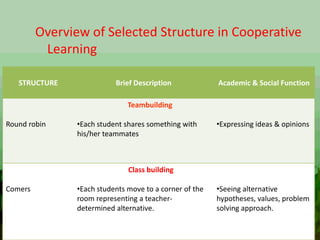
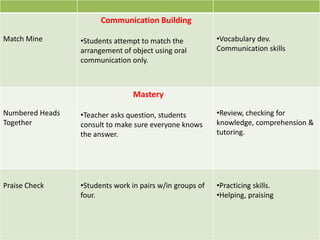
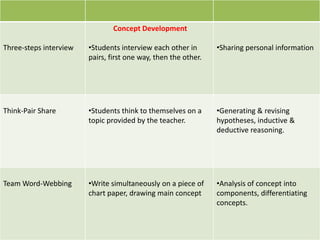
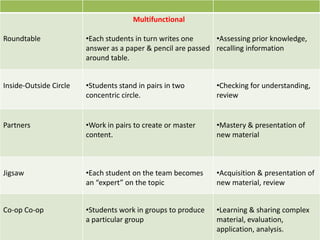
The document discusses various instructional approaches and methods, including direct/expositive instruction, deductive and inductive methods, demonstration method, inquiry/problem-solving method, project method, metacognitive approach, constructivist approach, cooperative learning approach, reflective teaching, peer tutoring/peer teaching, and partner learning. It provides details on the characteristics and strategies for each approach.