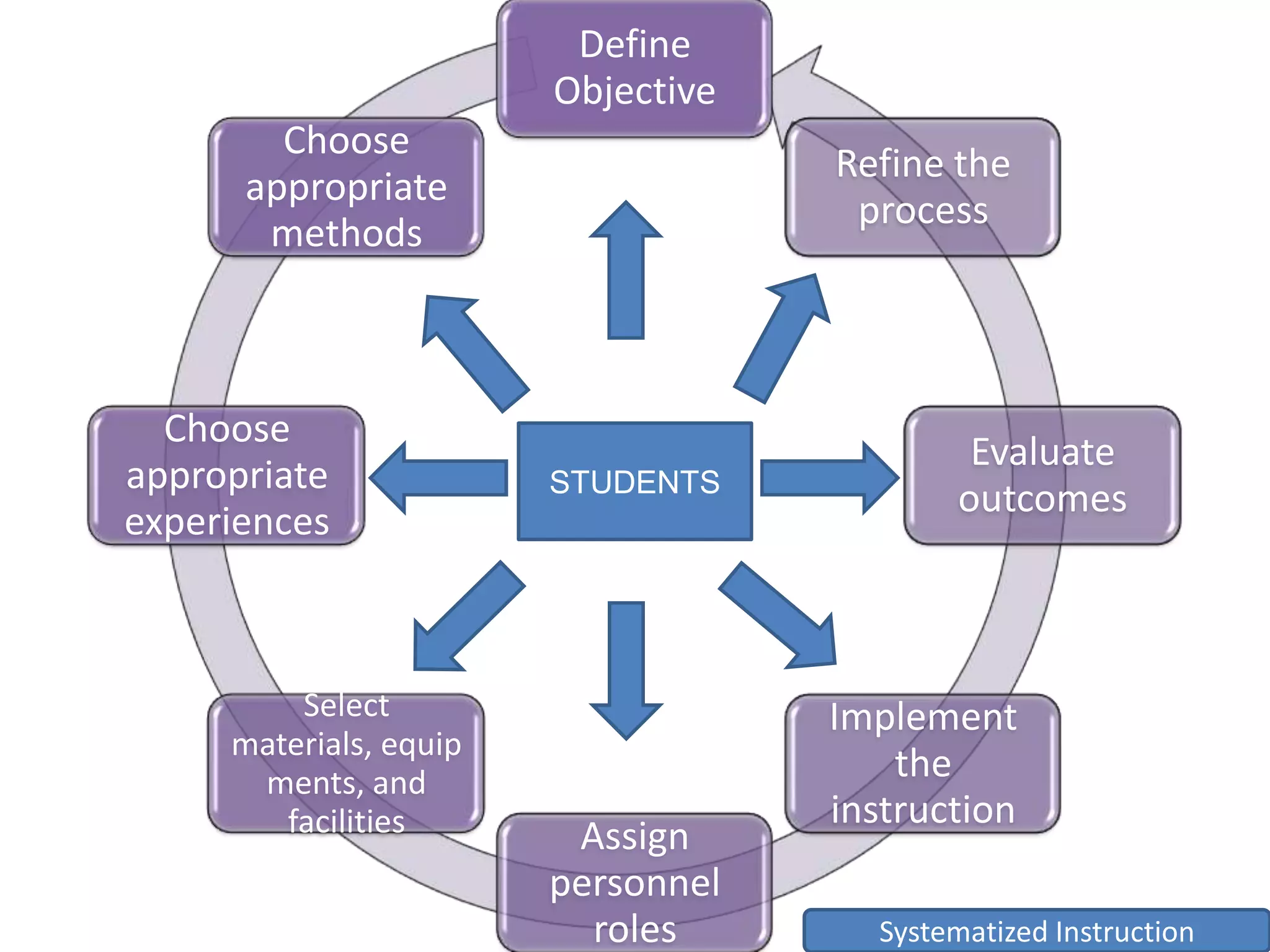
The document outlines a systematic approach to instructional design, emphasizing the integration of various educational components such as objectives, media, and learner needs. It introduces the ASSURE model as a practical guide for planning classroom instruction with a focus on analyzing learner characteristics and engaging them in active participation. The process concludes with evaluating outcomes and refining instructional strategies to improve effectiveness.