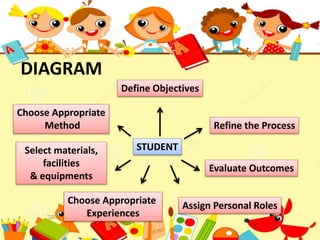
The document outlines the ASSURE model for systematic instructional planning. The ASSURE model involves 6 steps: 1) Analyzing the learner to define instructional objectives based on student needs, interests, and readiness, 2) Choosing an appropriate teaching method based on the objectives, 3) Selecting learning materials, equipment and facilities suited to the method, 4) Assigning roles to personnel to assist with resources, 5) Refining the process based on evaluation of outcomes, and 6) Choosing appropriate learning experiences to attain the objectives. The model emphasizes defining objectives based on students and selecting aligned methods, materials and roles to achieve the objectives.