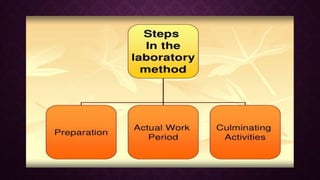
The document discusses different teaching methods: lecture-demonstration, project method, and laboratory method. It provides details on the project method, including its definition, steps involved, advantages like maintaining student interest, and disadvantages like potential misuse of time. The laboratory method is described as utilizing real data/materials to improve understanding and develop skills like observation. Preparation, the work period, and culminating activities are outlined for effective use of these methods.