- This document discusses general teaching methods and techniques. It outlines two main approaches: direct/expository and experiential.
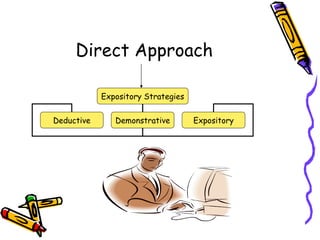
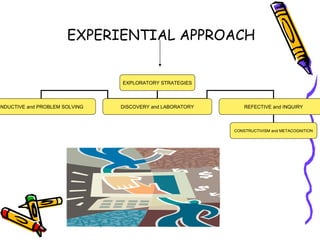
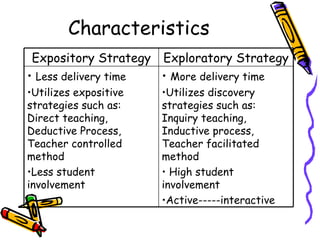
- The direct approach utilizes deductive, expository strategies and is teacher-controlled with less student involvement. The experiential approach uses inductive, exploratory strategies like inquiry, discovery and problem-solving to actively involve students.
- Specific teaching methods are also defined, including deductive, demonstration, inductive, discovery, problem-solving, project-based, laboratory, reflective and metacognitive teaching. Cooperative learning strategies like STAD and Jigsaw are provided as examples.