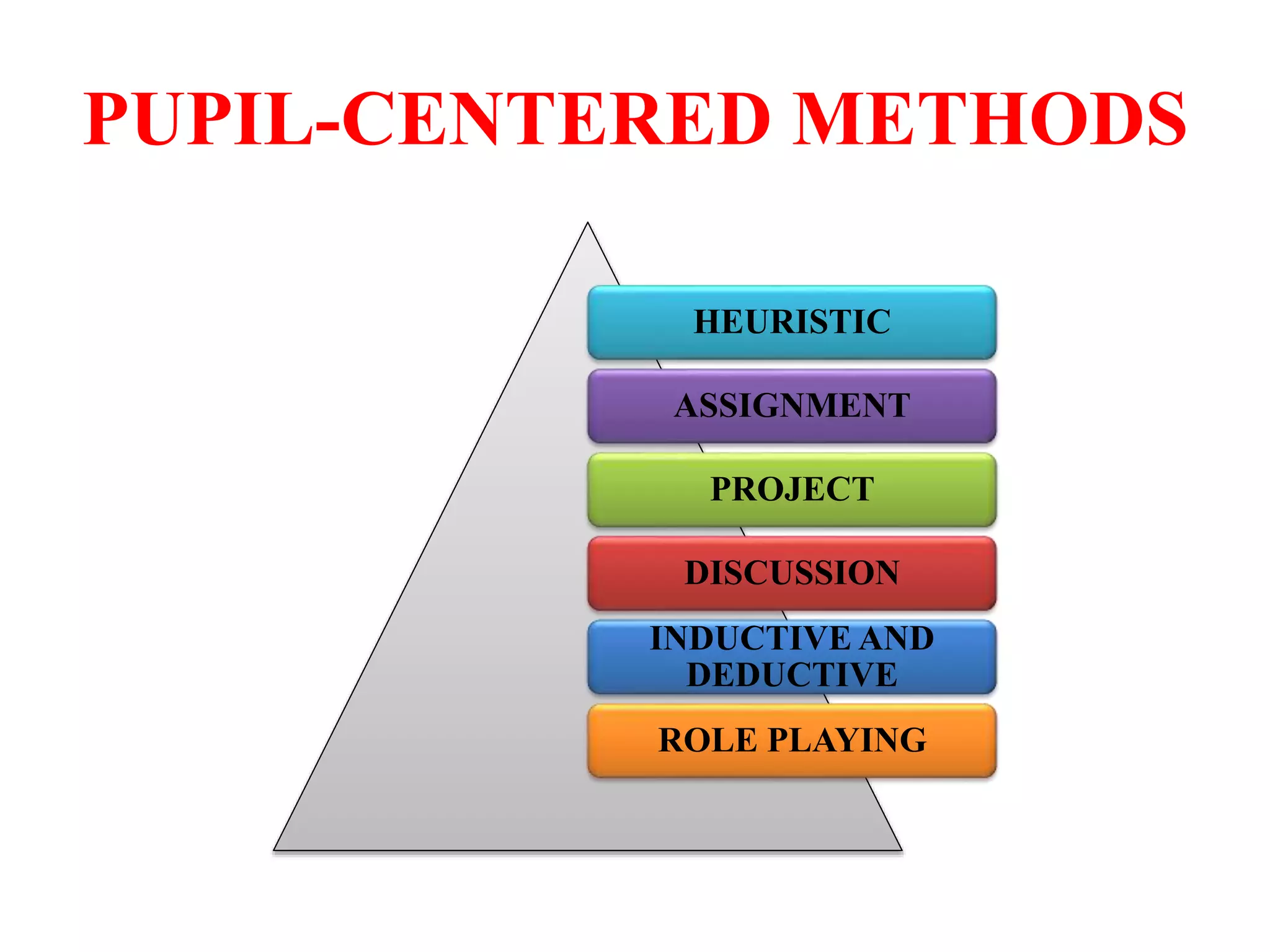
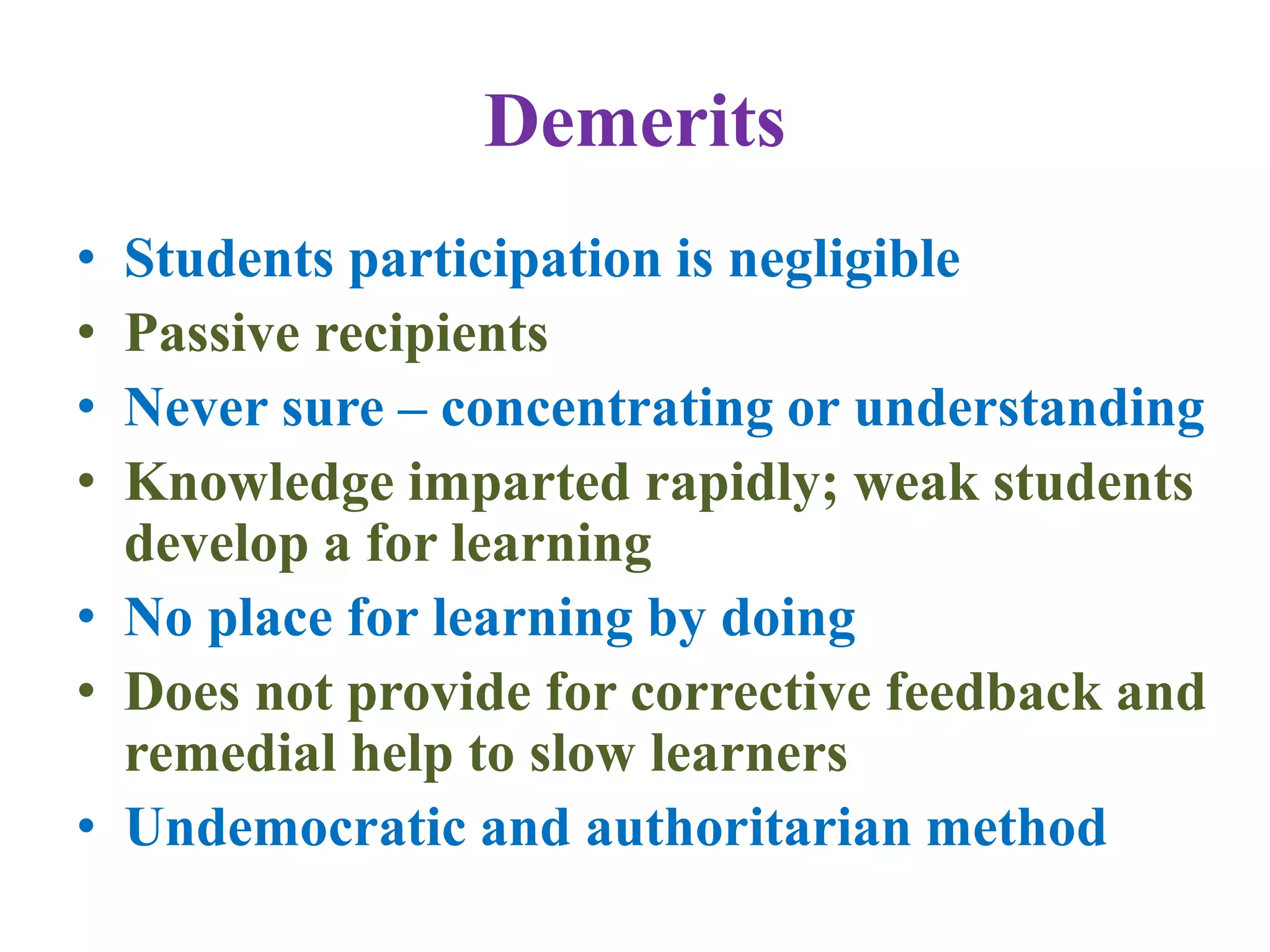
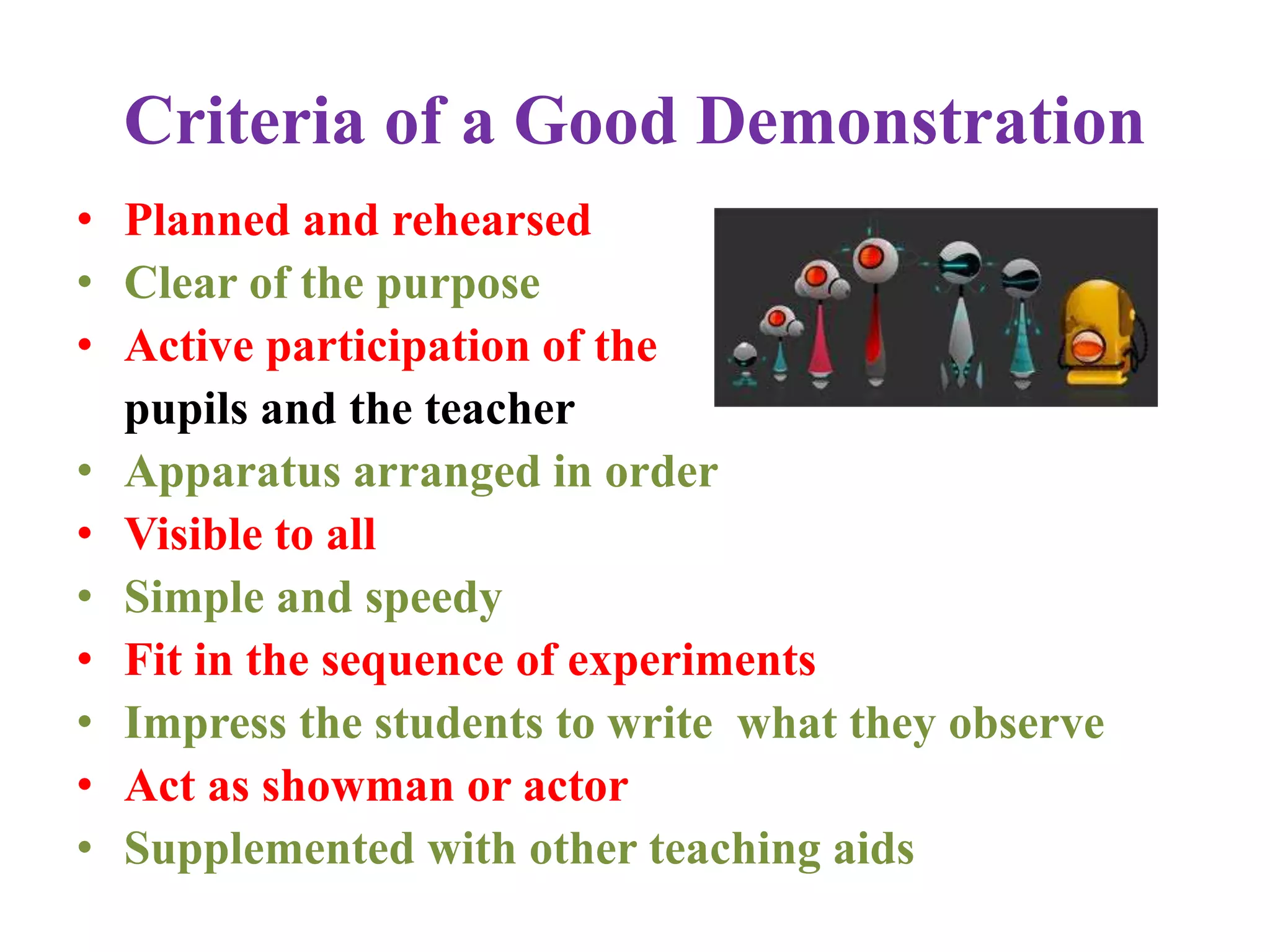
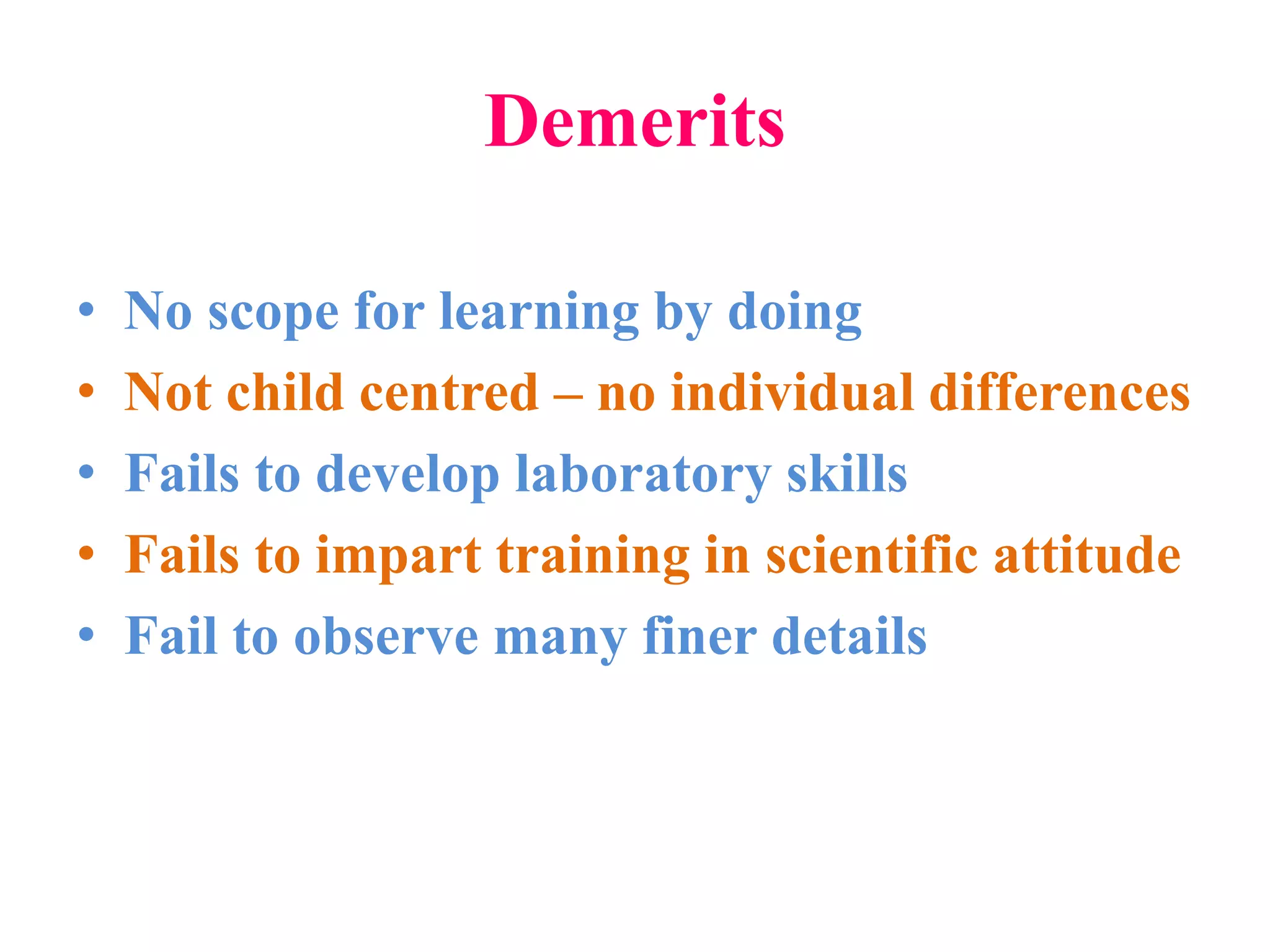
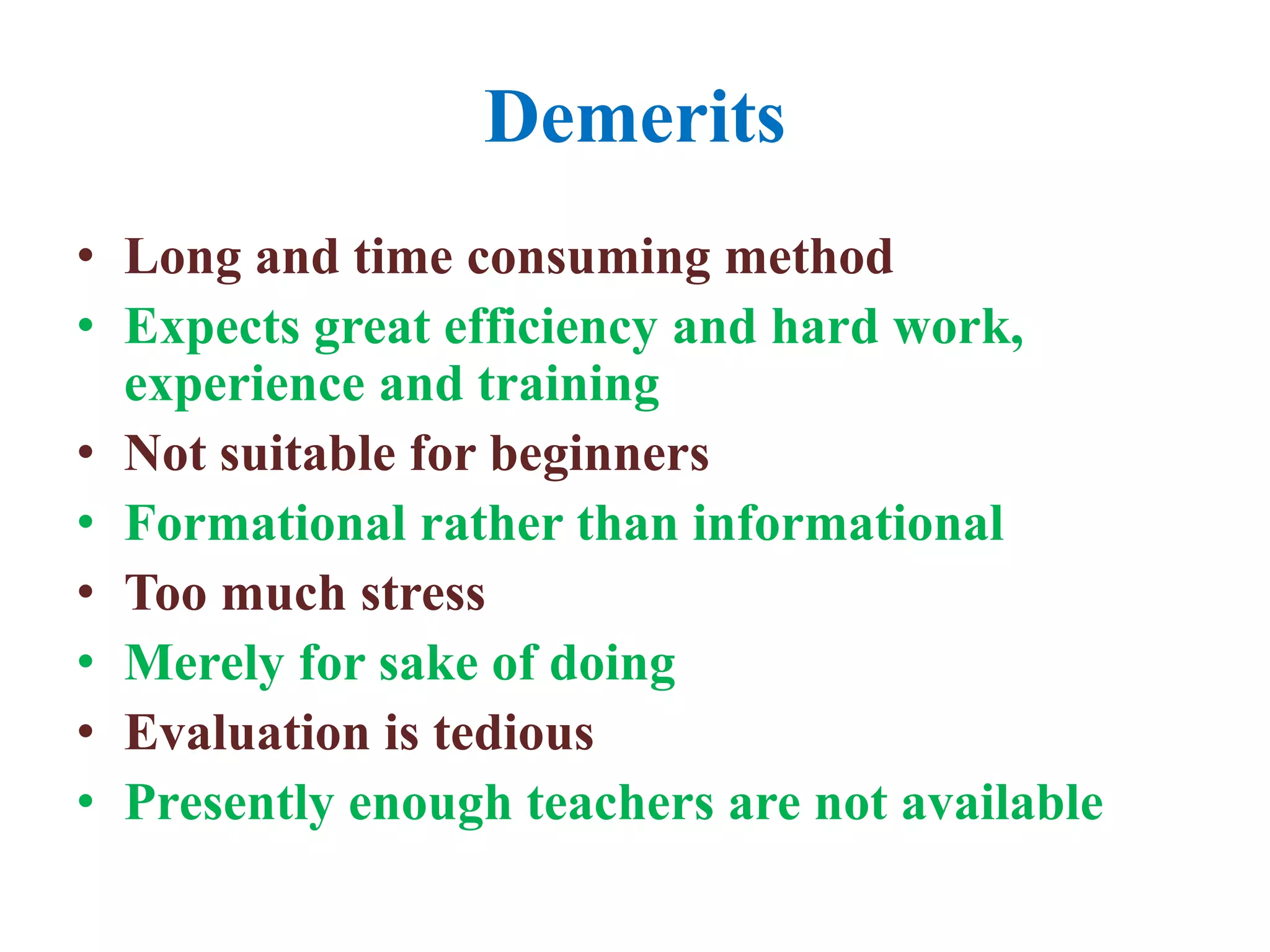
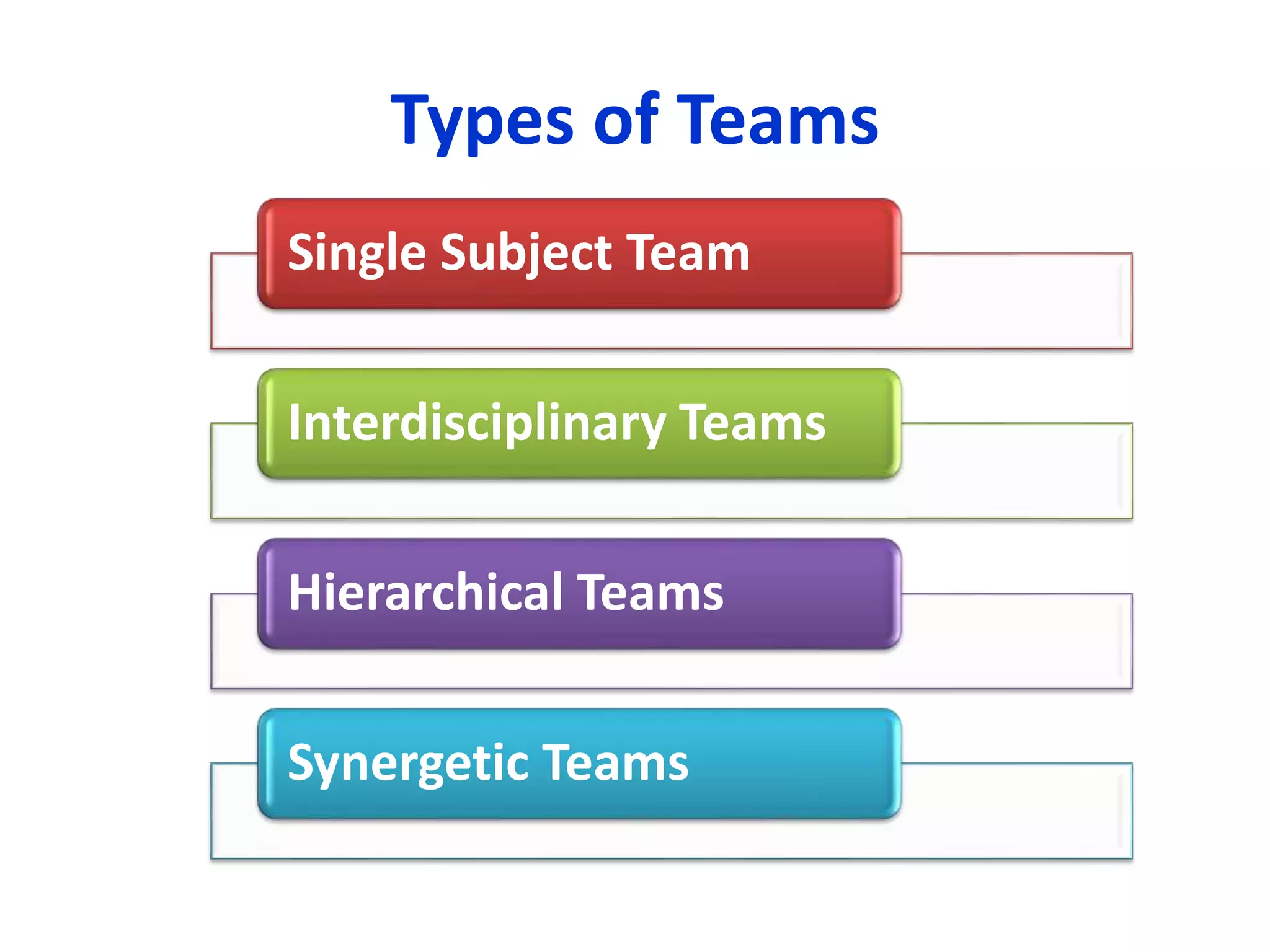
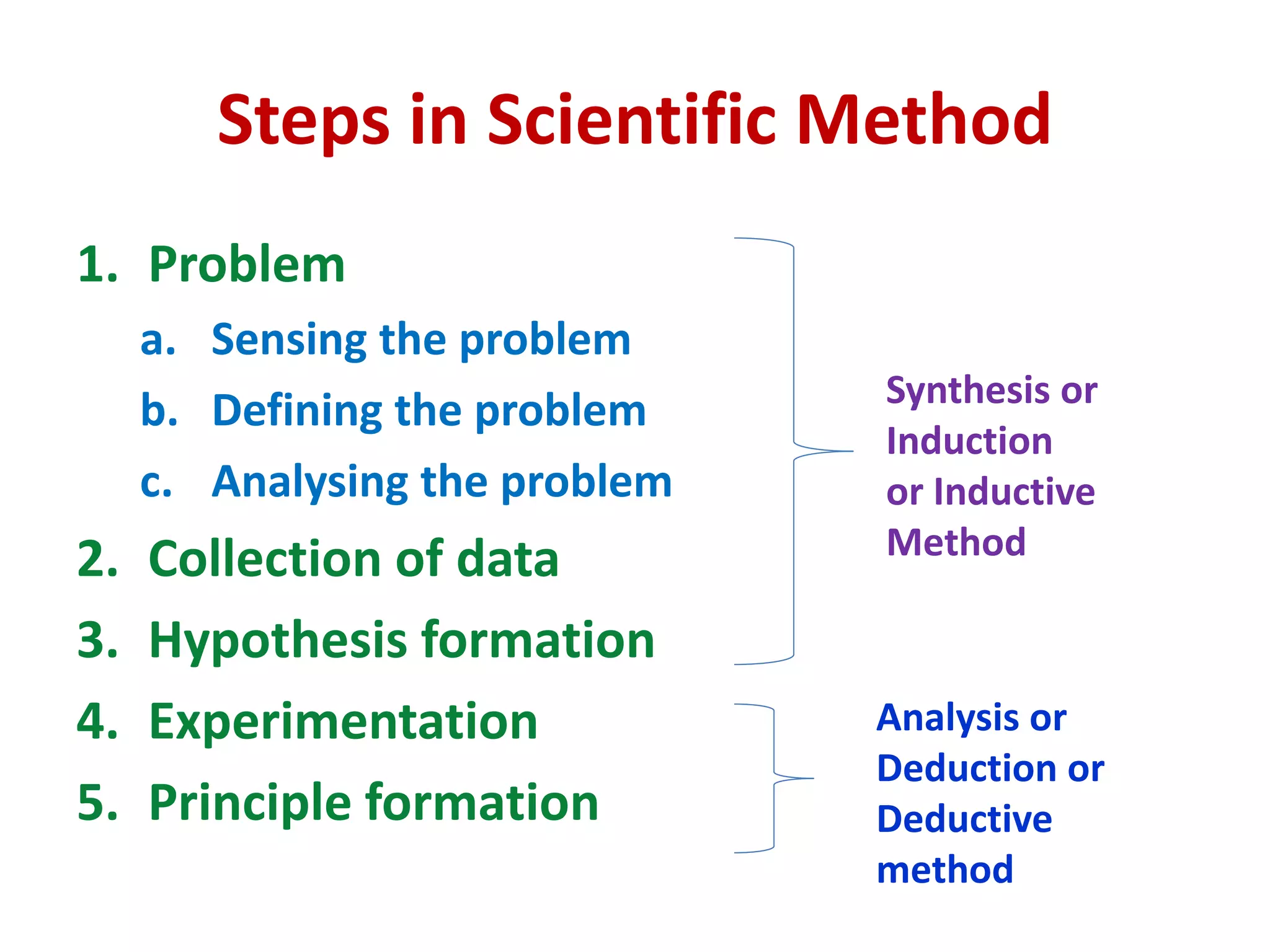
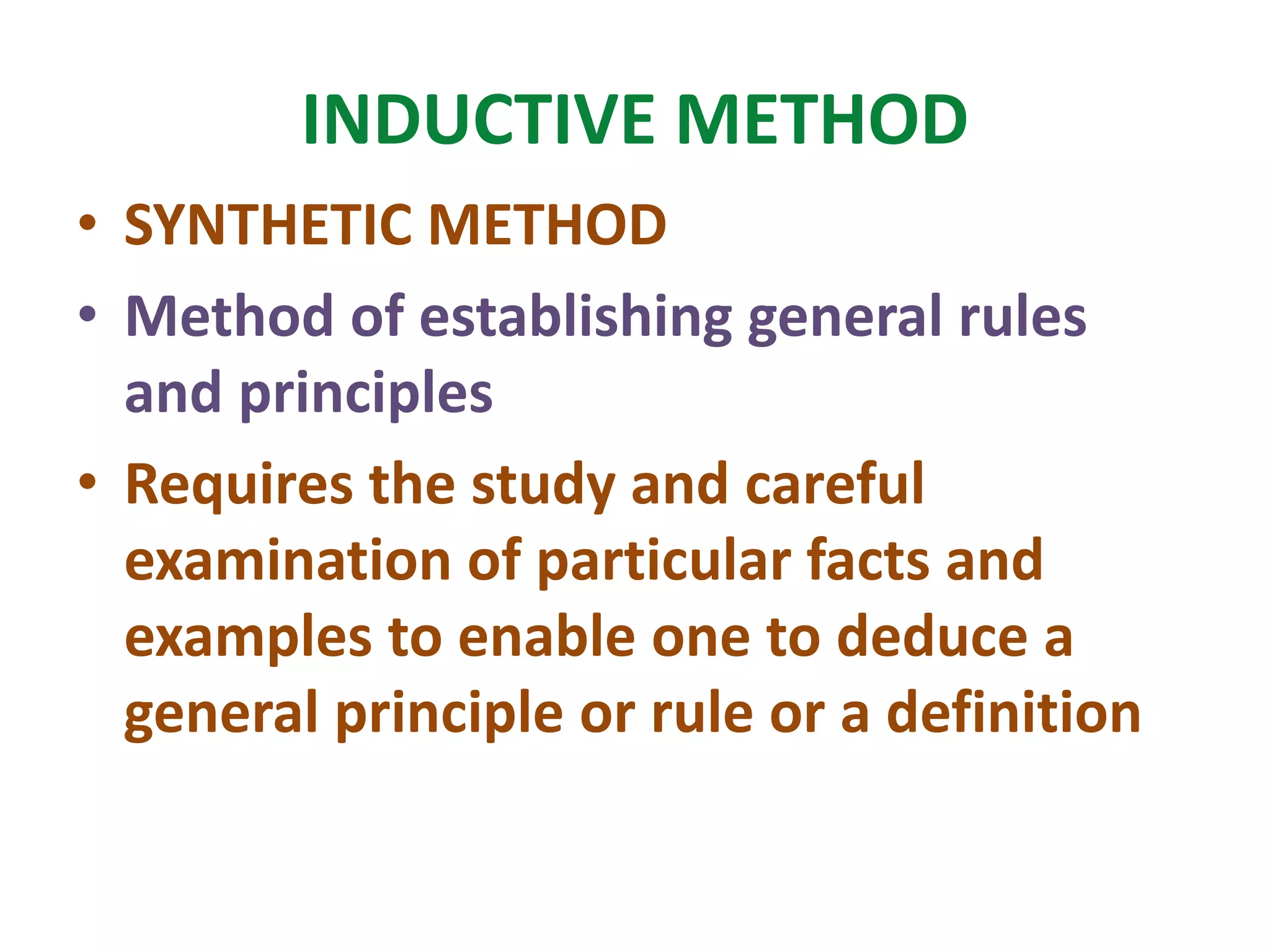
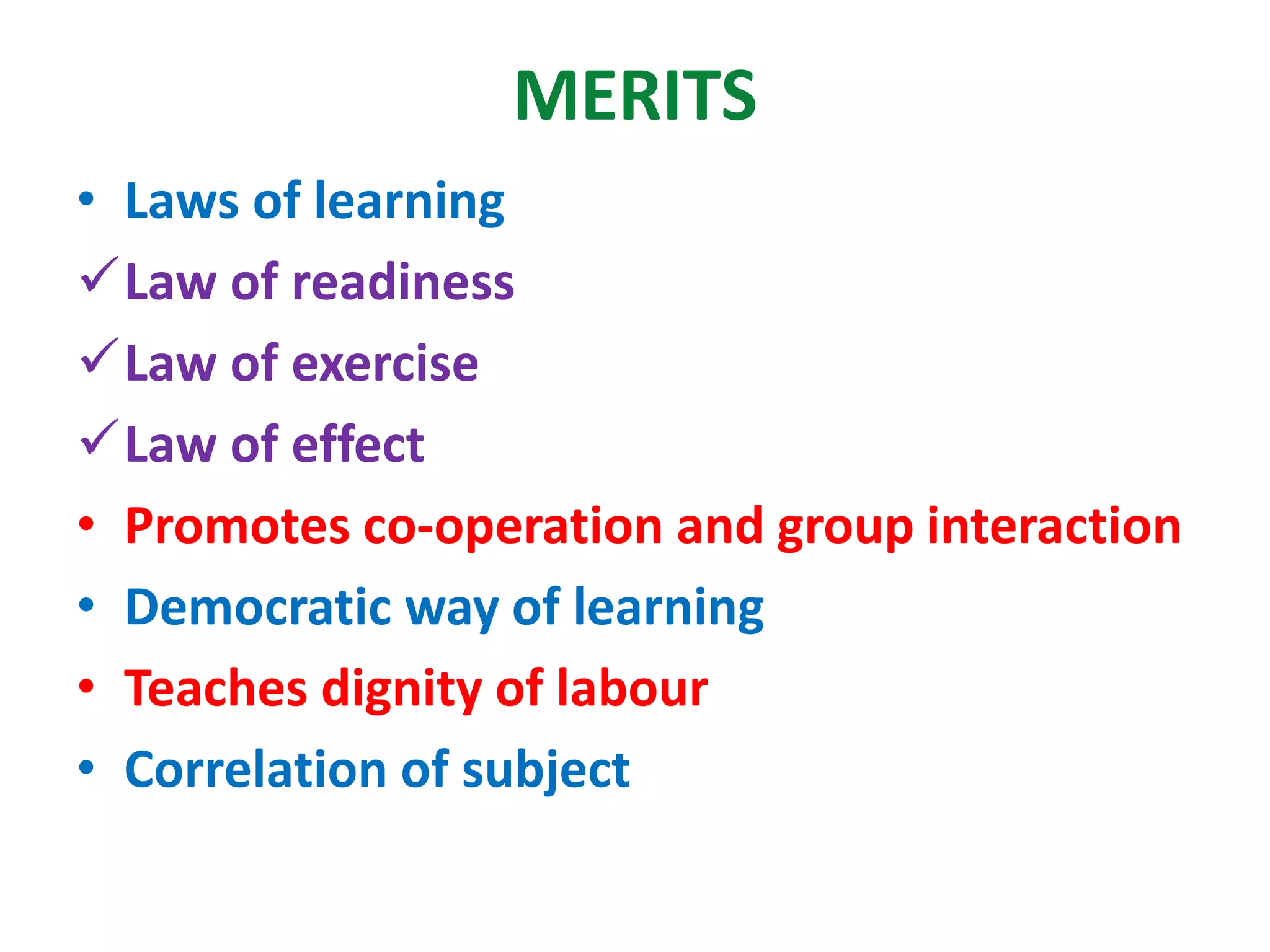
The document outlines various methods of teaching biological sciences, emphasizing the criteria for selecting methods based on class level, size, and subject matter. It categorizes teaching approaches into teacher-centered and pupil-centered methods, detailing techniques such as lectures, demonstrations, heuristics, and project-based learning. It highlights the importance of instructional technology and collaborative teaching strategies, advocating for methods that foster independent learning and problem-solving skills.